Happy Holidays! Despite political divisions and war in the Middle East and Ukraine, it is at this time of year that we celebrate life with great hope and faith. People of many faiths take time to reflect, respect, and resolve. Christians celebrate Christmas, the miraculous birth of Christ, the Son of God, and the Messiah. Jews celebrate Chanukah, the miraculous festival of lights, when one night’s oil provided enough light and safety for 8 nights. Both major faiths promote healthy lifestyles for the mind, body and spirit. These faiths are grounded in hope, faith, love and peace. It is no surprise that studies repeatedly demonstrate that faithful and spiritual people live longer and healthier lives! At this turbulent time in the world, it is important to note that people of all faiths benefited equally!
I purport that to be truly healthy; one must have faith because complete health is multidimensional. Socrates preached this message to his students thousands of years before Christ. One must have a healthy mind, which requires intellectual stimulation with attainable goals related to education and intellect. One must have a healthy body by eating well, engaging in physical activity and having attainable goals related to his/her body. Likewise, one must have a healthy spirit with faith, hope, prayer and meditation, comrades and counsel, and set attainable spiritual goals.
Being religious or spiritual has been shown to benefit your mind, body and spirit…

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

The “First Thanksgiving” was in 1621 between the Pilgrims of Plymouth Colony and the Wampanoag tribe in present day Massachusetts to celebrate the harvest and other blessings of the previous year. In 1789, President George Washington, at the request of Congress, proclaimed Thursday, November 26, as a day of national thanksgiving. In 1863, Abraham Lincoln proclaimed the national holiday of Thanksgiving to be the last Thursday of November.
Americans and Canadians continue to celebrate this holiday as a time for family and friends to gather, feast, and reflect upon their many blessings. Like most, I am very grateful for the simple things, family, good friends, food, shelter, and health. I am also thankful for the dedicated scientists who develop vaccinations and medications so we can safely enjoy Thanksgiving with our families. It turns out that being grateful is not only reflective and cleansing; it is also good for your health!
Grateful people are more likely to behave in a prosocial manner, even when it is not reciprocated. A study by the University of Kentucky found those ranking higher on gratitude scales were less likely to retaliate against others, even when others were less kind. Emmons and McCullough conducted one of the most detailed studies on thankfulness. They monitored the happiness of a group of people after they performed the following exercise:
There are many things in our lives, both large and small, that we might be grateful about. Think back over the past week and write down on the lines below up to five things in your life that you are grateful or thankful for.” The study showed that people who are encouraged to think of things they’re grateful for are approximately 10% happier than those who are not.
Amy Morin, psychotherapist, mental health trainer and bestselling author offers this advice: “Developing an “attitude of gratitude” is one of the simplest ways to improve your satisfaction with life. We all have the ability and opportunity to cultivate gratitude. Simply take a few moments to focus on all that you have, rather than complain about all the things you think you deserve.” So…be grateful and have a happy Thanksgiving!
Source: NIH, Forbes, Amy Morin “13 Things Mentally Strong People Don’t Do.”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body. Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month and there is good news to report!
A recent study in the Journal of the American Medical Association from Harvard has found that regular exercise can improve the survival of patients with breast cancer. I have discussed these findings with local physician, Dr. Christopher Peters of Northeast Radiation Oncology Center and he says that he regularly councils his patients about the value of exercise in the recovery from breast cancer. As found in the study, he recommends aerobic exercise such as walking and/or biking and mild resistance exercise. He also encourages patients to enroll in a formal rehabilitation program, especially to prevent a frozen shoulder if invasive surgery was performed.
Previous studies have shown many benefits of exercise for breast cancer patients including improving immune functioning and controlling depression. However, new research recently presented at the American Association for Cancer Research annual meeting was the first report to conclude that physical exercise may improve survival in breast cancer patients. Additional studies have shown other benefits of exercise. For example, a study conducted at Vanderbilt University found that women who had high activity levels throughout life were less likely to develop endometrial cancer. At the Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, researchers found that exercise with moderate intensity can reduce serum markers of inflammation (C-reactive protein), which, when elevated, are associated with chronic disease and poor cancer survival.
In the current study, conducted at Harvard University, researchers compared survival rates in women with breast cancer with exercise levels in terms of metabolic equivalent (MET) hours per week. While women with high activity levels of exercise had the best outcomes, even women with moderate exercise benefited.
Benefits of exercise in women with breast cancer:
In conclusion, current research supports the fact that exercise may improve breast cancer survival. The following guidelines are proposed:
Flexibility Exercises involve moving the arms, legs and trunk through comfortable range of motion to give you more mobility in order to improve your ability to perform daily activities such as tucking in a shirt, tying shoes or fastening a bra. Best if performed after strength exercises because the muscles and joints will be warm and limber. Always perform slowly with slight stretch sensation and no pain. No bouncing or overstretching!
These exercises are to be performed while sitting in a chair with a backrest, slowly, 5 repetitions, 3-5 times per week.
Balance Exercises involve strengthening muscles that keep the body upright and stable in standing in order to improve your ability to perform daily activities without falling. According to the NIH, 300,000 US hospital admissions for broken hips occur each year due to falls. Check with your physician if you have a history of dizziness before performing these exercises on your own. Best if performed with someone at home or some assistance. Always use a countertop or back of chair to hold onto for support.
Endurance Exercises involve any activity such as walking, swimming, biking or raking leaves that elevates your heart rate and breathing for an extended period of time. Check with your physician if you have a history of heart problems or dizziness before performing these exercises on your own. Best if performed with someone at home or some assistance. Start off slowly for only 5 minutes and add 1-2 minutes each week or 2. Wear good and comfortable shoes – no heels!
While not all of these endurance exercises may be appropriate for you, one or two of these may offer a good starting point.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body. Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

