As most sports enthusiasts know, in 2021 Tiger Woods ruptured his Achilles tendon while training at home and in 2023 Aaron Rodgers, a former Green Bay Packer quarterback, did the same in the first game of the 2023/24 NFL season with the New York Jets. As with many sports injuries, it is painful and devastating and best managed by PREVENTION!
Spring is here and as the days continue to get longer and temperatures begin a slow steady rise, athletes and weekend warriors are eager to get outdoors to play and exercise. However, be mindful of the weather (damp and rainy), temperature (cool mornings and evenings) and winter “dust” on your muscles and tendons. Many overjealous fitness enthusiasts will rush to pound the pavement and barely “fit in” a warm-up before participating. But, no matter how limited time is, skipping the warm-up is risky.
This time of year, one can expect to feel a little cold and stiff, especially if you are over 40, and therefore a little caution and preparation are in order to avoid muscle/tendon strain, or worse yet, muscle/tendon tears. The Achilles tendon is one of the more common tendons torn. Prevention of muscle tears, including the Achilles tendon includes; gradual introduction to new activities, good overall conditioning, sport specific training, pre-stretch warm-up, stretch, strengthening, proper shoes, clothing, and equipment for the sport and conditions.
A muscle contracts to move bones and joints in the body. The tendon is the fibrous tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Great force is transmitted across a tendon which, in the lower body, can be more than 5 times your body weight. Often, a tendon can become inflamed, irritated, strained or partially torn from improper mechanics or overuse. Although infrequent, occasionally tendons can also snap or rupture. A tendon is more vulnerable to a rupture for several reasons such as a history of repeated injections of steroids into a tendon and use of medications such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics. Certain diseases such as gout, arthritis, diabetes or hyperparathyroidism can contribute to tendon tears. Also, age, obesity and gender are significant risk factors as middle-aged, overweight males are more susceptible to tendon tears. Poor conditioning, improper warm-up and cold temperatures may also contribute to the problem.
Tendon rupture is very painful and debilitating and must not be left untreated. While conservative management is preferred, surgical management is usually required for complete tears. The purpose of this column is to present the signs, symptoms and management of Achilles tendon ruptures.
The Achilles tendon (also called the calcaneal tendon), is a large, strong cordlike band of fibrous tissue in the back of the ankle. The tendon (also called the heel cord) connects the powerful calf muscle to the heel bone (also called the calcaneus). When the calf muscle contracts, (as when you walk on the ball of your foot), the Achilles tendon is tightened, tension is created at the heel and the foot points down like pushing a gas pedal or walking on tip of your toes. This motion is essential for activities such as walking, running, and jumping. A partial tear of the tendon would make these activities weak and painful, while a full tear through the tendon would render these activities impossible.
With age, the Achilles tendon (and other tendons) gets weak, thin, and dehydrated, thus making it prone to inflammation, degeneration, partial tear or rupture. The middle-aged weekend warrior is at greatest risk. A full or complete tear (Achilles tendon rupture) usually occurs about 2 inches above the heel bone and is associated with a sudden burst of activity followed by a quick stop or a quick start or change in direction, as in tennis, racquet ball, and basketball.
In some instances, the tendon can be injured by a violent contraction of calf when you push off forcefully at the same time the knee is locked straight as in a sudden sprint. Other times, the tendon is injured when a sudden and unexpected force occurs as in a trip off a curb or sudden step into a hole or a quick attempt to break a fall.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
Next Week: Achilles tendon Part II of II
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

At least once a week, a patient jokingly asks if they can get a “lube job” to loosen up their stiff knee joint. I respond by providing them with information about osteoarthritis and viscosupplementation, a conservative treatment administered by injection and approved by the FDA for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is also known as degenerative arthritis. It is the most common form of arthritis in the knee. OA is usually a gradual, slow and progressive process of “wear and tear” to the cartilage in the knee joint which eventually wears down to the bony joint surface. It is most often found in middle-aged and older people and in weight bearing joints such as the hip, knee and ankle. Symptoms include: pain, swelling, stiffness, weakness and loss of function.
