Recently, two patients asked me when I thought it would be safe for them to return to their exercise programs after abdominal surgery. She stated that she was not sure how to properly and safely implement or return to her program.
This column will attempt to ensure a safe return to activity and exercise following general surgery such as gall bladder, appendix, hernia, etc. The post-operative patient has many questions: When is it safe to begin an exercise program? How do I begin? What is the best exercise? Which exercises are best? How do I know if the activity is too intense or not intense enough? Are there safe guidelines?
Before you begin, discuss your intention to exercise with your surgeon and primary care physician. Get medical clearance to make sure you can exercise safely. With the exception of short daily walks, don’t be disappointed if your surgeon requires you to wait at least until your 6 week post-op check-up to begin exercise.
While a 60 minute workout would be the long term goal, begin slowly at 15-20-30 minutes and add a few minutes each week. Make time to warm up and cool down.
Warm-up 5-10 minutes
Strength Training 10-15-20 minutes
Aerobic 10-15-20 minutes
Cool down 5-10 minutes
How to Monitor Your Exercise Program:
First, determine your resting heart rate by taking your HR (pulse) using your index finger on the thumb side of your wrist for 30 seconds and multiply it by two. 80 beats per minute is considered a normal HR but it varies. This is a good baseline to use as a goal to return to upon completion of your workout. For example, your HR may increase to 150 during exercise, but you want to return to your pre exercise HR (80) within 3-5 minutes after you complete the workout.
For those who are healthy, calculating your target heart rate (HR) is an easy and useful tool to monitor exercise intensity.
220 – Your Age = Maximum Heart Rate
EXAMPLE for a 45 year old: 220 – 45 = 175 beats per minute should not be exceeded during exercise.
For those concerned about calories expended during exercise.
NOTE: Keep the level at a light/moderate level for the first four to six weeks and advance to the moderate/heavy at week six. The Very Heavy Level may not be appropriate for 12 weeks post op is for those who have a reasonable fitness level and exercise 4-5 days per week.
Example of Data Found on Fitness Equipment
Remember, this is only accurate if you program your correct height, weight and age.
Level kCal/min MET
Light 2 - 4.9 1.6 – 3.9
Moderate 5 - 7.4 4 – 5.9
Heavy 7.5 - 9.9 6 - 7.9
Very Heavy 10 - 12.4 8 – 9.9
Always secure physician approval before engaging in an exercise program.
If the patient is on beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol, etc), it is important to use the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale (RPE) scale to determine safe exercise stress since exercise will not increase HR as expected:
0 - Nothing at all
1 - Very light
2 - Light
3 - Moderate
4 - Somewhat intense
5 - Intense (heavy)
6
7 - Very intense
8
9 - Very, very intense
10 - Maximum Intensity
NOTE: Keep the RPE at 2-3 the first 6 weeks post op and advance to level 3-4 at 8-12 weeks post op. Levels 5-6-7 are for those with a reasonable fitness level and exercise 4-5 days per week. The advanced levels should not be attained until 2-3 months of exercise and 3-4 months post op.
MEDICAL CONTRIBUTOR: Timothy Farrell, MD, is a general surgeon at GCMC.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Tennis elbow, also called lateral epicondylitis, is an inflammation of the lateral (outside) bony protuberance at the elbow. It is at this protuberance that the tendon of the long muscles of the hand, wrist and forearm attach to the bone. As the muscles repeatedly and forcefully contract, they pull on the bone, causing inflammation. The trauma is irritating when working the muscles in an awkward position with poor leverage like hitting a backhand in tennis.
It is not unusual for a patient to come to my office with severe pain on the outside of their elbow. Especially, after intensifying their tennis workouts or changing the racquet string tension. Others come to me with pain on the inside of the elbow (“golfer’s elbow”) from wrist action that advanced golfer’s use at impact. However, this problem is not only for tennis players and golfers. Laborers working with wrenches or screwdrivers with an awkward or extended arm can also develop tennis elbow. Others who are vulnerable are: those working for hours at a computer using a mouse as well as those working hard maintaining their lawns and gardens.