October is National Physical Therapy Month! The American Physical Therapy Association (APTA) would like to recognize the thousands of physical therapists as dedicated health care providers. Moreover, physical therapists would like to thank the public for allowing us to participate in your health and wellness. While PT’s may not save lives…we do save LIFESYLES!
This column will address a question that is frequently asked by people of all ages and activity levels…stretching. First, it is important to keep in mind that stretching should NEVER be performed without warming up your body and muscles first. This can be done by running slowly in place or around the block for 5-10 minutes. Second, stretching should NEVER be painful. Third, a good stretch should be performed slowly and feel like slight tension in the muscle. NEVER bounce or jerk. First, perform the stretches by actively moving your muscles slowly and deliberately 5-10 times. Then, hold the stretch for 5-10 seconds, repeat 5-10 times, 2-4 times per week.
Remember, flexibility is only one aspect of complete health and wellness. Strength training, cardiovascular fitness, meditation and stress management and proper nutrition are also necessary for a healthy lifestyle. Also, be careful not to overstretch before competition as it may weaken the muscle.
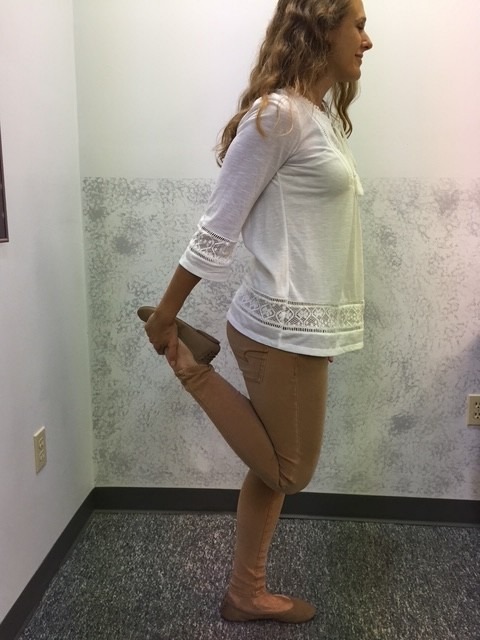
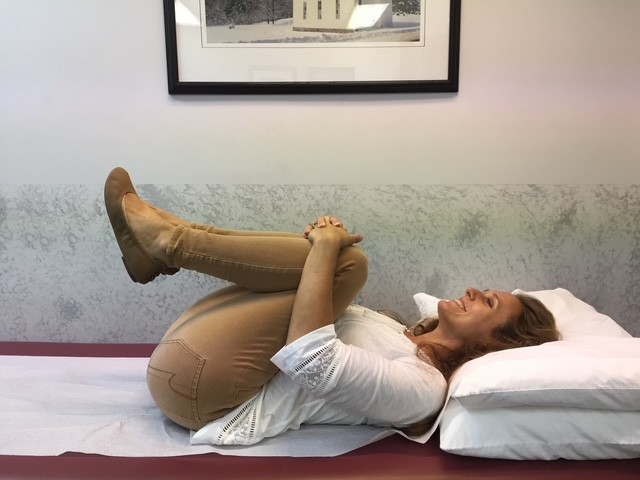
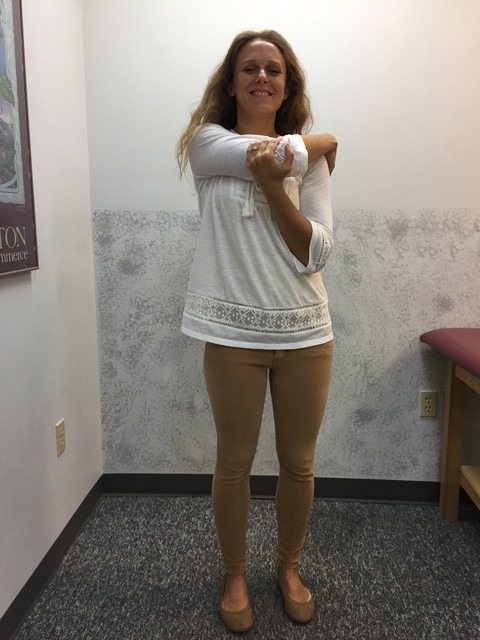

