Here are 10 most common exercise myths!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
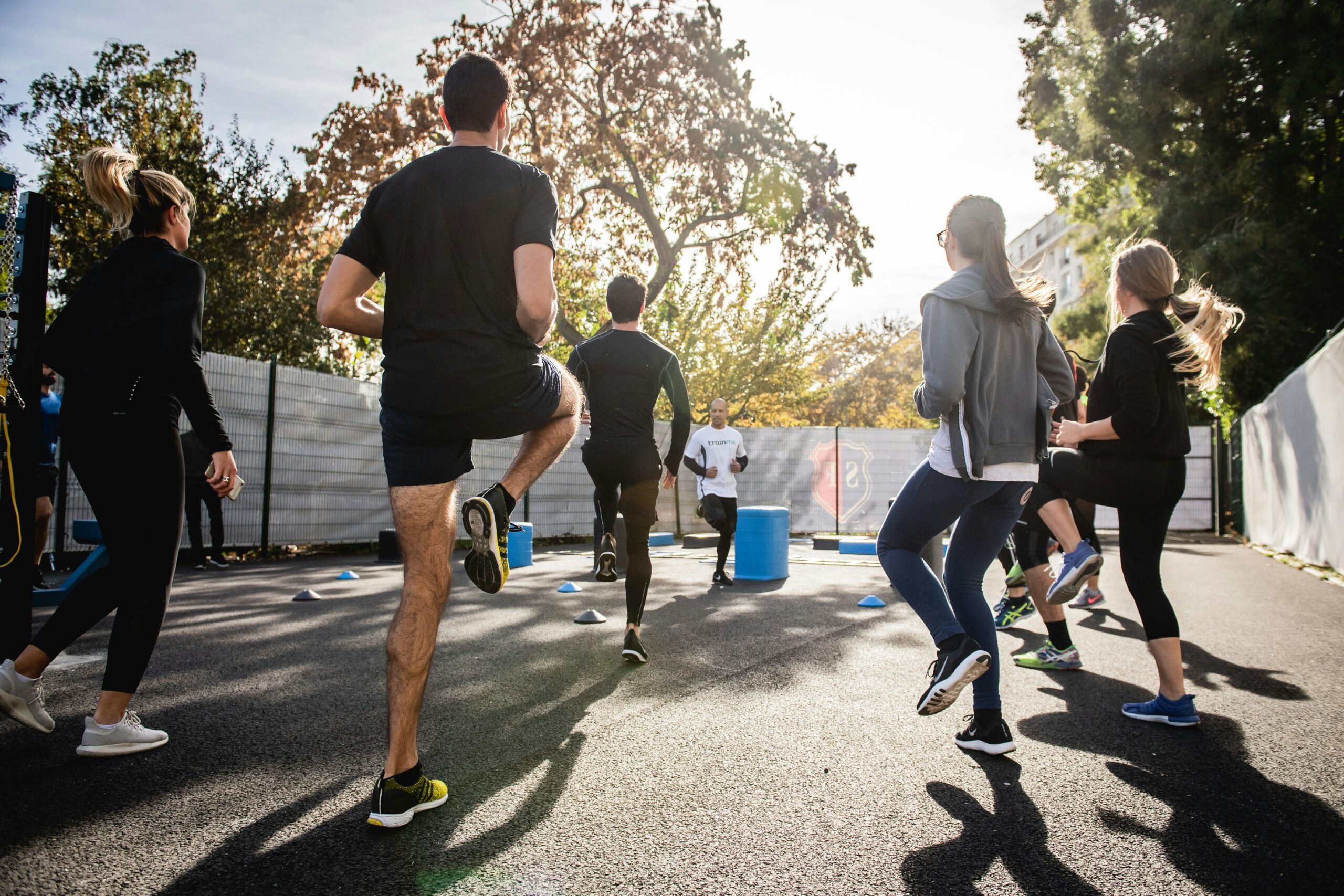