Your family physician will examine your knee to determine if you have arthritis. In more advanced cases you may be referred to an orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist for further examination and treatment. It will then be determined if you are a candidate for viscosupplementation. While this procedure is the most commonly used in the knee, it has also been used for osteoarthritis in the hip, shoulder and ankle.
Viscosupplementation is a procedure, usually performed by an orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist, in which medication injected into the knee joint acts like a lubricant.
The medication is hyaluronic acid is a natural substance that normally lubricates the knee. This natural lubricant allows the knee to move smoothly and absorbs shock. People with osteoarthritis have less hyaluronic acid in their knee joints. Injections of hyaluronic acid substances into the joint have been found to decrease pain, improve range of motion and function in people with osteoarthritis of the knee.
When conservative measures, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, steroid injections fail to provide long lasting relief, viscosupplementation may be a viable option. Often, physical therapy and exercise are more effective following this injection to provide additional long-term benefit. Unfortunately, if conservative measures, including viscosupplementation fails, surgery, including a joint replacement may be the next alternative.
In 1997 the FDA approved viscosupplementation for osteoarthritis of the knee. Presently, there are several products on the market. One type is a natural product made from the comb of a rooster. However, if you are allergic to eggs or poultry products or feathers, you should not use the natural product. The other medication is best used for patients with allergies because it is manufactured as a synthetic product.
The long-term effects of viscosupplementation is much greater when other conservative measures are employed:
SOURCES: Genzyme Co, Sanofi-Synthelabo Inc, Seikagaku Co. and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
While I normally do not address the topic of shoveling snow until January, considering recent weather events, I thought it might be valuable to present it sooner. Much has been written about the dangers of snow shoveling for your heart. However, while not fatal, low back pain is the most common injury sustained while shoveling snow. Heart attacks are also more common following wet and heavy snow.
Snow shoveling can place excessive stress on the structures of the spine. When overloaded and overstressed, these structures fail to support the spine properly. The lower back is at great risk of injury when bending forward, twisting, lifting a load, and lifting a load with a long lever. When all these factors are combined simultaneously, as in snow shoveling, the lower back is destined to fail. Low back pain from muscle strain or a herniated disc is very common following excessive snow shoveling.
Sources: The Colorado Comprehensive Spine Institute; American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

I have been advising my patients to exercise, keep active, and walk as long as they can in order to stay mobile and healthy. However, seniors often tell me activities that require prolonged walking is limited by ankle pain from arthritis. They often ask, “What is arthritis of the ankle?” How does it happen? What can I do about it?
Your family physician will examine your ankle to determine if you have arthritis. In more advanced cases you may be referred to a specialist such as a podiatrist, orthopaedic surgeon or rheumatologist for further examination and treatment. X-rays will show if the joint space between the bones in the ankle is getting narrow from wear and tear arthritis. If rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, blood tests and an MRI may be ordered. The diagnosis will determine if you problem if minor, moderate or severe.
In the early stages your treatment will be a conservative, nonsurgical approach, which may include; anti-inflammatory medication, orthopedic physical therapy, exercise, activity modifications, supplements, bracing, etc. You and your family physician, podiatrist, orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist will decide which choices are best.
When conservative measures no longer succeed in controlling pain and deformity, improving strength and function then more aggressive treatment may be necessary.
SOURCES: Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Ice baths have become a new trend or fad in health and fitness, especially among elite athletes and some celebrities. However, it is far from a new treatment modality. In fact, the Ancient Greeks employed cold-water immersion for fever, pain relief, relaxation and socialization. In addition, Hippocrates documented the use of cold for medicinal purposes for its analgesic benefits.
Ice baths, a type of cryotherapy, is also referred to as cold water immersion (CWI) or cold water therapy. This involves immersing your body in ice water for approximately 5-15 minutes from the neck down at 50-59 degrees. The ice baths are commonly used for pain, delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and inflammation and mood elevation.
In theory, the cold water lowers the temperature of your skin and body by vasoconstriction (narrow) of the blood vessels. When you get out of the cold, water the vasodilatation (widen) of the blood vessels. Immediately, this brings fresh oxygen and nutrient-rich blood back to the tissues to warm the body and in the process, reduce pain, inflammation and promote healing.