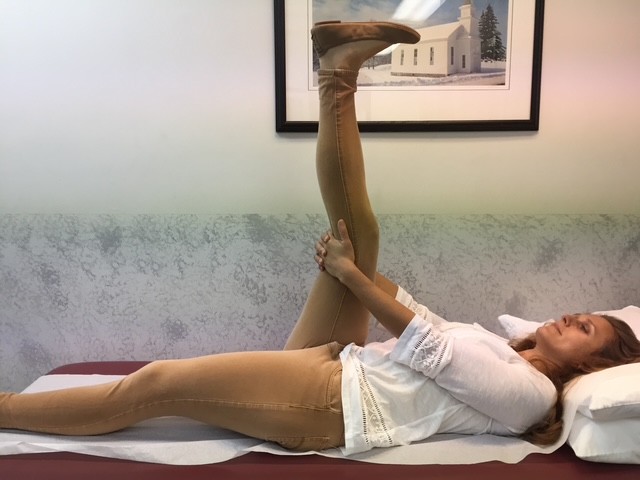

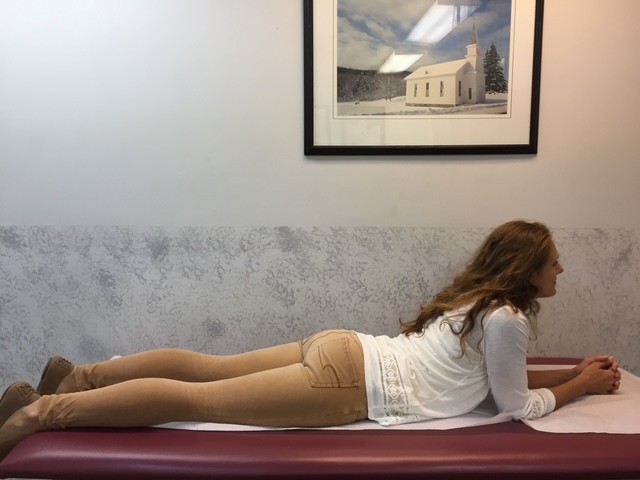

MODEL: Sarah Singer, PTA, Mackarey Physical Therapy

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

This column is repeated every year at this time with the intent of raising the level of awareness to prevent death or serious illness from heat stroke in athletes and other active people in hot, humid weather.
It is early August, and we have managed to survive two “heat waves” in NEPA. While it is important to have fun in the sun, please be mindful of how your body reacts to high humidity and heat and take appropriate precautions. Athletes are particularly vulnerable this time of year due to daytime practice sessions. In response to this potential problem, the PIAA has established acclimatization guidelines for fall sports beginning in August. Visit www.piaa.org for more information. Keep in mind, you don’t have to be running a marathon or playing football in full uniform to suffer from heat stroke.
Heat stroke, one of the most serious heat-related illnesses, is the result of long term exposure to the sun to the point which a person cannot sweat enough to lower the body temperature. The elderly and infants are most susceptible and it can be fatal if not managed properly and immediately. Believe it or not, the exact cause of heatstroke is unclear. Prevention is the best treatment because it can strike suddenly and without warning. It can also occur in non athletes at outdoor concerts, outdoor carnivals, or backyard activities.
Some “old school” folks think that wearing extra clothing and “breaking a good sweat” is an optimal goal for exercise. However, it may be potentially very dangerous in hot and humid conditions. When exercising in hot weather, the body is under additional stress. As the activity and the hot air increases your core temperature your body will to deliver more blood to your skin to cool it down. In doing so, your heart rate is increased and less blood is available for your muscles, which leads to cramping and other more serious problems. In humid conditions, problems are magnified as sweat cannot be evaporated from the skin to assist in cooling the body.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and The American College of Sports Medicine has the following recommendations which are appropriate for both the competitive athlete and weekend warrior:

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

While I fully expect to be at the “butt end” of many comments for this column, I feel compelled to address this topic at the request of several patients. It seems that many geriatric physical therapists commonly encounter patients that suffer from constipation which limits their participation in rehabilitation. Ironically, research demonstrates that exercise and activity actually help relieve constipation.
The National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC) reports that 3.1 million people in the United States suffer from constipation. The NDDIC further reports that this problem leads to almost 400,000 hospitalizations, 1.4 million visits to emergency rooms, 1 million prescriptions and 121 deaths each year. Constipation is defined by the Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine as three or less bowel movements per week. It is also estimated that more than 27 percent of the elderly are affected.
Severe constipation can result in immediate medical attention in some cases due to intestinal obstruction. In addition to infrequent bowel movements, some symptoms include: feeling poorly, weight loss, loss of appetite, abdominal distention and/or pain, and vomiting.
Healthy people must continue to keep active. Get into good exercise habits at a young age and continue through life. Maintaining a consistent schedule of eating and exercise is also helpful. Some simple suggestions for beginning an exercise program for prevention of constipation in the healthy population are:
Depending on your general health and ambulatory status, these endurance exercises may be appropriate for you. Therefore, consider one or two of the following as a good starting point:
IN CONCLUSION: KEEP MOVING YOUR BODY AND YOU WILL KEEP MOVING YOUR BOWELS!