In a more chronic problem, lateral elbow pain may arise by a degenerative condition of the tendon fibers on the bony prominence at the lateral elbow. Sporadic scar tissue forms from a poor attempt by the body to overcompensate and heal without eliminating the cause.
While symptoms may vary, pain on the outside of the elbow is almost universal. Patients also report severe burning pain that begins slowly and worsens over time when lifting, gripping or using fingers repetitively. In more severe cases, pain can radiate down the forearm.
Conservative treatment is almost always the first option and is successful in 85-90 percent of patients with tennis elbow. Your physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication (over the counter or prescribed). Physical/Occupational therapy, rest, ice, and a tennis elbow brace to protect and rest may be advised. Ergonomic changes in equipment, tools, technique and work-station may be necessary. Improvement should occur in 4-6 weeks. If not, a corticosteroid injection may be needed to apply the medication directly to the inflamed area. Physical therapy, range of motion, and stretching exercises may be necessary prior to a gradual return to activity. Deep friction massage can assist healing.
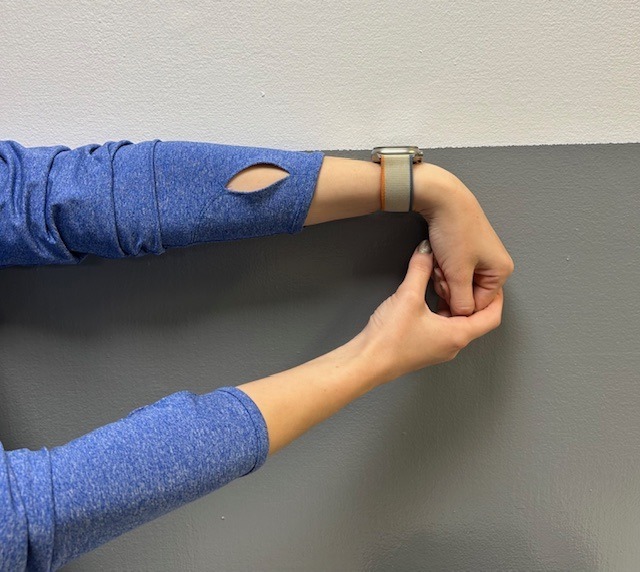

Exercises performed in a particular manner to isometrically hold and eccentrically lengthen the muscle with contraction.
New Conservative Treatment: Platelet-Rich-Plasma (PRP) is a new treatment for the conservative management of degenerated soft tissues that has recently received great media attention. In great part, due to its success in several high profile athletes. According to the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,(JAAOS), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is autologous (self-donated) blood with an above normal concentration of platelets. Normal blood contains both red and white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Platelets promote the production and revitalization of connective tissue by way of various growth factors on both a chemical and cellular level.
The actual PRP injection requires the patient to donate a small amount of their own blood. The blood is placed into a centrifuge (a machine that spins the blood at a high velocity to separate the different components of blood such as plasma, white and red blood cells), for approximately 15 minutes. Once separated, the physician draws the platelet-rich plasma to be injected directly into the damaged tissue. In theory, the high concentration of platelets, with its inherent ability to stimulate growth and regeneration of connective tissue, will promote and expedite healing.
Surgery for tennis elbow is only considered in patients with severe pain for longer than 6 months without improvement from conservative treatment. One surgical technique involves removing the degenerated portion of the tendon and reattaching the healthy tendon to bone. Recently, arthroscopic surgery developed to perform this technique. However, research does not support the value of one over the other at this point. Physical/occupational therapy is used after surgery. Return to work or athletics may require 4-6 months. More recently, a surgical technique using ultrasound to guide a needle to debride (clean) the area of scar tissue has been developed. If eligible for this procedure, the time required for healing, rehabilitation and return to activity is much shorter.
