Tennis elbow, also called lateral epicondylitis, is an inflammation of the lateral (outside) bony protuberance at the elbow. It is at this protuberance that the tendon of the long muscles of the hand, wrist and forearm attach to the bone. As the muscles repeatedly and forcefully contract, they pull on the bone, causing inflammation. The trauma is irritating when working the muscles in an awkward position with poor leverage like hitting a backhand in tennis.
It is not unusual for a patient to come to my office with severe pain on the outside of their elbow. Especially, after intensifying their tennis workouts or changing the racquet string tension. Others come to me with pain on the inside of the elbow (“golfer’s elbow”) from wrist action that advanced golfer’s use at impact. However, this problem is not only for tennis players and golfers. Laborers working with wrenches or screwdrivers with an awkward or extended arm can also develop tennis elbow. Others who are vulnerable are: those working for hours at a computer using a mouse as well as those working hard maintaining their lawns and gardens.
In a more chronic problem, lateral elbow pain may arise by a degenerative condition of the tendon fibers on the bony prominence at the lateral elbow. Sporadic scar tissue forms from a poor attempt by the body to overcompensate and heal without eliminating the cause.
While symptoms may vary, pain on the outside of the elbow is almost universal. Patients also report severe burning pain that begins slowly and worsens over time when lifting, gripping or using fingers repetitively. In more severe cases, pain can radiate down the forearm.
Conservative treatment is almost always the first option and is successful in 85-90 percent of patients with tennis elbow. Your physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication (over the counter or prescribed). Physical/Occupational therapy, rest, ice, and a tennis elbow brace to protect and rest may be advised. Ergonomic changes in equipment, tools, technique and work-station may be necessary. Improvement should occur in 4-6 weeks. If not, a corticosteroid injection may be needed to apply the medication directly to the inflamed area. Physical therapy, range of motion, and stretching exercises may be necessary prior to a gradual return to activity. Deep friction massage can assist healing.
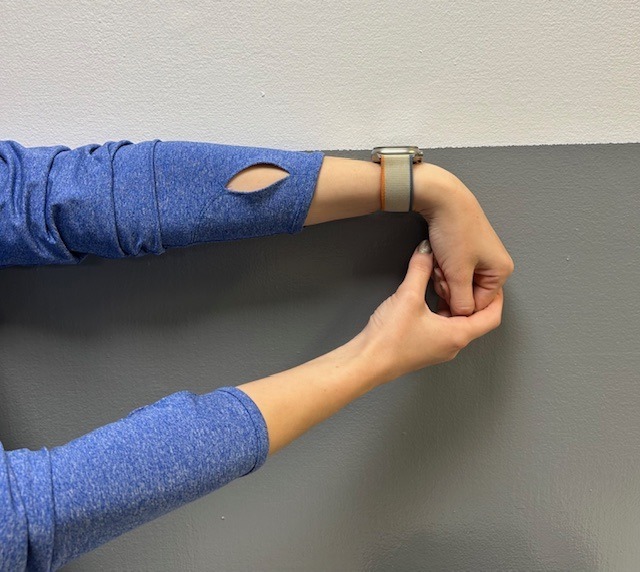

Exercises performed in a particular manner to isometrically hold and eccentrically lengthen the muscle with contraction.
New Conservative Treatment: Platelet-Rich-Plasma (PRP) is a new treatment for the conservative management of degenerated soft tissues that has recently received great media attention. In great part, due to its success in several high profile athletes. According to the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,(JAAOS), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is autologous (self-donated) blood with an above normal concentration of platelets. Normal blood contains both red and white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Platelets promote the production and revitalization of connective tissue by way of various growth factors on both a chemical and cellular level.
The actual PRP injection requires the patient to donate a small amount of their own blood. The blood is placed into a centrifuge (a machine that spins the blood at a high velocity to separate the different components of blood such as plasma, white and red blood cells), for approximately 15 minutes. Once separated, the physician draws the platelet-rich plasma to be injected directly into the damaged tissue. In theory, the high concentration of platelets, with its inherent ability to stimulate growth and regeneration of connective tissue, will promote and expedite healing.
Surgery for tennis elbow is only considered in patients with severe pain for longer than 6 months without improvement from conservative treatment. One surgical technique involves removing the degenerated portion of the tendon and reattaching the healthy tendon to bone. Recently, arthroscopic surgery developed to perform this technique. However, research does not support the value of one over the other at this point. Physical/occupational therapy is used after surgery. Return to work or athletics may require 4-6 months. More recently, a surgical technique using ultrasound to guide a needle to debride (clean) the area of scar tissue has been developed. If eligible for this procedure, the time required for healing, rehabilitation and return to activity is much shorter.