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, NEPA and all of Pennsylvania is experiencing a change in climate as indicated by a half a degree (F) in temperature, more frequent and heavy rainstorms and the tidal portion of the Delaware River is rising one inch every eight years. Last summer was one of our hottest on record and this summer has produced several heat waves with more expected. For those without air conditioning or access to a lake or pool, it will also be remembered as record setting warm temperatures. A local reader who cares for her elderly mother wrote to express her concern about dehydration in the elderly. Age, diet, illness and medications are some of the many reasons why elders suffer from dehydration not only in the summer heat, but year-round.
Next to oxygen, water is the nutrient most needed for life. A person can live without food for a month, but most can survive only three to four days without water. Even though proper hydration is essential for health, water gets overlooked as one of the six basic nutrients. Dehydration occurs when the amount of water taken into the body is less than the amount that is being lost. Dehydration can happen very rapidly (i.e. in less than eight hours); the consequences can be life threatening and the symptoms can be alarmingly swift.
In the body, water is needed to regulate body temperature, carry nutrients, remove toxins and waste materials, and provide the medium in which all cellular chemical reactions take place. Fluid balance is vital for body functions. A significant decrease in the total amount of body fluids leads to dehydration. Fluids can be lost through the urine, skin, or lungs. Along with fluids, essential electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, are also perilously depleted in a dehydrated individual.
Dehydration is the most common fluid and electrolyte disorder of frail elders, both in long term care facilities and in the community! Elders aged 85 to 99 years are six times more likely to be hospitalized for dehydration than those aged 65 to 69 years. More than 18% of those hospitalized for dehydration will die within 30 days, and associated mortality increases with age. Men appear to dehydrate more often than women and dehydration is often masked by other conditions.
Elderly individuals are at heightened risk for dehydration for several reasons. Compared to younger individuals, their regulatory system (i.e. kidneys and hormones) does not work as well and their bodies have lower water contents. Older adults often have a depressed thirst drive due to a decrease in a particular hormone. They do not feel thirsty when they are dehydrated. This is especially true in hot, humid weather, when they have a fever, are taking medications, or have vomiting or diarrhea. They have decreased taste, smell, and appetite which contribute to the muted perception of thirst. Because of dementia, depression, visual deficits, or motor impairments, elderly people may have difficulty getting fluids for themselves. Many elderly individuals limit their fluid intake in the belief that they will prevent incontinence and decrease the number of trips to the bathroom. The medications that they are taking (e.g. diuretics, laxatives, hypnotics) contribute to dehydration.
Elders may suffer headaches, fainting, disorientation, nausea, seizure, a stroke, or a heart attack as a result of dehydration. The minimum daily requirement to avoid dehydration is between 1,500 (6.34 cups) and 2,000 ml of fluid intake per day. Six to eight good-sized glasses of water a day should provide this amount. Better hydration improves well-being and medications work more effectively when an individual is properly hydrated.
Those who care for the elderly whether at home or in a health care facility need to be alert to the following symptoms:
By the way, plain old tap water is a good way to replenish fluid loss. Keep in mind that some energy drinks not only have excess and unneeded calories but also contain sugar that slows down the rate at which water can be absorbed from the stomach. Consuming alcoholic and caffeinated beverages actually have an opposite, diuretic effect!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