If you have the following health conditions, ice baths may not be the best therapeutic modality for you. Before you consider trying an ice bath, consult with your physician to avoid potentially serious problems:
While some studies have shown that subjects report less muscle soreness following CWI when compared to rest, most studies suggest that the reported effects are placebo. Also, reports of improved circulation, reduced inflammation and improved recovery or performance has not been scientifically validated. In view of this, it is recommended that those considering the use of CWI for pain and inflammation management, reduced muscle soreness, and mood elevation, should consult their physician to determine if the potential risks are worth the purported benefits.
SOURCES: nih; health.com; health.clevelandclinic.org; prevention.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Holiday shopping is stressful to your body as well as your wallet. Driving from store to store, getting in and out of the car, bundled in a sweater and winter coat, the expert shopper carries package after package from the store, to the car, over and over again. Six, eight, or ten hours later, the shopper arrives home exhausted, only to realize that 15, or 20 packages must be carried from the car into the house. This dilemma is compounded by the fact that the rain turned to sleet, and the sleet to snow. Travel by car and foot are treacherous. You are slipping and sliding all the way from the car to the house while carrying multiple packages of various sizes and shapes. The shopping bags get wet and tear, forcing you to tilt your body as you carry the packages. Of course, no one is home to help you unload the car and you make the trip several times alone. You get into the house exhausted and crash onto the couch. You fall asleep slouched and slumped in an overstuffed pillow chair. Hours later you wake up with a stiff neck and lower back pain. You wonder what happened to your neck and back. Consider the following:
Plan Ahead: It is very stressful on your spirit, wallet and back to do all of your shopping in the three weeks available after Thanksgiving. Even though we dislike “rushing” past Thanksgiving to the next holiday, try to begin holiday shopping in before
Use the Internet: Supporting local businesses is important. However, Internet shopping can save you lots of wear and tear. Sometimes, you can even get a gift wrapped.
Gift Certificates: While gift certificates may be impersonal, they are easy, convenient and can also be purchased over the internet.
Perform Stretching Exercises: Chin Tucks, Shoulder Blade Pinch, Back Extension. Stretch intermittently throughout the shopping day…try the three exercises below, gently, slowly, hold 3 seconds and relax, repeat 5 times.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
For all of Dr. Mackarey's Articles visit: mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine.
Patients often tell me that they would like to exercise but hesitate due to their knee or hip pain. They want to know what type of exercise is best for those suffering from osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis is also known as degenerative arthritis. It is the most common form of arthritis in the knee. It is usually a gradual, slow and progressive process of “wear and tear” to the cartilage in the joint which eventually wears down to the bony joint surface. It is most often found in middle-aged and older people and in weight bearing joints such as the hip, knee and ankle. It causes gradual onset of pain, swelling and stiffness in the involved joint, especially after increased activity and weakness with loss of function due to disuse.
However, OA is not an excuse to avoid exercise but it is important to be smart about it. Regular exercise is essential to maintain a normal lifestyle for those with OA. However, if you do the wrong exercise, use poor technique, or are too aggressive, you could flare-up your joints and do more harm than good.
When performed correctly, exercise for those with OA has many benefits:
Pain Control
Exercise controls OA pain by releasing natural pain control chemicals in the body called endorphins. It also controls pain by assisting in weight loss and improving range of motion.
Weight Control
We all know how well exercise burns calories and that increased body weight creates increase stress on the joints.
Prevention of Joint Stiffness
Exercise will help maintain joint range of motion. A stiff joint is a painful joint.
Prevention of Muscle Weakness
Exercise will help maintain muscle strength. Weak muscles will allow or increase in joint wear and tear.
Maintain Lifestyle
If a joint is stiff and weak, then they become painful which negatively impacts your lifestyle. Exercise can prevent this problem.
Start Slowly
Wean into exercise because if you advance too quickly, you will flare up the joint and have increased pain. For example, walk for 5-10 minutes the first session. If you do not have pain, add 1-2 minutes each session.
Lose Weight
Every pound lost equates to less stress on your joints. For example, a loss of 5 pounds of body weight translates to 20-30 pounds of stress through the knee, according to David Borenstein, MD, President of the American College of Rheumatology. Also, body weight has a direct impact on daily activities. For example, walking upstairs creates stress through the knee equal to 4 times body weight and seven times body weight going downstairs. Therefore, less body weight equals less stress.