If you feel you suffer from tennis elbow, ask your family physician which of these treatment options are best for you.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy

This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is repeated every year at this time with the intent of raising the level of awareness to prevent death or serious illness from heat stroke in athletes and other active people in hot, humid weather.
It is the end of July and we have managed to survive two “heat waves” in NEPA. While it is important to have fun in the sun, please be mindful of how your body reacts to high humidity and heat and take appropriate precautions. Athletes are particularly vulnerable this time of year due to daytime practice sessions. (August 5 & 6, 2024, first day of acclimatization and August 12, 2024, first day of practice for fall sports according to PIAA). Visit www.piaa.org for more information. Keep in mind, you don’t have to be running a marathon or playing football in full uniform to suffer from heat stroke.
Heat stroke, one of the most serious heat-related illnesses, is the result of long term exposure to the sun to the point which a person cannot sweat enough to lower the body temperature. The elderly and infants are most susceptible and it can be fatal if not managed properly and immediately. Believe it or not, the exact cause of heatstroke is unclear. Prevention is the best treatment because it can strike suddenly and without warning. It can also occur in non athletes at outdoor concerts, outdoor carnivals, or backyard activities.
Some “old school” folks think that wearing extra clothing and “breaking a good sweat” is an optimal goal for exercise. However, it may be potentially very dangerous in hot and humid conditions. When exercising in hot weather, the body is under additional stress. As the activity and the hot air increases your core temperature your body will to deliver more blood to your skin to cool it down. In doing so, your heart rate is increased and less blood is available for your muscles, which leads to cramping and other more serious problems. In humid conditions, problems are magnified as sweat cannot be evaporated from the skin to assist in cooling the body.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and The American College of Sports Medicine has the following recommendations which are appropriate for both the competitive athlete and weekend warrior:

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
I have been advising my patients to exercise, keep active, and walk as long as they can in order to stay mobile and healthy. However, seniors often tell me activities that require prolonged walking is limited by ankle pain from arthritis. They often ask, “What is arthritis of the ankle?” How does it happen? What can I do about it?
Your family physician will examine your ankle to determine if you have arthritis. In more advanced cases you may be referred to a specialist such as a podiatrist, orthopaedic surgeon or rheumatologist for further examination and treatment. X-rays will show if the joint space between the bones in the ankle is getting narrow from wear and tear arthritis. If rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, blood tests and an MRI may be ordered. The diagnosis will determine if you problem if minor, moderate or severe.
In the early stages your treatment will be a conservative, nonsurgical approach, which may include; anti-inflammatory medication, orthopedic physical therapy, exercise, activity modifications, supplements, bracing, etc. You and your family physician, podiatrist, orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist will decide which choices are best.
When conservative measures no longer succeed in controlling pain and deformity, improving strength and function then more aggressive treatment may be necessary.
SOURCES: Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Spring is here! So, too, is allergy season and spring sports! It seems this every year at this time a young little league baseball player wheezes as they cross home plate and desperately tries to catch their breath. Players, coaches, umpires, parents watch in dismay, deciding whether they need to call an ambulance. Minutes later the player recovers from this scary situation…until the next time. Could this be an example of exercised-induced asthma (EIA)?
Dr. Gregory Cali, a local pulmonologist, (lung doctor) was gracious enough to participate in an interview about this problem…exercise-induced asthma (EIA). The topic was chosen in response to an email question from a concerned mother of an athlete with asthma. Dr. Cali informed me that the first thing to know about exercise induced asthma (EIA) is that EIA is not a distinct disease in itself-but is one manifestation or presentation of asthma. Putting it simply, EIA occurs in patients who have develop narrowing of the bronchial tubes ( bronchoconstriction) when they exercise. Some experts would rather we use the phrase exercise induced bronchoconstriction which is what happens when someone has an asthma attack. This bronchoconstriction occurs because of spasm of the tiny muscles of the airways, plugging of the airways with thick mucous, and swelling or edema of the cells lining the airways.
In fact, it is inflammation of the airways, mostly due to allergies, that is at the root of most cases of asthma. This inflammation causes the bronchial tubes to become over-reactive-and predisposed to narrowing- when exposed to certain triggers. Exercise is one of those triggers in susceptible people. The patient with EIA complains of chest tightness, wheezing, and shortness of breath when exercising. Some patients only experience coughing with exercise. Symptoms are usually worse in cold, dry air. This is believed to be due to the drying and cooling of the airways, which occurs with exercise, especially if the patient opens his or her mouth while exercising. Nasal breathing is much better at warming and humidifying air and may help to reduce EIA.