If you feel you suffer from tennis elbow, ask your family physician which of these treatment options are best for you.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy

This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
I enjoy the privilege of working with people recovering from a wide variety of medical conditions. Many of these conditions can directly affect activities of daily living, particularly, the ability to drive safely: orthopedic and sports injuries, fractures, sprains and strains, joint replacements, hip fractures, shoulder and elbow surgeries and spinal fusions. Despite the many different types of problems, there is one question that is invariably asked, “When can I return to driving?” Unfortunately, the answer is not as simple as the question because it depends on many factors. Furthermore, the implications, such as a serious accident causing further damage to the injury or surgical site or harm to someone else, are significant and possibly critical. So, the next time you ask your physician this question, please follow instructions and be patient…remember, it could be your child or grandchild running into traffic to chase a ball and you would want the driver to be at optimal function to apply the brakes!
In our culture, the inability to drive has a significant impact on lifestyle and livelihood. A study published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, found that 74% of those unable to drive due to injury or surgery are dependent on family and most of the remainder depend on friends. 4% of those unable to drive have no help at all and more than 25% suffer major financial hardship.
The report also found that family physicians, orthopedic surgeons, podiatrists, and physical therapists are keenly aware of this dilemma but often fail to communicate effectively to patients about driving. Most medical professionals express serious concerns about liability regarding return to driving following an injury or surgery. They feel that there is a lack of data to support decisions and inadequate communication among each other. They agree that they must do a better job communicating with patients and their families so they can better prepare for a period of time during their recovery in which they cannot drive.
Recent studies published in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS) and the Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery (JFAS),determined that there are two significant components in the decision of safely returning to driving after an injury or surgery; the time required for healing and the time required for a return of function. Additionally, it was found that those wearing a surgical shoe or walking boot demonstrated a significantly slower braking response time even in healthy/non-injured individuals wearing the shoe/boot.
During the time required for healing, in addition to the fear of an additional trauma from a motor vehicle accident to the healing body part, there is a general concern about the potential damage that may come from over using the body part to drive before it is adequately healed. For example, a healing fracture in the right lower leg might be compromised or delayed if one must suddenly and forcefully apply the brakes. Also, during this time, it is not unusual for post-injury or post-surgery patients to use pain medications, including narcotics. This will also compromise judgment and reaction time while driving.
Most orthopedic conditions heal in 6 to 8 weeks. However, as many of you may fully know, once a cast or splint is removed, you are not ready to run or jump. Depending on the severity of the injury, it may take many weeks of aggressive physical therapy to regain strength, range-of-motion, agility and dexterity to function at a safe level for a full return to daily activities, including driving.
The current research reinforces the fact that driving safely requires good function of the entire body. For example, just because you broke your shoulder bone but did not fracture your right leg does not mean that you are able to drive safely. Wearing a sling after arm surgery also compromises driving. First, you need a stabilized and healed injury prior to driving. Then, you must work in rehab to make modifications to return to safe driving. Apply the same scenario to injuries or surgery to the spine (neck and lower back).
*Based on research using driving simulators
7 TIPS TO KNOW WHEN YOU ARE READY TO DRIVE:
Remember, every case is unique and there is no substitute for communication with your orthopedic surgeon, podiatrist, family physician and physical therapist.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Ice baths have become a new trend or fad in health and fitness, especially among elite athletes and some celebrities. However, it is far from a new treatment modality. In fact, the Ancient Greeks employed cold-water immersion for fever, pain relief, relaxation and socialization. In addition, Hippocrates documented the use of cold for medicinal purposes for its analgesic benefits.
Ice baths, a type of cryotherapy, is also referred to as cold water immersion (CWI) or cold water therapy. This involves immersing your body in ice water for approximately 5-15 minutes from the neck down at 50-59 degrees. The ice baths are commonly used for pain, delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and inflammation and mood elevation.
In theory, the cold water lowers the temperature of your skin and body by vasoconstriction (narrow) of the blood vessels. When you get out of the cold, water the vasodilatation (widen) of the blood vessels. Immediately, this brings fresh oxygen and nutrient-rich blood back to the tissues to warm the body and in the process, reduce pain, inflammation and promote healing.