Low Impact Workouts
Low impact exercise creates less stress on the joints while strengthening leg muscles and those who those who maintain leg muscle strength have less stress on their joints. It is even important not to load your arms with heavy objects when walking or using stairs to limit joint stress.
Some examples of low-impact exercises are: walking, swimming, elliptical trainer, and biking. Strength training is also low-impact and should be performed with low weight and high repetitions. Water therapy is great for those with OA, especially in a heated pool. It is a great low-impact exercise with less gravity and stress on the joints. Walk, swim and do mild resistance exercises in the water. Use a snorkel and mask for swimming to limit excessive neck turning and back extension.
Walking is a great form of exercise; however, walking softly is important for those with OA. Wear good running shoes and orthotics if necessary. Discuss this with your physical therapist or podiatrist. When possible, use soft surfaces like cinder, mulch or rubber. Avoid grass and soft stand due to instability and torsion that may irritate your joints.
Warm-Up
Warming up your body is critical to prevent injury to the muscles and tendons. This can be done by marching in place or using aerobic equipment such as a bike for 5 to 10 minutes before exercise. Always perform the warm-up activity at ½ your normal pace.
Balance & Relaxation Techniques
Tai Chi and ballroom dancing are two good examples of activities which promote balance and relaxation. Studies showed that those with OA who participated in Tia Chi two times a week for eight weeks reported less pain, increased range of motion and improved daily activities and function. They also noted less low back pain and better sleeping.
Proper Clothing
Stay warm in winter and consider wearing compression shorts. Be cool in the summer months with DrytechR type material.
Pre/Post Exercise First Aid
If you are sore for longer than 12 to 24 hours after exercise, then you overdid it and must make adjustments next time. Otherwise, use hot packs, bath or shower before you
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey NEW Article in“Health & Exercise Forum!”
For all of Dr. Mackarey articles visit https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum/
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
HEALTH AND EXERCISE FORUM
By: Dr. Paul J. Mackarey
This column is a monthly feature of “Health & Exercise Forum” in association with the students and faculty of Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine (formerly The Commonwealth Medical College).
Guest Columnist: Kevin Perry, MD
“Should I use heat or ice?” Several years ago, while working as a third year medical student at TCMC on orthopedic rotation, I was surprised to find that this is one of the most common questions asked by weekend warriors trying to relieve shoulder pain after playing tennis for the first time in 6 months. Now, as an orthopedic resident, the frequency of this inquiry has not changed. Trying to decide whether to use ice or heat to make it feel better and heal faster may not be so easy. Unfortunately, there is confusion, even among medical professionals, about the appropriate times to use heat or cold. However, if we review the basic science on this subject, there are some valuable guidelines to consider.
The Science
When an injury is sustained, such as a sprained ankle, chemical signals are released in the area of the injury, which increases blood supply to the damaged tissues to allow appropriate cells to repair the damage. This response is evident by the principle signs and symptoms of inflammation including heat, redness, swelling, pain, and loss of function. This reaction makes sense because anytime tissues are injured; the body is responsible to protect the site until repair can occur. To protect the injured site, the body causes swelling and pain to prevent excessive movement or overuse which will lead to further injury. With the site of injury protected, the appropriate cells are able to lay down new tissue to repair the damage. As tissues heal, a web of connective tissue pulls the damaged tissues back together and holds them in place while new tissue is formed. Once the tissue is completely repaired, the blood flow returns to normal and fluid drains from the site of injury allowing restoration of motion and function. However, the new tissue is fragile and unorganized and often sticks together leaving tightness and weakness. After repeated use, the new tissue adapts to the stress placed upon it and becomes functional.
The Application
When grounded in science, the use of heat or cold can be used to expedite the healing process. While inflammation is crucial to the repair of injured tissue, the response can be exaggerated and last longer than necessary. Therefore, ice and heat can be used to modify the bodies’ inflammatory response and help us return to activity sooner.
How Cold Works
Ice causes blood vessels to narrow and nerves to slow down. When ice is applied to tissue, the body responds by decreasing blood flow to the area to preserve the core body temperature. Also, as nerves cool down, the signals they send slow down and become less frequent, so the pain signals they send to your brain become less intense. Thus, we can use ice to decrease blood flow to inflamed tissue which will reduce swelling and decrease pain. Ice is ideally used immediately following most injuries to control pain and swelling.