Dr. Cali feels that the most important point about EIA is to make sure a specific diagnosis is made. It is difficult at times to differentiate asthma from the normal breathlessness, which occurs with exercise. The feature of EIA that distinguishes it from normal breathing, or being "out of shape" is the fact that EIA is ALWAYS associated with a decrease in airflow. This can be measured with either a peak flow meter or a spirometer. It is also important that a specific diagnosis be made so that a person will not be labeled as asthmatic when they may be "normal" or have other conditions such as heart problems or anemia.
Dr. Cali also recommends before a person is labeled asthmatic, they have spirometric testing. An improvement in airflow after inhaling. A bronchodilator is an important indicator of asthma. Sometimes a bronchial challenge test is needed to diagnose asthma. In this test, the subject breathes in a known bronchoconstrictor in small quantities and the response is noted. Patients with asthma almost always respond to the inhaled agent by a reduction in airflow.
Inform Coaches – If coaches are made aware, than they can be prepared for the onset of EIA. Provide emergency contacts and medications with instructions, such as inhalers, should be available.
Warm and Moisten Air - Whatever the patient can do to warm and moisten the inhaled air can help prevent EIA. Nose breathing during exercise or wearing a loose covering over the mouth in cold weather may help. Sometimes, in severe cases, switching to an indoor sport like swimming may be necessary.
Start Out Slowly - It is important to start out slowly and warm up first before exercising at full tilt. Slowly jog around the track or field before practice or a game to prepare your lungs for full-speed.
Medications – are often necessary. Quick- acting bronchodilators like Albuterol, used 15-20 minutes before planned exercise, is recommended. This can be repeated once more during the exercise, but if tightness or wheezing occurs, the exercise should be stopped. Many patients with asthma require preventative treatment with anti-inflammatory medications. Inhaled steroids and/or leukotriene inhibitors may have to be added if the asthma is not controlled with Albuterol alone. In fact, some patients with asthma who are overly reliant on quick acting bronchodilator medications can get into serious trouble if they do not use inhaled steroids. Be sure to communicate your needs with your coaches.
Play Smart - In conclusion, people with asthma should not shy away from exercise. With proper precautions, people with asthma should be able to participate in all kinds of sports activities: baseball, football, soccer, swimming, tennis and running (even a marathon)! The key point is that the asthma needs to be under control and monitored by the patient, parents, coaches and doctor as a team.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Medical Contributor: Gregory Cali, DO, pulmonary specialist, Dunmore, PA

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Seasonal allergies affect 30 % of adults and 40% of children in the United States. Avoiding the outdoors is often not an option…especially if you enjoy outdoor activities and sports. Not long ago, it was unthinkable that an athlete with serious seasonal allergies could compete at a high level, such as the Olympics. Now, in great part due to advanced research, medications and proper management, an Olympic gold medal for those suffering from seasonal allergies is a reality. Recently, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease at the National Institutes of Health have published research on this topic to provide a better understanding and make recommendations.
The most common allergic reactions which athletes suffer from are sneezing, itchy and watery eyes, runny nose and coughing. Moreover, 67% of those with these symptoms also suffer from asthma. The athlete in NEPA is particularly vulnerable when the pollen count is high during spring and fall for several reasons. One, after being indoors all winter, one might develop a heightened sensitivity to allergens. Also, increased rapid and deep breathing during exercise makes athletes more susceptible to significant symptoms when exposed to allergens such as tree, grass and weed pollens.
Allergy skin testing can be performed to determine the allergens to which you are susceptible. Once determined, allergy shots are effective in building up tolerance to these allergens. If appropriate, you may be able to use allergy drops, administered under the tongue and conveniently used at home.
Asthma suffers should use their inhaler BEFORE symptoms occur. A recent study found that pretreatment using a short-acting bronchodilator inhaler within 15 minutes before exercise is very effective in preventing asthma symptoms for more than four hours. It is important to keep a bronchodilator available. If you fail to benefit from this, see your physician for other methods to control your exercise-induced symptoms.
Whether you have allergic respiratory problems from rhinitis or asthma, you many benefit from conditioning your airways with a 10 to 15 minute warm-up before and cool-down after the activity. This may serve to gradually prepare your lungs for an increased demand.
In addition to preventing dehydration on hot and humid days, constant hydration is very important for the athlete with allergies to prevent dry airways in athletes.
Know the signs and symptoms of asthma (coughing, wheezing, tightness in chest, shortness of breath).