Have you ever noticed high level athletes warming up before a game or competition walking or running backwards? You may also see fitness enthusiasts in gyms emulating these athletes to improve their fitness or performance. I found the concept of backward walking, (also called retro walking) interesting and decided to research the topic for more information and validation. Walking backward does have many therapeutic benefits, however, before you attempt this activity on a treadmill or elliptical, please consult your physician and physical therapist and have a spotter nearby.
At a recent meeting of The American College of Sports Medicine, several studies were presented on the topic of backward waking. Most of the research was conducted while moving backward on a treadmill and an elliptical machine. When comparing two groups recovering from knee injuries, the backward motion group showed significant improvement in strength in the quadriceps (front thigh) and hamstring (back thigh) muscles when compared to the traditional forward walking group. Furthermore, the muscles of the front (tibialis anterior) and back (gastro/achilles) of the shin/ankle also demonstrated an increase in strength and endurance with backward walking. One explanation is that forward motion is routine in daily living that it has become very efficient and does not tax or stress the muscles the body. While this efficiency prevents fatigue in daily activities, it may not stress the muscles enough to gain strength as quickly as an unfamiliar exercise.
Due in great part to the increased strain of performing an unfamiliar exercise, backward walking on a treadmill or backward pedaling on an elliptical, offered a greater cardiovascular benefit and caloric expenditure than forward motion at all levels. Specifically, walking backward on a treadmill at 2.5 mph at grades of 5% - 10% has been found to significantly increase cardiovascular endurance than walking forward under the same conditions. This knowledge is useful for healthy individuals in need of greater cardio exercise. However, it may also serve as a precaution for those with cardio problems and should consult their physician prior to engaging in this activity.
A recent study in the International Journal of Obesity, found that those who performed new activities or increased the intensity of an activity, even if for a short duration (interval training) expended more energy and burned more calories than those who worked out at the same pace consistently for a longer duration. Moreover, when engaging in a new activity such as backward walking, even more calories were burned. This phenomenon may be due to the fact that routine activities such as forward walking are performed more efficiently and easily.
We challenge our body when we inefficiently perform a new motor skill such as backward walking and burn more calories. In other words, if you want to burn more calories without exercising for longer periods of time, than try a new activity and engage in higher intensity, intermittently, for part of the time. For example, walk backward on the treadmill for 30 minutes at 2.5 mph, but do so at a 5 – 10% incline for 1-2 minutes every 5 minutes.
Some studies show that using other muscle groups by performing different exercises not only prevents boredom, but also protects your muscles and tendons from overuse and joints from wear and tear. Specifically, the knee joint and the patella joint (the joint where the knee cap glides on the knee), benefits from backward walking due to less stress and compression forces on the joint. The thigh and ankle/foot muscles benefit from using a different form of contraction while lengthening the muscle. Some authors propose that this may also prevent strains and pulls and may be valuable to strengthen those with a history of shin splints and flat feet (pronation).
Mixing up your program prevents boredom. As a rule, those willing to change their exercise routine are more compliant and continue to exercise longer than those stuck in the same routine. A new challenge to improve distance, speed, and resistance while exercising in a different direction will be refreshing to your program.
Prevention of falls by improvement in balance and coordination has received a great deal of attention in the past few years. This is not only valuable to the athlete but may be even more important to those over 50. With age, balance centers are slow to react to changes in inclination, elevation, rotation and lateral movements. This slow reaction time leads to falls that may cause fractures, head injuries and more. Working on this problem by challenging the vestibular and balance centers before it is seriously compromised is important and backward walking is one way for this to be effectively accomplished.

Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

“When is it safe for my child to start weight training?” This is a very common question asked by parents of young athletes who are looking for advice regarding their children’s participation in weight training. This month, for example, I received three such inquiries. While some who are eager to get a “competitive edge” may not be satisfied with the answer, these recommendations are grounded in the scientific literature and medical specialist with the hope to prevent injury and dispel fear and fallacy.
Weight training, weight lifting or resistive training all describes the use of a resistive force on a muscle to improve strength. While much attention has been given to the benefits of weight training in adults, much less has been written about its application in children.
According to the Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, children less than 12 years old are considered prepubescent or before puberty. Teenagers who are between 12 and 19 are considered to be adolescents. Studies consistently demonstrate that strength gains are much more significant in adolescents than in preadolescents. It is important to note that these strength gains are not only from the enlargement of muscle fibers (hypertrophy), but also from the improvement in the coordination and efficiency in muscle contraction and the recruitment of motor units and fibers within the muscle.
Preadolescents lack the hormones necessary to develop masculine characteristics. Adolescents begin to produce the hormones of testosterone and androsterone to develop secondary sexual characteristics such as pubic hair and enlarged genitalia. In view of this, age 13-14 is the optimal age to safely begin and benefit from a well-designed weight training program.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