How Heat Works
Heat causes your blood vessels to open and increase blood flow to tissues. When heat is applied, blood flow and tissue temperature are increased and tight tissues relax and are better able to glide across one another. However, when applied too early in the healing process, heat, by increasing blood flow, can increase swelling and pain. Heat is ideally used after an injury has healed and there is residual tightness or protective muscle spasms.
Now that we know how ice and heat work in conjunction with the inflammatory process we can easily understand when to use each one. Ice is best used following an acute injury. For example, ice is effective day one through three following an ankle sprain, or until swelling is controlled. Anytime the principle signs and symptoms of inflammation are present, ice is the appropriate treatment of choice. Regardless of when the injury occurred, if there is swelling and pain, ice is the appropriate treatment. Heat should be used when there is tightness and stiffness and no signs of acute inflammation. For example, week two of three, following an ankle sprain if stiffness persists and swelling is controlled.
How To…
Apply ice using a bag of ice and water, ice pack, or bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a wet towel. Cover the injured and swollen area and if possible elevate the iced area above the level of your heart. You should apply ice for a maximum of 20 minutes and rest at least one hour between icing sessions so as not to cause harm. Never apply ice directly to skin and never fall asleep while icing.
Apply heat with a heating pad covered in a few towels or warm a bag of rice in a microwave. Cover in a towel and place the heat on the affected area for a maximum of 20 minutes and rest at least one hour between heating sessions. Never apply heat over skin that you cannot feel (numbness or loss of sensation) or on open wounds in the skin. Also, do not lie directly on the heating source and don’t fall asleep while using heat to avoid burns.
Hopefully this information is helpful in dispelling some of the confusion regarding when to use ice or heat. As you can see there is no “golden rule” or “72-hour rule” for advising when to use ice or heat. But if you stick to the principles discussed in this article, you should be treating your aches and pains appropriately. This has been a simplified explanation of a complex topic and if you have any further questions, please ask a medical professional.
Top Reasons for use of Ice (Cryotherapy):
Top Reasons for use of Heat (Thermotherapy):
Kevin Perry, MD graduated from The Commonwealth Medical College (GCSOM) in 2015. He is a resident in Orthopaedic Surgery at LSU Health Science Center Shreveport and will be moving back to Pennsylvania next month to pursuit a fellowship in orthopedic trauma at Penn State Health Milton S Hershey Medical Center. His special interests include pelvis and acetabulum trauma, complex periarticular fractures, malunions, nonunions, and deformity correction. Dr Perry completed his undergraduate education at Loyola University Maryland and graduate degree (doctor of physical therapy) at the University of Scranton.
Read all of Dr. Mackarey's articles in the Health and Exercise Forum at our website: https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum/
Read “Health & Exercise Forum” – Every Monday. This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
Part II of II
I think we would all agree, technology is a wonderful thing. However, like all good things, it comes at a price. Students and workers alike are suffering from the many physical effects of sitting for too many hours...especially with COVID-19 home confinement! Studies show the impact of prolonged sitting, especially with poor posture, are multifaceted: pain, headaches, vision problems, poor concentration, excess fat storage with weight gain. Studies strongly support the use of using good posture, ergonomic workstations, posture stretches and frequent changes of positions, including the use of standing desks to prevent pain and injury as we discussed last week in part I.
The Problem is Gravity!
The average head weighs 10 to 12 pounds and when tilted down at a 45 degree angle the forces of gravity are multiplied by 5. While reading, studying or working on the computer with poor posture, one must support 50 or more pounds of pressure on the neck, middle and lower back for hours on end. It is no wonder why this activity is associated with headaches, neck and back pain, numbness and tingling in arms and legs, muscle spasms etc. Some studies report the lifetime prevalence of neck and shoulder pain in office workers as high as 80%.