If you have the following health conditions, ice baths may not be the best therapeutic modality for you. Before you consider trying an ice bath, consult with your physician to avoid potentially serious problems:
While some studies have shown that subjects report less muscle soreness following CWI when compared to rest, most studies suggest that the reported effects are placebo. Also, reports of improved circulation, reduced inflammation and improved recovery or performance has not been scientifically validated. In view of this, it is recommended that those considering the use of CWI for pain and inflammation management, reduced muscle soreness, and mood elevation, should consult their physician to determine if the potential risks are worth the purported benefits.
SOURCES: nih; health.com; health.clevelandclinic.org; prevention.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
As most sports enthusiasts know, Aaron Rodgers, former Green Bay Packer quarterback and recent New York Jets QB (for just over a minute and half) suffered a season ending injury when he tore his Achilles tendon in the first game of the 2023/24 NFL season. Since then, I have been answering many questions from patients and sports fans about the nature of the Achilles Tendon rupture injury, recovery, and how to prevent it.
As the days continue to get shorter and temperatures begin a slow steady decline, athletes and exercise enthusiasts will work harder to warm-up and exercise during the winter months. A little caution and preparation are in order to avoid muscle/tendon strain, or worse yet, muscle/tendon tears, especially Achilles Tendon rupture. The Achilles tendon is one of the more common tendons torn.
This is the second of two columns on Achilles tendon rupture. Last week, I discussed the definition, sign and symptoms of the problem. This week will present examination, treatment and outcomes.
A thorough history and physical exam is the first and best method to assess the extent of the injury and determine accurate diagnosis. While a complete tear is relatively easy to determine, a partial or incomplete tear is less clear. Ultrasound and MRI are valuable tests in these cases. X-rays are not usually used and will not show tendon damage.