Some schools have a file on each student athlete with a allergic or asthmatic problem which requires medication. The file includes information such as medical doctor release and instruction, emergency contacts and medications. Students must have their medications on hand before they can enter the field. The National Athletic Trainers Association recommends using a peak flow meter to monitor at risk players and can determine when a player can return to the field.
If possible, find an alternate practice facility with climate control for athletes at risk. Plan practices for these athletes when the pollen count is low. Check the newspaper or internet for pollen counts in your area. Training by the water, (ocean) where there is a breeze and less pollen is helpful.
Shower and change clothing immediately after being outdoors
During a flare up, do less aerobic exercise to limit stress on respiratory system. Try strength training indoors instead.
When pollen count is high, keep windows shut at home and in your car….use air-conditioning.
Keep pets out of your bedroom…especially when sleeping
Dry clothing in dryer…do not hang on clothesline outdoors
Sources: American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. National Athletic Trainers Association.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is dedicated to the memory of John R. O’Brien, Esq., who recently passed due to medical complications associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). John was a source of joy and inspiration for those fortunate to have known him. Twenty years ago, John hesitantly agreed to contribute to my column on MS with two requirements: one, if the column would be valuable to those affected by MS and two, he would remain anonymous. When speaking with his dedicated wife, Sally, it became very apparent that any discussion of John’s life would be diminished if it was defined by the disease because he was committed to turning his “DISABILITY INTO AN ABILITY!”
With the help of his loving wife, family, friends, and devices such as an electric scooter and adaptive car, John not only lived but thrived! He was a skilled lawyer, a respected member of the Bar, and an active member of the community. John served on the executive committee of the Lackawanna Bar Association. In addition, the Lackawanna Pro Bono honored him recently. He also taught business law and healthcare law and coached Prep’s mock trial team.
John shared his thoughts with me about the challenges of redefining life… from Golf Club Champion to living with a physically disabling disease. Anyone who knew him would agree that he succeeded in doing so through his keen intellect and sharp wit and humor…his heart and brain overcompensated for his body! In addition to reading books in Latin and Greek, he had his crossword puzzles published in The New York Times and Los Angeles Times. In September 2023, John conducted an interview with presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin before a full house at the Scranton Cultural Center. Ms. Goodwin later reported that John was the most knowledgeable, effective and enjoyable interviewer she’s encountered.
John’s absence will be deeply felt and his legacy will continue to shape our community for years to come!
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic disease. While it may lay dormant and stable for a period of time, living a healthy lifestyle will make a positive contribution toward how you and your family live with Multiple Sclerosis. Studies show that a life of family, love, and support are essential to maintain a positive attitude with a chronic illness. This combined with a healthy diet and proper exercise can contribute greatly toward taking control and living a relatively normal life with MS.
As I have mentioned in many other columns, studies show that people with good attitudes and great faith live longer than others. This is especially helpful when living with chronic disease like Multiple Sclerosis. The Cleveland Clinic offers some suggestions how to maintain a positive attitude:
Many sources, including the Cleveland Clinic suggest that exercise, when performed properly, can have a positive impact on Multiple Sclerosis symptoms both physically and psychologically. However, because you have a chronic illness, you should consult with you family physician and physical therapist before beginning an exercise program. They will advise you on the proper type and amount of exercise.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is dedicated to the memory of John R. O’Brien, Esq., who recently passed due to medical complications associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). John was a source of joy and inspiration for those fortunate to have known him. Twenty years ago, John hesitantly agreed to contribute to my column on MS with two requirements: one, if the column would be valuable to those affected by MS and two, he would remain anonymous. When speaking with his dedicated wife, Sally, it became very apparent that any discussion of John’s life would be diminished if it was defined by the disease because he was committed to turning his “DISABILITY INTO AN ABILITY!”
With the help of his loving wife, family, friends, and devices such as an electric scooter and adaptive car, John not only lived but thrived! He was a skilled lawyer, a respected member of the Bar, and an active member of the community. John served on the executive committee of the Lackawanna Bar Association and was recently honored by the Lackawanna Pro Bono. He also taught business law and healthcare law and coached Prep’s mock trial team.
John shared his thoughts with me about the challenges of redefining life… from Golf Club Champion to living with a physically disabling disease. Anyone who knew him would agree that he succeeded in doing so through his keen intellect and sharp wit and humor…his heart and brain overcompensated for his body! In addition to reading books in Latin and Greek, he had his crossword puzzles published in The New York Times and Los Angeles Times. In September 2023, John conducted an interview with presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin before a full house at the Scranton Cultural Center. Ms. Goodwin later reported that John was the most knowledgeable, effective and enjoyable interviewer she’s encountered.