PEOPLE OFTEN ASK ME, “IS THERE SUCH A THING AS AN EXERCISE RUT?”. THEY WANT TO KNOW WHY THEY DO NOT SEEM TO BE IMPROVING WITH THEIR EXERCISE PROGRAM. They exercise 3-4 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes and they feel frustrated and STUCK in a rut.
The purpose of this column is to offer suggestions to improve or get more out of a “stale” exercise program. Last week’s column offered tips to improve a stale cardiovascular and strength program. We will discuss flexibility and functional training tips, including the components necessary for a healthy mind, body and spirit connection.
Flexibility training involves the careful stretching of the muscles, tendons and joints to improve range of motion in order to safely perform daily activities and sports without injuring or tearing soft tissues. It is probably the most neglected part of the fitness program. However, while the amount of inherent flexibility varies for each person, a minimal range is necessary as it relates to daily activities and sports. For example, as you age it is important to have enough flexibility in your back, hips and knees to wash your feet, put shoes and socks on. After a warm –up activity, perform flexibility exercises slowly and gently. There are two types of flexibility exercises; dynamic and static. Perform dynamic stretching with movement such as pushing the ankle up and down like a gas pedal. Complete passive stretching using an outside force, such as a towel to pull the ankle up to stretch the calf. Dynamic should be performed before an activity (before running or playing tennis) and static performed after the activity is over in order to increase range of motion for future activities.
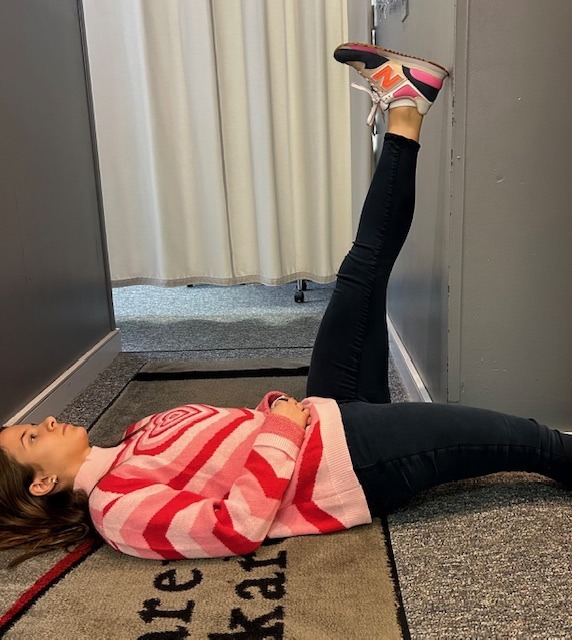

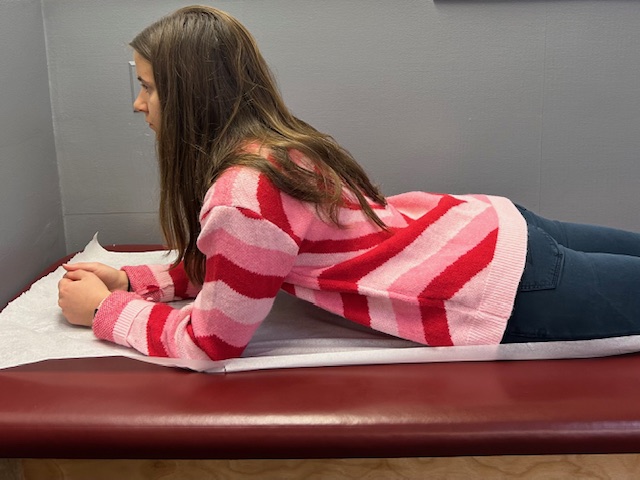
In order to prevent an exercise program from getting stale, one must incorporate all aspects of wellness…a healthy mind, body and spirit!
It is easy for fitness enthusiasts to get so focused on maintaining a routine that they allow their program to become stale and ineffective. It is essential to reassess and update your program to prevent stagnation.
Make sure the routine has all three fundamental components of a well-balanced exercise program; cardiovascular, strength and flexibility training. Moreover, to be truly healthy, one must work toward a “Healthy Mind, Body, and Spirit. Therefore, in addition to traditional exercise one must incorporate the following: nutrition; meditation, relaxation techniques, yoga, core fitness; functional/sports specific training; leisure sports and activities
In order to prevent an exercise program from getting stale, one must incorporate all aspects of wellness…a healthy mind, body and spirit!
While each component offers its own specific benefit, the combination of all three cooperatively provides unique value. Too often, fitness enthusiasts concentrate on the exercises they LIKE or are good at more than the ones they NEED.
Sources: National Institutes of Health; American Council on Exercise
Model: Lily Smith, Physical Therapy Student, University of Scranton, PT aide, Mackarey Physical Therapy