Consultation with an orthopedic or podiatric surgeon will determine the best treatment option for you. When conservative measures fail and for tendons completely torn, surgical intervention is usually considered to be the best option with a lower incidence of re-rupture. Surgery involves reattaching the two torn ends. In some instances, a graft using another tendon is required. A cast or walking boot is used post-operatively for 6-8 weeks followed by physical therapy.
Most people return to close to normal activity with proper management. In the competitive athlete or very active individual, surgery offers the best outcome for those with significant or complete tears, to withstand the rigors of sports. Also, an aggressive rehabilitation program will expedite the process and improve the outcome. Walking with full weight on the leg after surgery usually begins at 6 -8 weeks and often requires a heel lift to protect the tendon. Advanced exercises often begin at 12 weeks and running and jumping 5-6 months. While a small bump remains on the tendon at the site of surgery, the tendon is well healed at 6 months and re-injury does not usually occur.
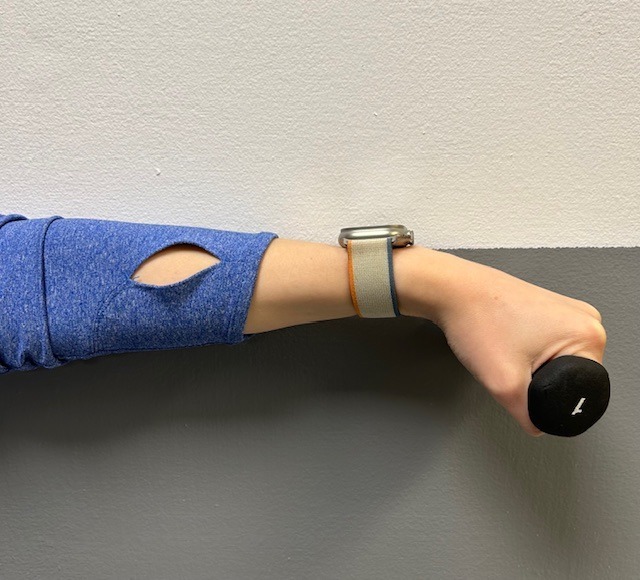
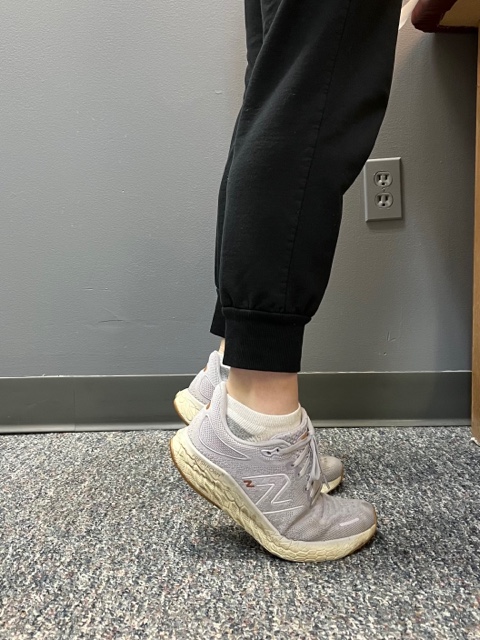
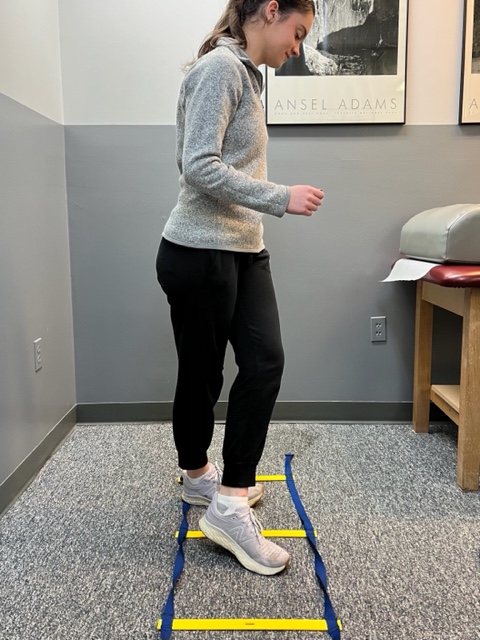
Prevention of muscle and tendon tears is critical for healthy longevity in sports and activities. In addition to the Achilles tendon, the tendons of the quadriceps (knee) and rotator cuff (shoulder) are also vulnerable. A comprehensive prevention program includes: gradual introduction to new activities, good overall conditioning, sport specific training, pre-stretch warm-up, stretch, strengthening, proper shoes, clothing, and equipment for the sport and conditions. Also, utilizing interval training, eccentric exercise (lowering body weight slowly against gravity – Photo 1) and proprioceptive and agility drills are essential (Photos 2 & 3).
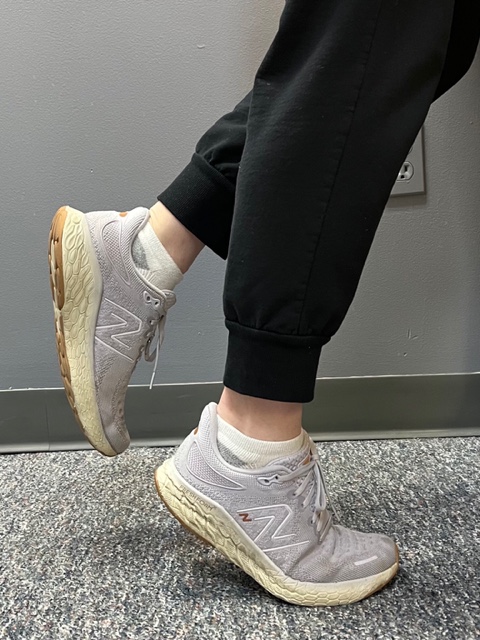

In PHOTO 1a & 1b: Eccentric Lowering and Lengthening: for the Achillies tendon during exercise. Beginning on the ball of both feet (1a), bend the strong knee to shift the weight onto the weak leg (1b). Slowly lowering the ankle/heel to the ground over 5-6 seconds. Repeat.