John’s absence will be deeply felt and his legacy will continue to shape our community for years to come!
According to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, Multiple Sclerosis affects approximately 400,000 people in the United States. Multiple Sclerosis is second only to trauma as the most common cause of neurological disability for those in early to middle adulthood. MS is almost three times as common in women. Multiple Sclerosis is very uncommon before adolescence or after 50. However, the risk increases from teen years to age 50.
Multiple sclerosis is considered to be an autoimmune disease. The immune system of the body does not work properly when it fails to attack and protect the body against substances foreign to the body such as bacteria. Instead, the system allows the body to attack normal tissues and create diseases such as MS, rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
In MS, the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system. Each nerve has an outer covering of a fatty material (myelin) for insulation to improve the transmission and conductivity of impulses or messages to and from the brain. The damage to the myelin of the nervous system interrupts the ability of messages to travel to and from the brain, through the spinal cord and to other areas of the body such as the muscles in the arms and legs. Due to this “short circuiting” the brain becomes unable to send or receive messages. In multiple sclerosis, scar tissue or plaques (sclerosis) replaces the fatty myelin in “multiple” areas. This is also called demyelination.
The symptoms associated with MS vary greatly from person to person. The amount, frequency and speed of the demyelination process vary greatly and are directly related to the loss of strength and function in daily activities. Some people are independent and ambulatory with mild and infrequent episodes of weakness and disability and live a relatively normal life. Others suffer from frequent and aggressive episodes that significantly weaken and disable. Some common symptoms in the early stages include: muscle weakness, loss of coordination, blurred vision, pain in the eyes, double vision. Some common symptoms as the disease progresses are: muscle stiffness with muscle spasms, pain, difficulty controlling urination, difficulty thinking clearly.
The diagnosis of MS can be very difficulty in the early stages because the symptoms are often vague and temporary. Also, MS symptoms are very similar to other neurological problems. A neurologist will run several tests to rule out other possible problems. However, an MRI showing demyelination of the nerves is a primary confirmation.
Treatment for MS depends upon many factors and requires consultation with your physician. Some medications can control the frequency and severity of MS symptoms such as pain, weakness, and spasticity. Also, some drugs can slow the progression of certain types of MS. Additional treatments for MS include: diet, exercise, physical therapy, support groups, and counseling for the MS patient and their family. Part II of Multiple Sclerosis will discuss these options in further detail next week.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy - NEXT WEEK: PART II OF II - MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria no longer respond to the drugs designed to kill them. For more than a decade, the Centers for Disease Control along with other national and international agencies has supported an initiative called “Antibiotic Stewardship” the hallmark of which is the judicious, appropriate use of antimicrobials.
It’s told in some sobering statistics from the CDC, World Health Organization, and Food and Drug Administration:
Patients and providers must take equal responsibility. When we get sick, we often feel we need an antibiotic right away. In fact, we often demand one. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018 found that to achieve a patient satisfaction rating in the 90th percentile physicians needed to prescribe antibiotics 75% of the time. Is this the correct approach to therapy? Are we using antibiotics too readily? What are the consequences of profuse antibiotic use?
In which of the following situations are antibiotics warranted?
A. Cold symptoms (runny nose, sore throat, headache) with a fever of 101F for 2 days
B. Cold symptoms lasting 12 days with persistent stuffiness and headache
C. Cold symptoms for 3 days with yellow-green mucous discharge
D. all of the above
The correct answer is B. Let’s discuss the reasons. Symptoms experienced as part of the common cold can include green/yellow sputum, cough, runny nose, stuffiness, sore throat, headache, fever, and mild muscle aches. This illness is caused by a virus, most likely a rhinovirus. Currently, 160 identified strains of rhinovirus are know.
Antibiotics work to destroy bacteria, not viruses since they have no activity against viruses. Antibiotics target specific bacterial structures or functions. Common bacterial targets for antibiotics include the cell wall (amoxicillin), ribosome activity (azithromycin), and bacterial DNA (levofloxacin). All of those are lacking in the very primitive structure of a virus. So, you could sit in a bathtub full of penicillin and not cure your cold with an antibiotic because there is simply nothing for the antibiotic to destroy in the viral structure.
Why are antibiotics appropriate after 10 days with cold symptoms? The typical common cold lasts between five and ten days with symptoms peaking around three or four days and waning at day six. If symptoms are consistent or regress and then become worse it is likely a sign of bacterial superinfections (super = on top of).