It is the middle of summer in NEPA with plenty of time to have some fun in the sun…but don’t forget to protect your skin! A little awareness and some precautions can go a long way to make golfing, swimming, kayaking, biking, hiking, water skiing and other outdoor activities safer!
Despite the fact that we have limited exposure to sunny days in NEPA (50%), skin cancer still exists in large numbers. Skin cancer is the most common cause of cancer in the United States. While there are several types of skin cancer and not necessarily all are deadly, procedures to remove these skin cancers are both costly and frequently result in unsightly scars. The most dangerous type of skin cancer, called melanoma, results in an estimated 10,000 deaths per year. The good news? Nearly all skin cancers are preventable!
The majority of skin cancers are caused by harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun. Two major types are UVA and UVB:
In the field of anti-aging, advertisers make lofty promises for many products that claim to contain or boost collagen. Whether or not these work is a whole other discussion, but what is collagen and what does it have to do with wrinkles?
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body. It is found in nearly all tissues and organs, and plays a crucial role in maintaining structural integrity. Unfortunately, collagen production naturally decreases with age. This causes many of the findings we associate with older age, such as sagging skin and wrinkles, as well as joint pain. Collagen also works together with another important protein called elastin, which helps to maintain elasticity – a feature commonly associated with youthful skin.
When exposed to UV rays, these proteins can become damaged. For instance, studies have shown that skin exposed to UV rays increases the expression of proteins called matrix metalloproteinases, or MMPs. You can think of these MMPs as collagen’s enemy, as they cause their degradation. This results in a decrease in collagen’s structural function leading to loose and wrinkled skin. UV rays can also stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species. These are substances such as hydrogen peroxide and bleach, which further cause destruction of skin’s microscopic structure.
So, you’re convinced and have decided to keep your skin healthy and youthful – what next? With so many different products on the market, choosing a daily sunscreen can become a difficult task. Here are a few pointers:
Another consideration when choosing a sunscreen is chemical versus physical blockers:
If preventing skin cancer isn’t incentive enough to wear sunscreen daily and avoid excessive sun exposure (and indoor tanning booths!), then consider the rapid effects on aging the sun’s rays can have. While a tan may look good for a week, avoiding exposure to UV rays will both delay and prevent aging for years.
For more information on skin cancer and prevention, please visit the Center for Disease Control’s website (https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/skin/) and contact your physician for specific concerns regarding spots on your skin.
Guest Contributor: Eduardo Ortiz, MD, Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine 2018