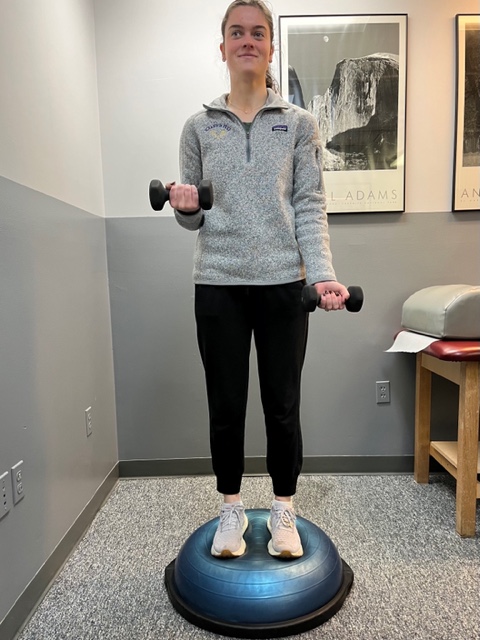
In PHOTO 2: Proprioceptive Training: for the Achillies tendon. Standing on a Bosu Ball while exercising the upper body (for example, biceps curls, shrugs, rows, lats) while maintaining balance on the ball.
PHOTO 3: Agility Drills: for the Achilles tendon involves stepping through a “gait ladder” in various patterns and at various speeds.
MODEL: Kerry McGrath, student physical therapy aide at Mackarey Physical Therapy
Sources: MayoClinic.com;Christopher C Nannini, MD, Northwest Medical Center;Scott H Plantz, MD, Mount Sinai School of Medicine

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Runners will attempt to conquer 26.2 miles from Forest City to downtown Scranton in the 26th Annual Steamtown Marathon this Sunday. Participants may want to consider new research that suggests the use of compression socks may prevent post race blood clots.
Completing the long and arduous 26.2 mile journey is not an easy task. In fact, the mechanical and physiological toll on your body is tremendous; from painful joints, muscles, tendons, to black and blue toes. Not so obvious, however, is the damage to your deep veins and tissues of the circulatory system. New research indicates that strenuous endurance exercise, such as marathon running, stimulates the clotting mechanisms in your body in response to the multiple micro traumas sustained over 2 or more hours. While most healthy athletes will naturally heal from post exercise clot formation, others may be at risk…those traveling more than 1 hour (by car, bus, train or plane). The risk increases substantially for those with a longer period of travel/sitting post-race, history of previous trauma, blood clots or have the genetic predisposition for clot formation.
Compression socks are familiar to most people as the tight knee-high support stockings worn after a surgical procedure such as a knee or hip replacement to prevent blood clots. They are made with a special fabric and weave design to provide graduated compression (stronger compression at foot and ankle and less at the top of the sock) to promote better circulation and movement of fluids from the foot, ankle and calf back to the upper leg and ultimately the heart. Compression socks work similarly in runners. As the stagnant fluid with lactic acid and other byproducts of exercise is removed from the space, fresh blood, nutrients and oxygen is replaced to foster healing of micro damage to tissue and promote more efficient use of the muscles.
The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research published a study that found wearing compression socks improved running performance. However, similar studies have failed to support this claim. One finding that has been repeatedly supported in the literature, including The British Journal of Sports Medicine, found that compression socks worn in soccer players and runners improved the rate and magnitude of recovery. Moreover, recent studies, including a study with the Boston Marathon, have demonstrated the reduction in clotting mechanisms in those wearing compression socks AFTER the marathon, as compared with those wearing “sham” socks. Benefits seem to be less obvious for short duration activities or when running 10km or less.
In conclusion, only time will tell if compression socks will improve performance in runners will or be merely a fad based on placebo or true fact supported by scientific research. Based on current wisdom, these socks may offer value and benefit AFTER activities of long duration (more than 1 hour) or long distance running (more than 10km) to expedite the recovery from exercise-induced blood clot formation, muscle soreness from the accumulation of lactic acid and other muscle damage byproducts.
It is this author’s opinion that this product is worth a try. However, whenever you try something new for your sport, trials should occur during practice and if successful used during competition. Consider trying a lower compression to begin (the socks come in different degrees of compression). Even if one is hesitant to use the product while running, it appears the greatest value of the sock is after a prolonged training session or competition to reduce exercise-induced muscle soreness and prevent blood clots, especially in athletes at risk for clotting and those traveling for an hour or more after the race. Additionally, in view of the fact that some studies which showed only minimal to moderate improvement in well-trained athletes, it may be that those in greater need, such as deconditioned individuals attempting to begin a fitness program and novice weekend athletes, may benefit more from compression socks than elite athletes.