Usually, we carry certain bacteria with us as part of our “normal flora”. The mouth, nasal passages, large intestines, and skin host the most bacteria in the body. These bacteria work with our body and provide various “services” including protection against other more dangerous bacteria, digestion of food, and production of vitamins. A viral infection disturbs the normal balance of bacteria, allowing for proliferation and subsequent bacterial infection.
Why should we be careful about antibiotic use?
Antibiotics are not innocuous substances. They have significant side effect profiles. Adverse drug reactions associated with antibiotics can be less severe and consist of mild rash or nausea. More serious reactions include heart arrhythmias, tendon rupture, Stevens Johnson Syndrome (severe skin rash resembling thermal burns), and liver and kidney damage. Remember – every drug – not only antibiotics – has the potential to cause unpredictable adverse reactions
The most compelling reason to be careful about antibiotic use is resistance. Each time bacteria are exposed to an antibiotic, some are destroyed but others adapt to resist the antibiotic and live to see another day (remember Darwin’s Survival of the Fittest?). Antibiotics are unique in that the more they are used, the less effective they become. When antibiotics are used inappropriately – not taking them on schedule, for the right duration, taking them for a viral illness – bacteria have a chance to adapt to overcome the antibiotic activity. The resistant bacteria may go on to set up a resistant infection in you or that bacteria may be transmitted to others.
There are several ways we can combat this problem according to the Joint Commission on Healthcare Accreditation 2020 Standards. It is important to identify the causative agent if possible.
For example, a sore throat should not be treated with antibiotics until a throat culture or rapid strep test is obtained and a bacterial cause is identified. According to the Infectious Disease Society of America, 90 percent of adult sore throats have a viral cause, not bacterial. Avoid unneeded clinic or urgent care visits and utilize OTC and non-drug measures to manage non-bacterial infection symptoms.
Mislabeled allergy status leads to more expensive, less optimal antibiotic choices, more complex administration, increased resistance rates, and more treatment failures. The most common listed drug allergy in the US is Penicillin. According to the CDC, 10% percent of patients reports an allergy, however, < 1% of patients have a true allergy precluding penicillin or penicillin-like agents (the biggest class of antibiotic agents).
Vaccines may prevent bacterial infections or prevent viral infections which will avert a bacterial superinfection. Here are two examples of where vaccines can lower antibiotic use. The pneumococcal “pneumonia” vaccine protects against the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. Following the current guidelines for vaccination during childhood and adulthood decreases pneumococcal infections. According to the CDC, this vaccine has reduced pneumococcal infections by more than 90% in children. In addition, antibiotic-resistant pneumococcal infections have decreased in the United States since the pneumococcal vaccine was introduced.
The shingles vaccine also minimizes antibiotic use. The shingles vaccine “Shingrix”, is currently approved for individuals 50 years old (and older) as a two-dose series. Not only does it effectively prevent the occurrence of shingles, a painful, debilitating re-emergence of the chickenpox virus, but also reduces the risk of a potential secondary bacterial skin superinfection. Vaccine prevention of viral illness may subsequently eliminate antibiotic use.
Educating patients and prescribers will lead to the proper use of antibiotics to curb antibiotic resistance.
Guest Author: Dr. Gretchen Welby, PharmD, MHA
Dr. Welby received degrees from Keystone College and Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science. She received a Master of Health Administration Degree from the University of Scranton and a Doctor of Pharmacy degree from Temple University. She is currently the Academic Director of the Physician Assistant Program at Marywood University where she teaches Anatomy, Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Pharmacology.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Ice baths have become a new trend or fad in health and fitness, especially among elite athletes and some celebrities. However, it is far from a new treatment modality. In fact, the Ancient Greeks employed cold-water immersion for fever, pain relief, relaxation and socialization. In addition, Hippocrates documented the use of cold for medicinal purposes for its analgesic benefits.
Ice baths, a type of cryotherapy, is also referred to as cold water immersion (CWI) or cold water therapy. This involves immersing your body in ice water for approximately 5-15 minutes from the neck down at 50-59 degrees. The ice baths are commonly used for pain, delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and inflammation and mood elevation.
In theory, the cold water lowers the temperature of your skin and body by vasoconstriction (narrow) of the blood vessels. When you get out of the cold, water the vasodilatation (widen) of the blood vessels. Immediately, this brings fresh oxygen and nutrient-rich blood back to the tissues to warm the body and in the process, reduce pain, inflammation and promote healing.
If you have the following health conditions, ice baths may not be the best therapeutic modality for you. Before you consider trying an ice bath, consult with your physician to avoid potentially serious problems:
While some studies have shown that subjects report less muscle soreness following CWI when compared to rest, most studies suggest that the reported effects are placebo. Also, reports of improved circulation, reduced inflammation and improved recovery or performance has not been scientifically validated. In view of this, it is recommended that those considering the use of CWI for pain and inflammation management, reduced muscle soreness, and mood elevation, should consult their physician to determine if the potential risks are worth the purported benefits.