Spine problems can be prevented with good posture and proper body mechanics. Poor posture and improper body mechanics subject the spine to abnormal stresses that, over time, can lead to degeneration and pain. Good posture and proper body mechanics and frequent changes in positions, can minimize current spine pain and prevent recurrent episodes. Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity. Good posture involves positions that place the least amount of stress on the spine. Good posture maintains the spine in a “neutral” position. In a neutral spine, the three normal curves are preserved (a small hollow at the base of the neck, a small roundness at the midback and a small hollow in the low back). When viewed from the side, the upper back appears straight with a small hollow in the lower back.
GOOD POSTURE
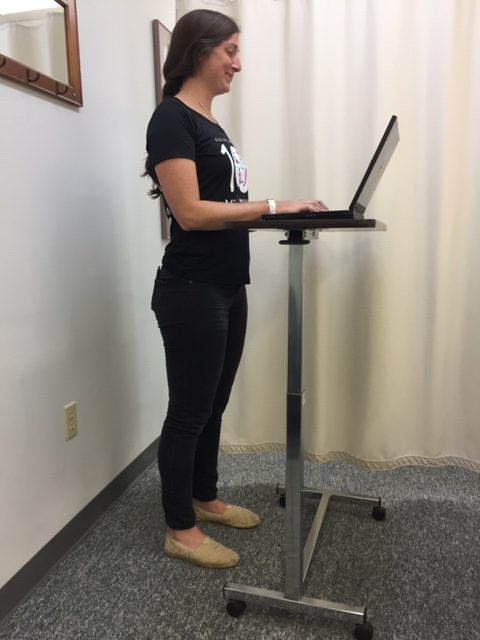
Standing: Feet should be shoulder width apart. Distribute body weight evenly through both feet. Do not lock knees. Maintain a small hollow in lower back with “tailbone” slightly tucked down. Lift the breastbone by drawing shoulder blades back and down. Make chin level. Earlobes should be in line with the middle of shoulders. Relax jaw and neck muscles by resting tongue on the roof of mouth.
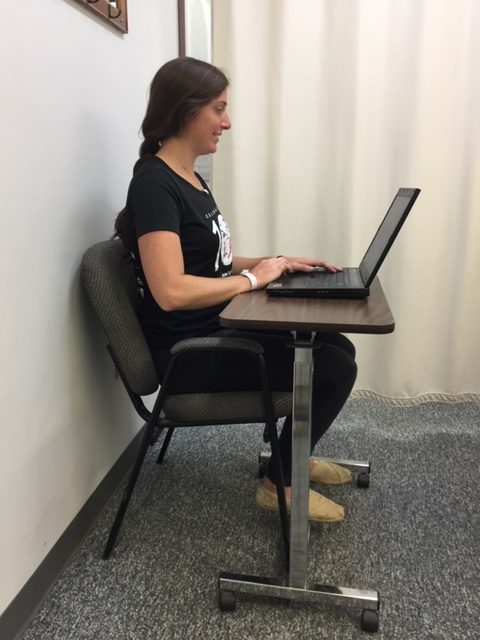
Sitting: Sit in a firm, high-back, straight-back chair. Buttocks should touch the back of chair while maintaining a small space between the back of knees and the seat of the chair. Distribute body weight evenly on both hips. Maintain an arch in the low back. A lumbar roll is recommended. It is a foam roll, 4” to 5” in diameter and 12” long, placed at belt level. Place feet flat on the floor with hips and knees bent at a right angle. Keep knees even with or slightly higher than hips. Use a footstool or footrest if necessary. Do not cross legs! Lift the breastbone by drawing shoulder blades back and down. Earlobes should be in line with the middle of shoulders. Position the armrests properly allowing elbows and forearms to rest with shoulders relaxed. If armrests are too high shoulders will shrug up and if too low will cause slouching.
POSTURE EXERCISES
The following exercises should be performed throughout the day as a break from sitting, studying or working at home, school or the office. They should be performed gently, slowly, held for 3-5 seconds and repeated 5-10 times. The exercises should only cause a slight stretch but NOT PAIN.