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

After such a long, cold and wet spring, we are all grateful that the 4th of July holiday weekend is here! There is still plenty of time to be outdoors in NEPA and experience so many activities such as: biking, hiking, running, walking, swimming, boating, golfing, and playing tennis to name a few. It is a wonderful opportunity to discover your inner child, mix it up and try something new! Below are some new and exciting ways to stay active and have fun in the sun:
Spending time on any of the beautiful lakes in NEPA is time well spent. From an exercise standpoint, rowing, canoeing and kayaking offer a very special experience. Most kayaks are light weight, easy to use and maneuverable on a lake. Sitting low on the water offers a unique perspective as you feel yourself gliding across the lake. The Countryside Conservancy, in partnership with Lackawanna State Park, sponsors moonlight kayak events on the lake at the park. With a bright full moon, you can begin at 8 pm and return at 10 pm. Bring bug spray and headlights to enjoy the sunset and moon rise on the lake. You will feel like a kid breaking the rules of the park by being on the water after dark!
NOTE: Try kayaking in the daytime first and then advance to sunset trips before staying on the water for the moonlight. Rentals are available at the park.
Website: www.countrysideconservancy.org; www.dcnr.state.pa.us/stateparks.org
Stand up paddleboarding (SUP) is becoming a fast-growing sport among water enthusiasts. It is a fun way to exercise your core, improve balance, and tone your upper body. Stand Up Paddleboarding requires minimal equipment; a board that is essentially a long and wide surfboard and a long paddle to use while standing on the board. It can be done in the ocean surf, bay, lakes, or rivers; however, beginners would be wise to stay in calm water. Rentals are available at most beaches.
Check out the video for more information: REI paddleboard basics
What is it? Imagine a standup paddleboard with a handlebar and pedals like a exercise stepper machine. Instead of using a paddle, you step up and down on the pedals and fins under the board propel you through the water.
Check it out…Hobie Mirage Eclipse Stand Up Pedalboard; Dick’s Sporting Goods
Zumba is a very popular form of dance aerobics spiced up with Latin music. When adding water and sun to this already cool activity, you are assured to have fun while exercising. As with any aquatic exercise, the added resistance from the water gives arm rows and leg kicks more challenge. Female participants report an additional benefit; they are uninhibited to “shake that thing” to the music under the cover of the water. So, beat the heat, let loose and get some fun in the sun while you exercise.
NOTE: Consider trying regular Zumba first to get the hang of it. Amy Sekol is a local certified Zumba instructor and also offers Aqua Zumba. (amys.zumba.com)
Website: www.zumba.com
I love this idea…why didn’t I think of it first! In the gym I enjoy the elliptical machine because it simulates running without the impact on my joints but of course, I would rather be outdoors. Well, this is the answer to my prayers…an elliptical machine that is attached to a bike with handle bars and brakes included. I think it will probably be difficult on steep hills but it is something I MUST TRY!
Website: www.elliptigo.com; www.mywingflyer.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