SOURCES: nih; health.com; health.clevelandclinic.org; prevention.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
As most sports enthusiasts know, Aaron Rodgers, former Green Bay Packer quarterback and recent New York Jets QB (for just over a minute and half) suffered a season ending injury when he tore his Achilles tendon in the first game of the 2023/24 NFL season. Since then, I have been answering many questions from patients and sports fans about the nature of the Achilles Tendon rupture injury, recovery, and how to prevent it.
As the days continue to get shorter and temperatures begin a slow steady decline, athletes and exercise enthusiasts will work harder to warm-up and exercise during the winter months. A little caution and preparation are in order to avoid muscle/tendon strain, or worse yet, muscle/tendon tears, especially Achilles Tendon rupture. The Achilles tendon is one of the more common tendons torn.
This is the second of two columns on Achilles tendon rupture. Last week, I discussed the definition, sign and symptoms of the problem. This week will present examination, treatment and outcomes.
A thorough history and physical exam is the first and best method to assess the extent of the injury and determine accurate diagnosis. While a complete tear is relatively easy to determine, a partial or incomplete tear is less clear. Ultrasound and MRI are valuable tests in these cases. X-rays are not usually used and will not show tendon damage.
Consultation with an orthopedic or podiatric surgeon will determine the best treatment option for you. When conservative measures fail and for tendons completely torn, surgical intervention is usually considered to be the best option with a lower incidence of re-rupture. Surgery involves reattaching the two torn ends. In some instances, a graft using another tendon is required. A cast or walking boot is used post-operatively for 6-8 weeks followed by physical therapy.