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
PEOPLE WILL OFTEN ASK ME, “IS THERE SUCH A THING AS AN EXERCISE RUT?” THEY WANT TO KNOW WHY THEY DO NOT SEEM TO BE IMPROVING WITH THEIR EXERCISE PROGRAM…they exercise 3-4 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes and they feel frustrated and STUCK in a rut. While initially responding favorably to exercise, after 6 -9 months or more, they do not notice progress in weight loss, strength, tone, endurance or daily function.
The purpose of this column will be to offer suggestions on how to improve or get more out of a “stale” exercise program or an exercise rut. Step one is to build an exercise program that is grounded in the basics. Next step two, which begins after the basics have been mastered, includes the components necessary for a healthy mind, body and spirit connection and translates into functional activities of daily living including work and leisure sports.
Make sure your routine has all three fundamental components of a well-balanced exercise program; cardiovascular, strength and flexibility training. While each component offers its own specific benefit, the combination of all three cooperatively provides unique value. Too often, fitness enthusiasts concentrate on the exercises they LIKE or are good at more than the ones they NEED. A well-balanced program includes what you like and need! In fact, recent studies show that those performing all three components surpassed those performing one or any combination of two of the training types when tested for efficient oxygen uptake (VO2 Max), production of HDL (good cholesterol), lower body fat percentage, and lower blood glucose levels.
Cardiovascular exercise is any activity that raises your heart rate and respiratory rate. This type of exercise strengthens the heart muscle and the muscles that assist in breathing. When these muscles are stronger, they in turn work more efficiently to deliver oxygen to your muscles and other parts of the body. Ultimately, these oxygenated muscles can work harder and longer to burn fat during exercise and at rest.
Examples of Cardiovascular Exercises: Running, Brisk Walking, Swimming, Biking, Rowing, Elliptical Training and Stepper Training. Most experts recommend at least 30 minutes of sustained cardio, 3-4 days per week. However, recent studies support the notion of performing 10-15 minutes, twice daily, 4 days per week. For those “stuck” in a fitness or exercise rut, to advance your program, cardio should be performed 5-6 days per week for 45-60 minutes.
Strength training is an activity that provides any type of resistance to muscle contraction to build strength in the muscle. The resistance can be without movement against an immovable object such as pushing against a wall (isometric) or with movement such as lifting up or lowering a weight down against gravity (isotonic/dynamic). There are two types of isotonic muscle contraction; concentric, which involves raising the weight against gravity as the muscle shortens and eccentric which involves lowering a weight against gravity as the muscle lengthens. A standing biceps curl is an example that incorporates both concentric and eccentric contractions. A progressive strength training program includes all three types of muscle contraction. By using the classic bicep muscle curl these photos will demonstrate all three types of muscle contraction:
-Isometric Bicep Muscle Curl – pull up on door knob without allowing any movement of the arm.
-Concentric Bicep Muscle Curl – raise a dumbbell up against gravity as the muscle shortens.
-Eccentric Bicep Muscle Curl – lower a dumbbell slowly (4-6 seconds) against gravity as the muscle lengthens.
Sources: National Institutes of Health; American Council on Exercise

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
NEXT WEEK! Read Stuck in an Exercise Rut…Part II of II:
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!