I wish I could tell you that after turning 50, there are health issues associated with age I plan to be mindful of and address proactively. Unfortunately, that ship has sailed for me well more than a decade ago. So, I share this medical information, not only as a health professional but also as an experienced senior.
Entering the fifth decade is not all dome and gloom. Often, this decade is associated with an established family, gratifying career, good health and acquired self-confidence…realizing that life does not have to be perfect to be wonderful!
However, research tells us that as the body ages, even small changes at the cellular level can be manifested into big changes and problems over time. Nine of ten older adults have some type of chronic disease and eight of ten have more than one. But the good news is that, with a modicum of effort, most of these illnesses can be controlled or prevented, including regular doctor visits, health screening and testing, and lifestyle changes.
While it is normal to experience some weight gain is expected with age. However, uncontrolled, the average person will gain 1-2 pounds per year, leading to 11 pounds per decade, according to the National Institutes of Health. Consequently, almost 45% of Americans between 40 to 60 are obese. Obesity is associated with at least 20 chronic illnesses such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and arthritis.
SCREEN: Body Mass Index (BMI)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications, Surgery
With age, the flexibility of blood vessels loses elasticity and, unchecked, two out of three adults over 60 have high blood pressure. While genetics is a factor, there are a few things that you can control such as diet (salt, calories), exercise, weight, stress, and smoking.
SCREEN: Blood Pressure Test, Lab Tests, Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications
Plaque buildup in the arteries of the heart begins in childhood and advances rapidly with age. 6-7 percent of US adults between the ages of 40 and 60. 20% of men and almost 10% of women between the ages of 60 and 80 have heart disease.
SCREEN: Blood Pressure, Cholesterol testing, Blood Sugar Testing, Imaging (ECG/MRI)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications, Surgery
10 % of Americans have diabetes and the percent only increases with age. Diabetes is associated with many serious chronic illnesses such as heart disease, blindness, kidney disease and others.
SCREEN: Blood Test for blood sugar levels such as A1C, fasting plasma glucose test and random plasma glucose test
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications
In many cases osteoarthritis (wear and tear of joints) is often associated with age. However, lifestyle, joint injuries, inactivity, obesity and diabetes play a significant role.
SCREEN: Physical Exam, Functional Scores, Xrays, MRI, CT, US
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, Medications (NSAID’s, Steroids, Viscosupplementation), Bracing, Surgery
Loss of bone density and strength is associated with age and certain metabolic conditions such as early menopause, thyroid disease, prolonged use of blood thinners and steroids. However, a diet rich in vitamin D, regular weight bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, dancing etc can go a long way.
SCREEN: Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, Medications (Oral and Injection)
Losing balance with age is a common problem due to changes in the vestibular system (balance system in the brain), loss of muscle strength and joint flexibility, and compromised vision and hearing. This can often lead to falls, head injuries and fractures.
SCREEN: Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test, Morse Fall Scale
TREATMENT: Physical Therapy – Falls Prevention Program/Balance Training , Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Environmental Modification, Vision/Hearing Testing
Almost 10% of adults between the ages of 55 and 65 have some form of vision and/or hearing loss. This can lead to many problems such as balance and falls as well as isolation and depression.
SCREEN: Regular Hearing Tests/Vision Testing
TREATMENT: Corrective Devices
Both men and women suffer from bladder problems with age... especially frequency and control. It can impact lifestyles in many ways. Often adults fail to hydrate properly, especially when traveling, to control urgency. This can lead to other health problems.
SCREEN: Urine Analysis, PSA, Imaging, CT Urogram, Urine Cystoscopy, Ultrasound,
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Avoid Caffeine and heavy lifting, Medications, Surgery
As the body ages, so too do the cells that make it up. Often these cells change into cancer different parts of the body. Skin, colon, breast, prostate, lung, throat, etc. Today, however, much progress has been made for early detection and treatment.
SCREEN: Physical Exam (Skin Exams), Lab Tests (blood work, PSA), Imaging (CT, Mammography, MRI), Genetic Testing, Pap Smears, HPV Tests, Colonoscopies/Stool Tests, Multi-Cancer Early Detection (MCED)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, Medications, Chemotherapy, Radiation, Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy Surgery specific to the cancer type.
Age related mental health issues are vastly unreported and diagnosed. Medical problems can contribute to mental health such as high blood sugar levels and some infections. Overall, lifestyle, environmental factors and family structure and support are particularly important.
SCREEN: No Single Test – Combination of Tools including - Neurological and Cognitive Tests, Brain Scans (CT/MRI), Blood tests, Genetic Testing
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, (avoid excessive toxins like alcohol and nicotine), Medications, Environmental Modifications.
SOURCES: WebMD, NIH, Mayo Clinic, Alzheimer’s Association, American Cancer Society, American Heart Association, American Diabetes Association

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