Most people return to close to normal activity with proper management. In the competitive athlete or very active individual, surgery offers the best outcome for those with significant or complete tears, to withstand the rigors of sports. Also, an aggressive rehabilitation program will expedite the process and improve the outcome. Walking with full weight on the leg after surgery usually begins at 6 -8 weeks and often requires a heel lift to protect the tendon. Advanced exercises often begin at 12 weeks and running and jumping 5-6 months. While a small bump remains on the tendon at the site of surgery, the tendon is well healed at 6 months and re-injury does not usually occur.
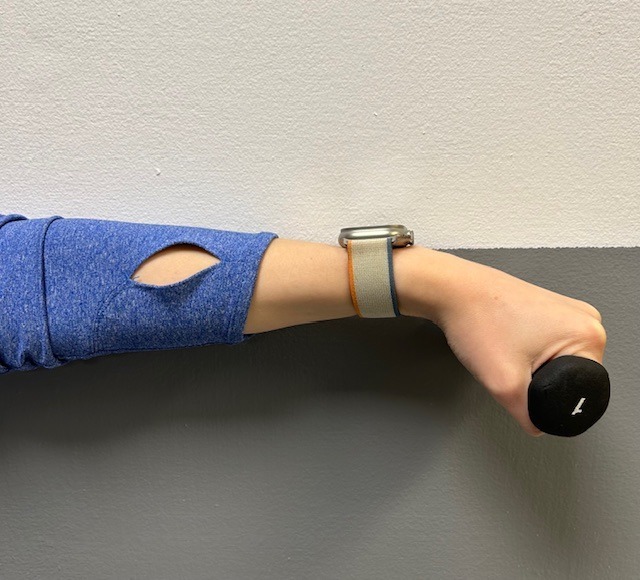
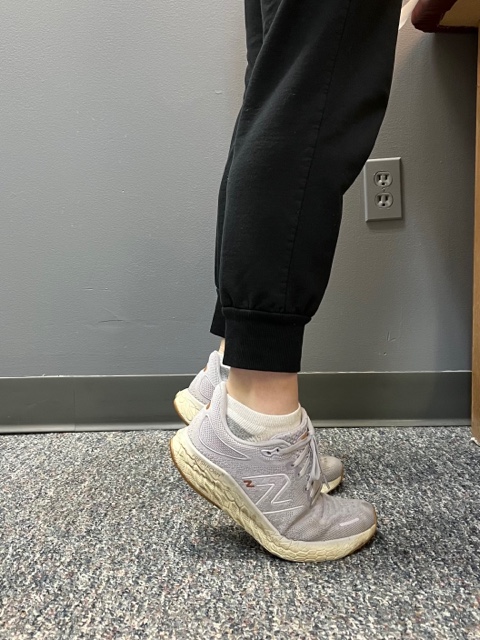
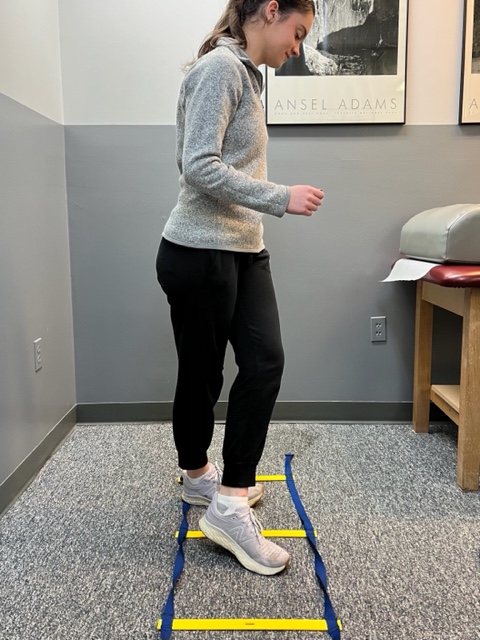
Prevention of muscle and tendon tears is critical for healthy longevity in sports and activities. In addition to the Achilles tendon, the tendons of the quadriceps (knee) and rotator cuff (shoulder) are also vulnerable. A comprehensive prevention program includes: gradual introduction to new activities, good overall conditioning, sport specific training, pre-stretch warm-up, stretch, strengthening, proper shoes, clothing, and equipment for the sport and conditions. Also, utilizing interval training, eccentric exercise (lowering body weight slowly against gravity – Photo 1) and proprioceptive and agility drills are essential (Photos 2 & 3).

In PHOTO 1a & 1b: Eccentric Lowering and Lengthening: for the Achillies tendon during exercise. Beginning on the ball of both feet (1a), bend the strong knee to shift the weight onto the weak leg (1b). Slowly lowering the ankle/heel to the ground over 5-6 seconds. Repeat.
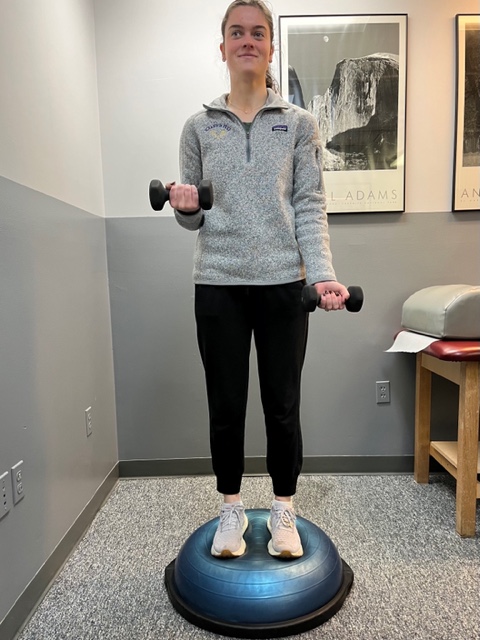
In PHOTO 2: Proprioceptive Training: for the Achillies tendon. Standing on a Bosu Ball while exercising the upper body (for example, biceps curls, shrugs, rows, lats) while maintaining balance on the ball.
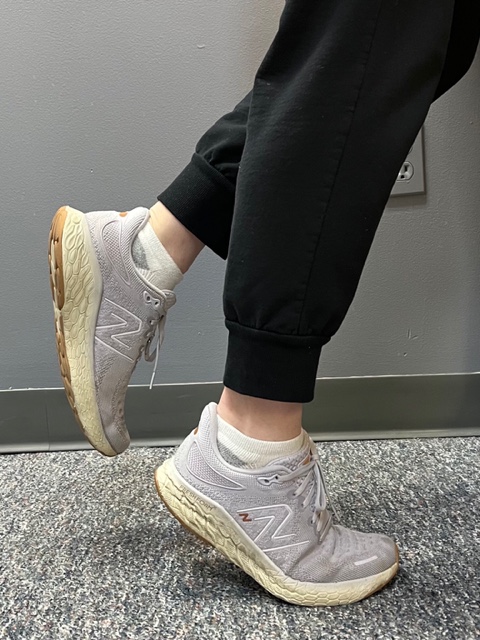
PHOTO 3: Agility Drills: for the Achilles tendon involves stepping through a “gait ladder” in various patterns and at various speeds.
MODEL: Kerry McGrath, student physical therapy aide at Mackarey Physical Therapy
Sources: MayoClinic.com;Christopher C Nannini, MD, Northwest Medical Center;Scott H Plantz, MD, Mount Sinai School of Medicine

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!