TAKE HOME: Runners, cyclists, triathletes, soccer players and others participating in endurance sports should consider compression socks, if not during the activity, certainly following the activity for 24 to 48 hours…especially those at risk for blood clots and those traveling for more than one hour after the race.
Sunday consider trying compression socks and see if they work for you during and more importantly, after your long training runs.
Where to find compression socks:
2XU Compression Racing Sock – www.2XU.com
Scranton Running Company – Olive Street - Scranton
Visit your family doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
A local high school teacher came to my office with weakness and numbness on one side of her face. This well-groomed, attractive middle-aged woman was unable to smile, frown, pout, speak, or eat with facial symmetry. She suffered from a cold, on and off, for about two months. It was not a bad cold, but it would not go away. One day in early summer, while engaged in bird watching, one of her favorite pastimes, she noticed that she could not look through her binoculars. She noticed that her eye would not open and close at will. The next day she woke with ear pain, flaccid muscles on one side of her face, and an inability to close her eye. She had difficulty speaking with clarity due to weak mouth muscles and feared she had a stroke.
She immediately saw her family physician who determined that she had shingles in her ear and developed Bell’s palsy. She was prescribed a steroid anti-inflammatory (Prednisone), antiviral medicine (Acyclovir), and a topical cream (Zovirax). Once she got over the initial fear and shock, she was grateful that her problem of facial weakness was not due to a more serious problem, such as a stroke or brain tumor. She began physical therapy and improved slowly. Her story, along with many other patients, reminded me of the need to raise awareness about cause, diagnosis, symptoms, complications and treatment of Bell’s palsy.
Bell’s palsy, a facial nerve paralysis, occurs when the nerve that is responsible for the movement and sensation of the muscle and skin of the face becomes damaged. The end result of this damage is paralysis of the muscles and numbness of the skin on one side of the face. Typically, the first sign of this disorder is the inability to close one eye or smile on one side of the face. While this problem can occur in any age group, it is rarely seen in people less than 15 or more than 60 years of age. The good news is that most people show signs of improvement within 3-4 weeks and have complete recovery in 4-6 months. The bad news is that reoccurrence can occur on the other side of the face in approximately 10 percent of those affected.
Bell’s palsy is caused by a viral infection. The most common virus is the herpes simplex virus, the same virus that causes cold sores and genital herpes. Other viruses that can cause Bell’s palsy are herpes zoster virus that causes chicken pox and shingles and Epstein-Barr virus, which causes mononucleosis, and cytomegalovirus. When one of these viruses causes inflammation to the facial nerve, it becomes swollen and irritated in the narrow tunnel of bone by the ear. As pressure on the facial nerve increases, damage progresses to the point that the muscles and skin of the face are unable to receive messages from the nerve, leading to paralysis, numbness and other symptoms.
The hallmark symptom of Bell’s palsy is sudden onset of facial muscle weakness and numbness on one side of the face. As a result, it is difficult to close the eye and smile on the weak side. Other symptoms on the affected side can include: the inability to make facial expressions, speak clearly (especially vowel sounds), diminished sense of taste, pain in the area of the jaw or ear, sensitivity of sound, headaches, and changes in production of tears and saliva.
While Bell’s palsy can occur in anyone, it is more common among those who are: pregnant, (especially during the third trimester or first week after birth), diabetic, or suffering from a cold or flu. Also, some research suggests that there may be a genetic predisposition to this problem.
In mild cases of Bell’s palsy, symptoms are completely resolved within 4-6 weeks. As mentioned before, most cases resolve in 4-6 months. However, recovery for those with complete paralysis may vary. For example, permanent facial weakness, facial muscle twitching, and visual problems due to the inability to close the eye, can occur.