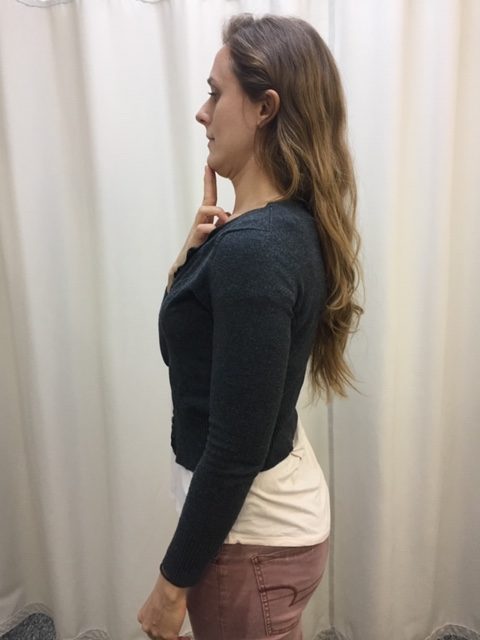
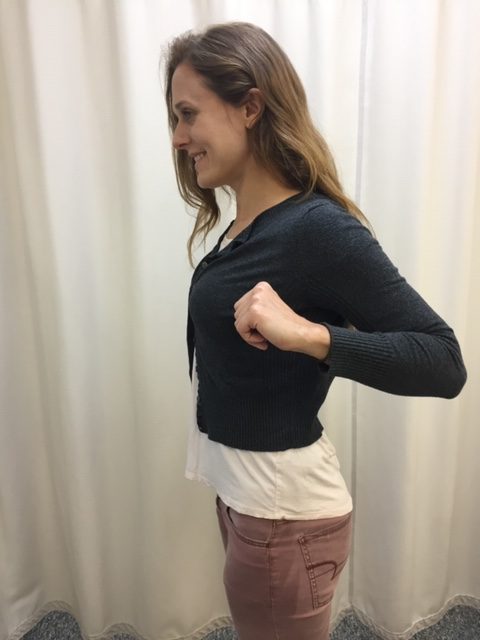
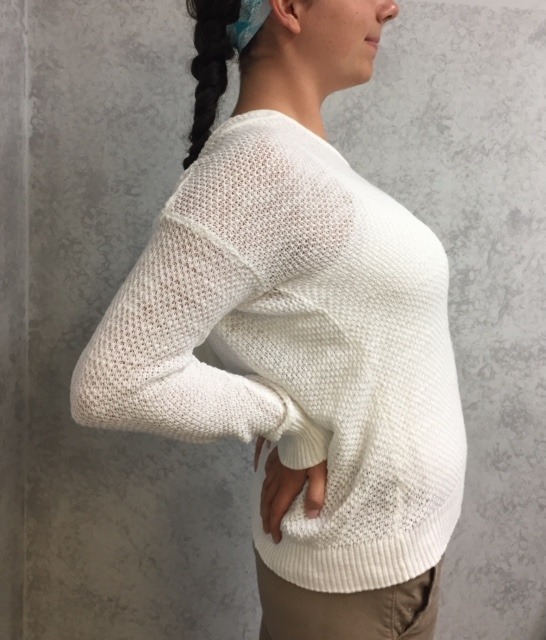



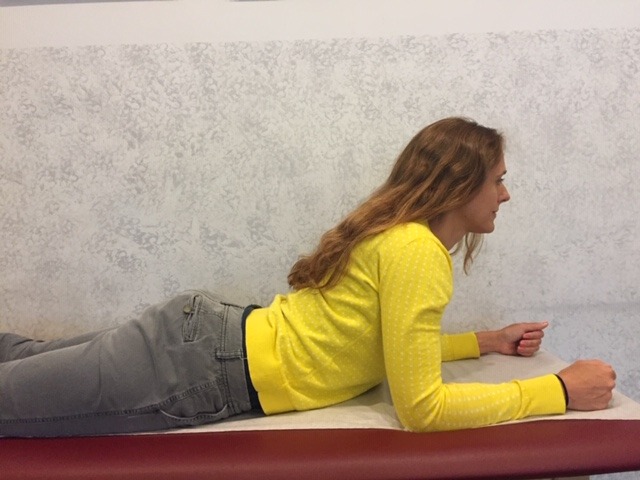


For all of Dr. Mackarey's Articles visit our health care forum at https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum/
Dr. Mackarey’s Health & Exercise Forum – every Monday
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com. Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine.