Contact you primary care physician immediately, because these symptoms may be associated with a more serious medical condition such as a stroke. Remember, most people with Bell’s palsy make a complete recovery, but early intervention can expedite the process. In severe cases, a neurologist may be consulted. Two commonly used medications are corticosteroids and antiviral drugs. Corticosteroids such as prednisone are strong anti-inflammatory drugs used to reduce the swelling and inflammation on the facial nerve. Antiviral drugs such as acyclovir are used to stop the viral infection that may have caused the inflammation. Studies show that these drugs, when used in combination, are most effective when administered in the first 3 days of the appearance of symptoms.
Physical therapy can also assist in the restoration of facial muscle recovery. Ultrasound with anti-inflammatory drugs, electric stimulation, massage and exercise are commonly performed. While the use of electric stimulation has limited support in the literature, a home exercise program that concentrates on facial muscles, is an essential part of the therapy program. Some simple exercises performed in front of a mirror are: raise eyebrows, bring eyebrows together, open/close eye, fill cheeks with air, suck in cheeks, smile, frown, whistle, say vowels.
Surgery, to relieve pressure on the nerve by removing bone, is rarely performed. Plastic surgery, to improve the appearance of the face, may be an option in cases with permanent paralysis.
Sources: Mayo Clinic; WebMD

NEXT WEEK! Read “Health & Exercise Forum” – Every Monday. This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is an Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine at GCSOM.
For all Dr. Paul's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Congratulations to the enthusiastic and dedicated runners who finished the 25th Annual Steamtown Marathon yesterday. Most, if not all of you are waking up this morning with a little less jump in your step than you had yesterday.
As active people by nature, many of you will resist the logic of rest, despite the pain and stiffness in your muscles and joints. Therefore, I would like to offer some words of wisdom, based on science, to encourage you to adequately rest and allow your body to recover.
With adequate rest and recovery, an elite runner can quickly regain full form in 3-4 weeks, while an average runner may require 4-6 weeks. Meb Keflezighi, an elite American runner and winner of the 2014 Boston Marathon, is an excellent example of the merits of rest and recovery. However, he discovered it by accident…following the 2012 New York City Marathon, Meb developed a foot infection which required three weeks rest. With the Olympic Trials just 70 days away, Meb quickly regained his pre-injury fitness level to win the 2012 US Olympic Marathon Trials and join the US Olympic Team in London. It may be that his injury was fortuitous and allowed him adequate recovery time, (that he might not have otherwise allowed), preparing him for intensive training leading up to the trials.
One of the most obvious effects of running a marathon is significant muscle and joint pain and stiffness. It will set in after you sit for a while and attempt to get up and move around. For most, it will be more pronounced the day after the marathon, as you get out of bed and limp to the bathroom. Studies show that the leg muscles, (especially the calf muscles) display significant inflammation and necrosis (dead tissue) in the fibers of the muscle. In other words, the trauma to the muscles is so severe that tissue damage causes muscle cells to die. Consequently, studies found that muscle strength, power and endurance is compromised and required significant time to recover… sometimes as long as 4-6 weeks!
Additionally, many runners report severe bone and joint pain following the race. Some studies report findings of microfractures or bone bruising from the repeated and prolonged pounding of the marathon. It is purported that the stress on the joints may be related to: weight and body type, running shoes, running style and mechanics. While not dangerous, again, it is important to respect the stress placed on the body and allow adequate healing…LISTEN TO YOUR BODY!
Creatine kinase is an enzyme found in the brain, skeletal muscles and heart. It is found in elevated levels in the presence of cellular damage to these tissues, for example, following a heart attack. Similarly, significantly elevated creatine kinase levels are found in the blood of runners up to 4 days post marathon, demonstrating extensive tissue damage at the cellular level. It is important to note, that these enzyme markers are present, even if a runner does not experience muscle soreness. So, adequate rest for healing and recovery is required, regardless of soreness.
It is not a coincidence that the runners are more likely to contract colds and flu after intensive training or running 26.2 miles. The immune system is severely compromised after a marathon and without adequate recovery; a runner can become ill and ultimately lose more training time or will underperform.

This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
See all of Dr. Mackarey's articles in our Health and Exercise Forum!