SITTING TOO MUCH? ZOOM CLASS FROM HOME…WORKING FROM HOME…
Can lead to stiff neck and back pain
Part I of II
Standing while studying, working, reading … good for children and adults to learn, work and be healthier!
I think we would all agree, technology is a wonderful thing. However, like all good things, it comes at a price. Students and workers alike have always suffered from the many physical effects of sitting for too many hours. But now, with a full day of Zoom classes, virtual meetings and long hours working from home, I have heard from many people suffering from neck, middle and lower back pain as well as headaches associated with prolonged sitting and computer use.
Studies show the impact of prolonged sitting, especially with poor posture, are multifaceted; pain, headaches, vision problems, poor concentration, excess fat storage with weight gain. Studies strongly support the use of using good posture, ergonomic workstations, posture stretches and frequent changes of positions, including the use of standing desks to prevent pain and injury. In fact, standing desks are not a new invention; they have been used by many to promote health and stimulate thought…Hemingway, Franklin and Jefferson all stood while they worked.
The Problem is Gravity!
The average head weighs 10 to 12 pounds and when tilted down at a 45 degree angle the forces of gravity are multiplied by 5. While reading, studying or working on the computer with poor posture, one must support 50 or more pounds of pressure on the neck, middle and lower back for hours on end. It is no wonder why this activity is associated with headaches, neck and back pain, numbness and tingling in arms and legs, muscle spasms etc. Some studies report the lifetime prevalence of neck and shoulder pain in office workers as high as 80%.
Recent research has also correlated the amount of time an individual sits to a decrease in their average life expectancy. Seriously, watching television and sitting is literally killing us. The Heart and Diabetes Institute of Australia conducted extensive research on sedentary behavior, including a review of almost one million people. They used actuary science, adjusted for smoking, waist circumference, and diet and exercise habits to assess the specific effects that the hours of sitting in a day impacts a person’s life span. They found that sitting too long results in a decrease in muscle contraction of the big leg muscles and because these unused muscles need less fuel, more unused glucose (fuel) is stored in the muscle. High glucose levels result in high blood sugar, which leads to adult onset diabetes and other health issues.
Sitting in a Virtual or Real Classroom…
The deleterious effects of sitting in children have also come under scrutiny and it may impact the classroom. Due to technology, today’s classroom is more advanced in many ways. However, the traditional hard chair and desk remain unchanged. Not only are these, “one size fits all,” desks uncomfortable, current research suggests that they may also limit learning.
Recent studies show that standing desks promote not only a physically healthier child by expending more calories and lowering obesity, but also improves focus and concentration to improve academic outcomes.
Research from Texas A&M Health Science Center found two landmark things about children who worked at standing desks such as Stand2LearnR, when compared to those seated: One, children burned more calories and obese children burned more than normal-weight peers. Two, children were more attentive in the classroom and engaged more with their teacher and their work when allowed to stand. Teachers in the study not only found the results to be favorable for fidgety, high-energy kids, but those who tend to be overweight and tired benefited greatly.
Researchers were quick to point out that there may be many ways to promote movement and limit sitting in the classroom that may also promote learning in a healthy way such as sitting on exercise balls or inflatable discs.
Sitting in the Home Office or Work Office …
The average office worker sits for more than 10 hours per day between office work, sitting at lunch, checking email and social media at home. Amazingly, studies suggest that even vigorous exercise before and after work cannot overcome the damage from prolonged sitting. New products such as the “TrekDeskR,” allows a worker to work on a computer, phone, or do paperwork, while walking on a treadmill, has health benefits. Also, other products such as VariDeskR, allows for frequent positional changes from sitting to standing while working. Even without using a standing desk, changing positions, such as standing during phone calls or meetings has proven to be valuable.
TrekDesk; VariDesk; Stand2Learn Desk
Caption: Standing desks have been used by many to promote health and stimulate thought…Hemingway, Franklin and Jefferson all stood while they worked.
(use TrekDesk photo (www.trekdesk.com) from previous column and refer to column date or link) Photo of VariDesk (www.varidesk.com); Photo of Stand2Learn Desk (www.stand2learn.com).
For more of Dr. Mackarey's articles visit our Health and Exercsie Forum: https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum/
Dr. Mackarey’s Health & Exercise Forum – every MondayThis article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com. Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine.