Patients often tell me that they would like to exercise but hesitate due to their knee or hip pain. They want to know what type of exercise is best for those suffering from osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis is also known as degenerative arthritis. It is the most common form of arthritis in the knee. It is usually a gradual, slow and progressive process of “wear and tear” to the cartilage in the joint which eventually wears down to the bony joint surface. It is most often found in middle-aged and older people and in weight bearing joints such as the hip, knee and ankle. It causes gradual onset of pain, swelling and stiffness in the involved joint, especially after increased activity and weakness with loss of function due to disuse.
However, OA is not an excuse to avoid exercise but it is important to be smart about it. Regular exercise is essential to maintain a normal lifestyle for those with OA. However, if you do the wrong exercise, use poor technique, or are too aggressive, you could flare-up your joints and do more harm than good.
When performed correctly, exercise for those with OA has many benefits:
Pain Control
Exercise controls OA pain by releasing natural pain control chemicals in the body called endorphins. It also controls pain by assisting in weight loss and improving range of motion.
Weight Control
We all know how well exercise burns calories and that increased body weight creates increase stress on the joints.
Prevention of Joint Stiffness
Exercise will help maintain joint range of motion. A stiff joint is a painful joint.
Prevention of Muscle Weakness
Exercise will help maintain muscle strength. Weak muscles will allow or increase in joint wear and tear.
Maintain Lifestyle
If a joint is stiff and weak, then they become painful which negatively impacts your lifestyle. Exercise can prevent this problem.
Start Slowly
Wean into exercise because if you advance too quickly, you will flare up the joint and have increased pain. For example, walk for 5-10 minutes the first session. If you do not have pain, add 1-2 minutes each session.
Lose Weight
Every pound lost equates to less stress on your joints. For example, a loss of 5 pounds of body weight translates to 20-30 pounds of stress through the knee, according to David Borenstein, MD, President of the American College of Rheumatology. Also, body weight has a direct impact on daily activities. For example, walking upstairs creates stress through the knee equal to 4 times body weight and seven times body weight going downstairs. Therefore, less body weight equals less stress.
Low Impact Workouts
Low impact exercise creates less stress on the joints while strengthening leg muscles and those who those who maintain leg muscle strength have less stress on their joints. It is even important not to load your arms with heavy objects when walking or using stairs to limit joint stress.
Some examples of low-impact exercises are: walking, swimming, elliptical trainer, and biking. Strength training is also low-impact and should be performed with low weight and high repetitions. Water therapy is great for those with OA, especially in a heated pool. It is a great low-impact exercise with less gravity and stress on the joints. Walk, swim and do mild resistance exercises in the water. Use a snorkel and mask for swimming to limit excessive neck turning and back extension.
Walking is a great form of exercise; however, walking softly is important for those with OA. Wear good running shoes and orthotics if necessary. Discuss this with your physical therapist or podiatrist. When possible, use soft surfaces like cinder, mulch or rubber. Avoid grass and soft stand due to instability and torsion that may irritate your joints.
Warm-Up
Warming up your body is critical to prevent injury to the muscles and tendons. This can be done by marching in place or using aerobic equipment such as a bike for 5 to 10 minutes before exercise. Always perform the warm-up activity at ½ your normal pace.
Balance & Relaxation Techniques
Tai Chi and ballroom dancing are two good examples of activities which promote balance and relaxation. Studies showed that those with OA who participated in Tia Chi two times a week for eight weeks reported less pain, increased range of motion and improved daily activities and function. They also noted less low back pain and better sleeping.
Proper Clothing
Stay warm in winter and consider wearing compression shorts. Be cool in the summer months with DrytechR type material.
Pre/Post Exercise First Aid
If you are sore for longer than 12 to 24 hours after exercise, then you overdid it and must make adjustments next time. Otherwise, use hot packs, bath or shower before you exercise to loosen up and apply ice to your joints after exercise, especially if they are sore.
Post Exercise Stretch
Gentle, active range of motion stretches after exercise is important to maintain mobility. Do not bounce or cause pain. For example: Low Back – knees to chest; Arms – row –the – boat, arms behind head, arms behind back; Legs – wall lean calf stretch, bend and extend knees, open and close hips.
SOURCES: Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; www.lifescript.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Tennis elbow, also called lateral epicondylitis, is an inflammation of the lateral (outside) bony protuberance at the elbow. It is at this protuberance that the tendon of the long muscles of the hand, wrist and forearm attach to the bone. As the muscles repeatedly and forcefully contract, they pull on the bone, causing inflammation. The trauma is irritating when working the muscles in an awkward position with poor leverage like hitting a backhand in tennis.
It is not unusual for a patient to come to my office with severe pain on the outside of their elbow. Especially, after intensifying their tennis workouts or changing the racquet string tension. Others come to me with pain on the inside of the elbow (“golfer’s elbow”) from wrist action that advanced golfer’s use at impact. However, this problem is not only for tennis players and golfers. Laborers working with wrenches or screwdrivers with an awkward or extended arm can also develop tennis elbow. Others who are vulnerable are: those working for hours at a computer using a mouse as well as those working hard maintaining their lawns and gardens.
In a more chronic problem, lateral elbow pain may arise by a degenerative condition of the tendon fibers on the bony prominence at the lateral elbow. Sporadic scar tissue forms from a poor attempt by the body to overcompensate and heal without eliminating the cause.
While symptoms may vary, pain on the outside of the elbow is almost universal. Patients also report severe burning pain that begins slowly and worsens over time when lifting, gripping or using fingers repetitively. In more severe cases, pain can radiate down the forearm.
Conservative treatment is almost always the first option and is successful in 85-90 percent of patients with tennis elbow. Your physician may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication (over the counter or prescribed). Physical/Occupational therapy, rest, ice, and a tennis elbow brace to protect and rest may be advised. Ergonomic changes in equipment, tools, technique and work-station may be necessary. Improvement should occur in 4-6 weeks. If not, a corticosteroid injection may be needed to apply the medication directly to the inflamed area. Physical therapy, range of motion, and stretching exercises may be necessary prior to a gradual return to activity. Deep friction massage can assist healing.
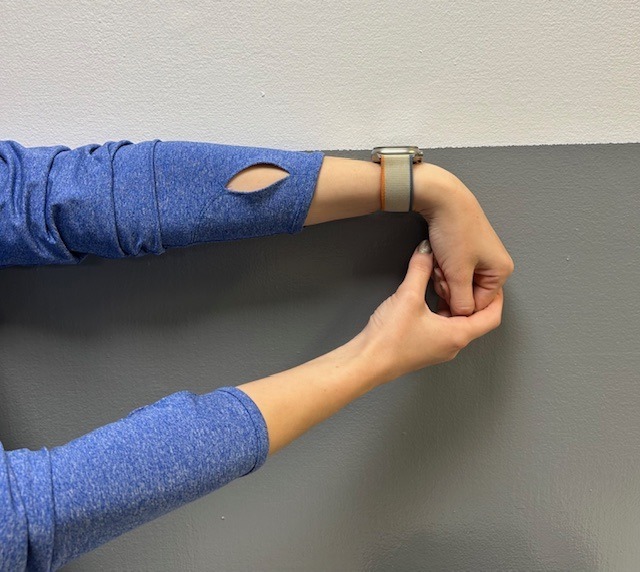

Exercises performed in a particular manner to isometrically hold and eccentrically lengthen the muscle with contraction.
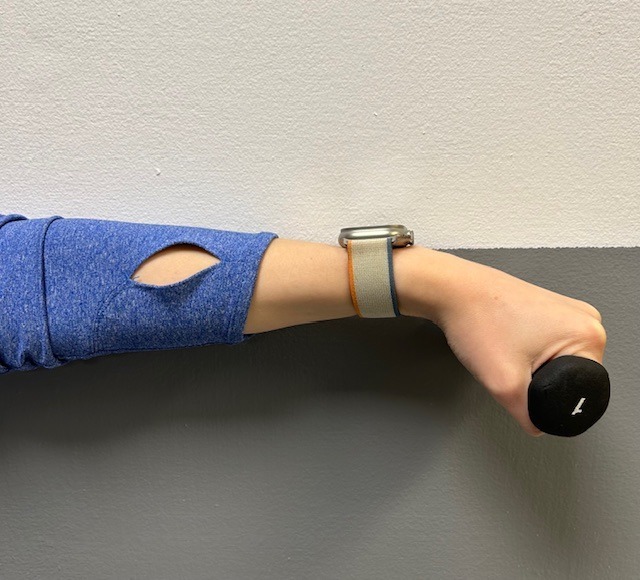
New Conservative Treatment: Platelet-Rich-Plasma (PRP) is a new treatment for the conservative management of degenerated soft tissues that has recently received great media attention. In great part, due to its success in several high profile athletes. According to the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,(JAAOS), platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is autologous (self-donated) blood with an above normal concentration of platelets. Normal blood contains both red and white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Platelets promote the production and revitalization of connective tissue by way of various growth factors on both a chemical and cellular level.
The actual PRP injection requires the patient to donate a small amount of their own blood. The blood is placed into a centrifuge (a machine that spins the blood at a high velocity to separate the different components of blood such as plasma, white and red blood cells), for approximately 15 minutes. Once separated, the physician draws the platelet-rich plasma to be injected directly into the damaged tissue. In theory, the high concentration of platelets, with its inherent ability to stimulate growth and regeneration of connective tissue, will promote and expedite healing.
Surgery for tennis elbow is only considered in patients with severe pain for longer than 6 months without improvement from conservative treatment. One surgical technique involves removing the degenerated portion of the tendon and reattaching the healthy tendon to bone. Recently, arthroscopic surgery developed to perform this technique. However, research does not support the value of one over the other at this point. Physical/occupational therapy is used after surgery. Return to work or athletics may require 4-6 months. More recently, a surgical technique using ultrasound to guide a needle to debride (clean) the area of scar tissue has been developed. If eligible for this procedure, the time required for healing, rehabilitation and return to activity is much shorter.
If you feel you suffer from tennis elbow, ask your family physician which of these treatment options are best for you.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy

This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
There is still plenty of summer remaining and its not too late to think of your pleasure puddle in different light…a health spa! It may very well be the exercise of choice for many people. Many have discovered the benefits of moving their limbs in the warm water of a home pool following knee or shoulder surgery. Also, long distance runners who often look for cross training methods without joint compression and arthritis sufferers who are often limited in exercise choices by joint pain from compressive forces when bearing weight, can enjoy the buoyancy effects of water. These are good examples of the benefits or water exercise…aerobic and resistive exercise without joint compression.
Most doctors recommend some form of exercise with arthritis. Pain and fatigue are the most limiting factors for the person with arthritis. Pool exercise may be the answer. With proper technique, adequate rest periods, appropriate resistance and repetitions, water exercise can be very effective.
The following are some of the benefits of water exercise:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
JUNE IS GREAT OUTDOORS MONTH! AS WE KICK OFF SUMMER AND CELEBRATE THE FOUR OF JULY, MAKE TIME TO GET THE HECK OUTSIDE! Research shows that spending time outdoors has many positive effects on your health. While there are many year-round activity options, in Northeastern Pennsylvania our short-lived summer is the inspiration to “suck the marrow out of a sunny day!” Summer in NEPA is enjoyed in many ways such as walking, running, hiking, biking, horseback riding, boating, kayaking, and swimming. Studies show that even less vigorous activities such as fishing, picnicking camping, barbequing, or reading a good book on the porch are healthier than being indoors.
It is reported that Americans spend 90% of their lives indoors and that number increases with age. Worse yet, for some, venturing outdoors is considered risky behavior with fear of the sun, ticks, wind, mosquitoes, and other creatures of God. Well, the truth of the matter is the risk of being one with nature is far less than the ill effects of a life stuck indoors. Please consider the following benefits of spending time outdoors.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
I have been advising my patients to exercise, keep active, and walk as long as they can in order to stay mobile and healthy. However, seniors often tell me activities that require prolonged walking is limited by ankle pain from arthritis. They often ask, “What is arthritis of the ankle?” How does it happen? What can I do about it?
Your family physician will examine your ankle to determine if you have arthritis. In more advanced cases you may be referred to a specialist such as a podiatrist, orthopaedic surgeon or rheumatologist for further examination and treatment. X-rays will show if the joint space between the bones in the ankle is getting narrow from wear and tear arthritis. If rheumatoid arthritis is suspected, blood tests and an MRI may be ordered. The diagnosis will determine if you problem if minor, moderate or severe.
In the early stages your treatment will be a conservative, nonsurgical approach, which may include; anti-inflammatory medication, orthopedic physical therapy, exercise, activity modifications, supplements, bracing, etc. You and your family physician, podiatrist, orthopedic surgeon or rheumatologist will decide which choices are best.
When conservative measures no longer succeed in controlling pain and deformity, improving strength and function then more aggressive treatment may be necessary.
SOURCES: Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Human beings were designed to move…walk, run, climb, lift, hunt, and gather. Contemporary man has suffered greatly from a technologically driven inactive and sedentary lifestyle. Inactivity is associated with many health problems; obesity, adult-onset diabetes, high blood pressure to name a few. The problems associated with lack of movement are many:
The more you move your body, the more you colon moves! A regular and consistent exercise and activity regime, results in a more consistent bowel schedule, especially with age. Healthy muscle tone in your abdominal muscles and diaphragm is also the key to moving waste through your digestive tract.
Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and many inflammatory or auto-immune diseases can cause achy and stiff joints. However, even healthy joints can also stiffen when you don’t use them enough. Put them to work so they don't get tight and cause pain.
All muscles get weak from lack of use, including the muscles that help your lungs expand and contract as you breathe if you don’t work them out regularly. The less exercise or activity you do, the more you experience shortness of breath, even during easy daily tasks.
Physical problems are not the only complication of inactivity. A lack of movement can also increase feelings of anxiety and depression. Aerobic exercises like walking, biking, swimming, or running, have been proven to stimulate endorphins to boost and steady your mood, and even improve your self-esteem.
Many studies have found that regular movement improves energy. Exercise helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to your tissues. When you sit or are inactive, tissues are not getting the same amount of fuel they need to keep you going.
Movement stimulates your metabolism. Hyperactive people burn more calories…just by fidgeting! Even if you are not hyperactive, the more active you are, the more calories you burn each time you move.
One of the first recommendations sleep doctors make to their patients suffering from insomnia is exercise. When you keep a regular exercise routine, you fall asleep faster, and you sleep deeper once you drift off.
Regular exercise tells your body to make more chemicals called growth factors. They boost blood vessel production in your brain. The more blood that gets to your brain, the better you can think, remember, and make decisions.
Spending most of your time sitting raises your risk of heart disease, in great part due to the fact that partly you’re more likely to have high blood pressure. This is a big risk factor for heart issues like coronary artery disease and heart attack.
When physical activity is a regular part of your life, your body has an easier time keeping your blood glucose under control. Exercise can stabilize blood sugar levels and keep you out of the type 2 diabetes danger zone.
When your core muscles are weak from lack of use, they can’t support your back the way they should. This makes it much easier to tweak your back muscles during everyday movements like standing or reaching. Pilates, yoga, and other exercises that use stretching are good for building a stronger back. Schedule an appointment with a good orthopedic and sports PT.
Logically, one might think that you’d be hungry more often if you exercised more, but the opposite is usually true. Aerobic exercise like biking, swimming, walking, and running can actually decrease your appetite because it changes the levels of certain “hunger hormones” in your body.
Studies show the more moderate activity you get, the lower your chance of catching a cold or other germs. When you make exercise a habit, your immune system gets stronger.
If your skin looks duller than usual, a lack of movement may be to blame. Some studies show that moderate exercise boosts your circulation and your immune system, which helps your skin keep that youthful glow.
SOURCE: WebMD

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Several years ago, while hiking to the bottom of the Grand Canyon with my family, my wife Esther developed “canyon knee,” also known as “hiker’s knee” or in medical terms, “patellar tendonitis.” Regardless of the term, the end result was that she had severe pain in the tendon below her knee cap and was unable to walk up the trail to get out of the canyon. In addition to ice, rest, bracing, and non-steroidal anti inflammatory medications, the National Park Ranger insisted that she use two trekking poles on her ascent to the rim.
Prior to that experience, I always thought that “walking, hiking sticks or trekking poles” were for show or those in need of a walking aide. Well, I could not have been more incorrect. Needless to say, Esther made it out of the canyon safely and, with the use of our life saving trekking poles; we have lived “happily ever after!” Now, 15 years later, I rarely walk more than 5 miles without my poles.
As a result of this experience, I have been recommending walking or trekking poles to my patients. These poles are an essential part of hiking or distance walking gear, for the novice and expert alike. Specifically, for those over 50 who have degenerative arthritis and pain in their lower back, hips, knees, ankles or feet, these simple devices have been shown to improve the efficiency of the exercise and lessen the impact on the spine and lower extremities. Additionally, using poles reduces the likelihood of ankle sprains and falls during walking. Trekking poles are also a safe option for those with compromised balance. If you want to walk distances for exercise and need a little stability but don’t want the stigma of a cane, trekking poles are for you.
Early explorers, Europeans and Native Americans have been using walking sticks for centuries. More recently, in the 1968 classic hiker’s bible, “The Complete Walker,” Colin Fletcher praised his “walking staff” for its multipurpose use: for balance and assistance with walking and climbing, protection from rattlesnakes, and for use as a fishing rod. Today, these sticks are now versatile poles made from light-weight materials.
Trekking poles are made of light-weight aluminum and vary in cost and quality. But, like most things, “you get what you pay for!” These hollow tubes can telescope to fit any person and collapse to pack in luggage for travel. Better poles offer multiple removable tips for various uses, conditions and terrains. For example, abasket to prevent sinking too deeply in snow, mud or sand; a blunt rubber tip for hard surfaces like asphalt or concrete, or the pointed metal tip to grip ice or hard dirt/gravel. Better quality poles offer an ergonomic hand grip and strap and a spring system to absorb shock through your hands, wrists and arms upon impact.
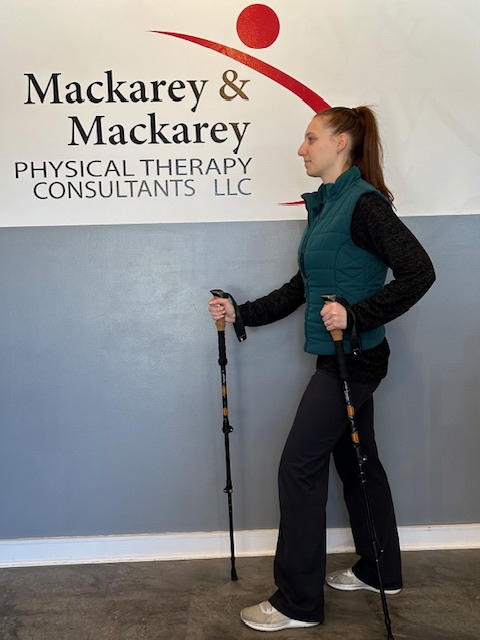
The poles should be properly adjusted to fit each individual. When your hand is griping the handle the elbow should be at a 90 degree angle. Proper use is simple; just walk with a normal gait pattern of opposite arm and leg swing. For example, left leg and right arm/pole swings forward to plant while the left arm/pole remain behind with the right leg .
This pattern is reciprocated with as normal gait advances (opposite arm and leg). I have been very pleased with my moderately priced poles (Cascade Mountain Tech from Dick’s Sporting Goods ($34.99 per pole). Prices range from $19.99 to 79.95 per pole. dickssportinggoods.com; montem.com; leki.com; rei.com. However, if you travel frequently to hike the State and National Parks, you may want to purchase more expensive poles that collapse and retighten more efficiently. (montem.com; leki.com;)
Montem Trekking Poles - with close-up of easy adjustable locking clasp.

There are numerous studies to support the use of trekking poles, especially research that supports their use for health and safety. One study compared hikers in 3 different conditions; no backpack, a pack with 15% body weight and a pack with 30% body weight. Biomechanical analysis was performed blindly on the three groups and a significant reduction in forces on lower extremity joints (hip, knee, and ankle) was noted for all three groups when using poles compared to those not using poles.
Another study confirmed that trekking poles reduced the incidence of ankle fractures through improved balance and stability. Additional studies support the theory that trekking poles reduce exercise induced muscle soreness from hiking or walking steep terrain and another study found that while less energy is expended in the lower body muscles using poles, increase energy is used in the upper body; therefore, the net caloric expenditure is equal as it is simply transferred from the legs to the arms.
In conclusion, it is important to remember that trekking poles for hiking or distance walking are much more than a style statement. They are proven to be an invaluable tool for health, safety and wellness by reducing lower extremity joint stress, improving stability and balance, and enhancing efficiency for muscle recovery.
Sources: Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. The Complete Walker, by Colin Fletcher
Model: Andrea Molitoris, PT, DPT at Mackarey Physical Therapy

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
In addition to lowering blood pressure, this gentle form of exercise can help maintain strength, balance, flexibility and mental health and is an ideal activity for all ages!
This research was brought to my attention by my friend and mentor from Dalton, Peter Frieder, Chairman,Gentex Corporation and current Board Chair at WVIA. Peter is celebrating his birthday today with a number of years that clearly does not represent his physiological age, in great part due to his dedication to health and wellness. Happy Birthday and thank you!
According to a new study by the China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (CACMS), the ancient martial art practice of Tai Chi is effective in lowering blood pressure as much, if not more, than traditional aerobic exercise. For those with prehypertension or hypertension and are unable to tolerate the repetitive and prolonged weight bearing stresses of running, walking or cycling, these results have tremendous implications. The slow, gentle and controlled movements and positions of Tai Chi coupled with controlled breathing and meditation may be a valuable alternative, especially for those with aging muscles and joints. Improved strength, flexibility balance, posture and mental health are additional bonuses.
Tai Chi is multifaceted in that it combines martial arts, slow gentle and controlled movements, sustained postures, a focused and meditative mind, and controlled breathing. It is considered by many to be “meditation or medication in motion.”
Tai Chi involves slow-motion movements transitioning with control from one position to another. The positions have historically been named for the actions of animals, for example:
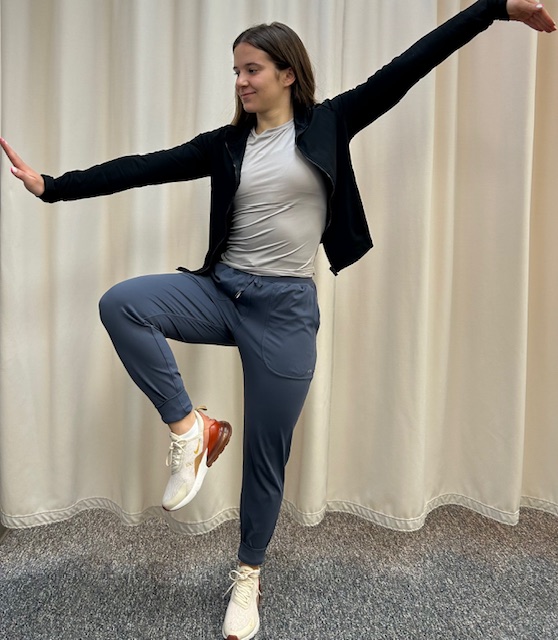

Deep and purposeful breathing, mental focus, body awareness and meditation are integral components of the exercise. The beauty of Tai Chi is not only in the physical form, but also in its safety for all levels of fitness. It is helpful for individuals from high level athletes to those with physical disabilities. The movements are natural and gentle without forcing the muscles and joints to extreme or uncomfortable positions. It is often used as an adjunct therapy in the wellness as well as rehabilitation of a variety of athletic (ACL surgery, joint replacements) and neurological conditions (Parkinson’s, MS, head trauma), to name a few. Based on the aforementioned Chinese study, Tia Chi can be applied as a technique to control or lower blood pressure, especially for those who cannot utilize traditional aerobic exercise.
Tai Chi has been found to offer many physical and mental benefits. Some of these include:
Muscle Strength – upper and lower body, trunk and core strength
Flexibility – participants report improved range of motion and flexibility of the spine and extremities
Balance and Proprioception – some studies report a reduction of falls due to a variety of sustained positionsand improved awareness of one’s body in space
Aerobic Conditioning - recent studies have found that participants have lower heart rate and blood pressure
Mental Health – through improved balance, strength, and flexibility, studies show participants have gained confidence and control as well as lower blood pressure and stress reduction.
All Tai Chi classes begin with four basic principles: warm-up, instruction, practice and breathing.
Warm-up- gentle easy motions to warm-up and loosen the joints and muscles to prevent injury.
Tai Chi Forms – “Short Forms” are beginner movements which are gentle, slow, and short in duration while “Long Forms” are more advanced.
Breath Work – gentle breathing combined with movement to relax the mind and focus energy
Don’t be intimidated by the language or history – Yang, Wu, Cheng are only brands of movements with a history of martial arts but this in no way impacts participation.
Get medical clearance – check with your physician to see if Tai Chi is safe for you. Some orthopedic or vestibular problems might require special attention.
Observe or take a beginner class – often available at local fitness clubs or senior centers. Research options in your area and find a friend to join you. Consider an introductory instructional video to get a feel for Tai Chi. (See local Tia Chi classes below)
Meet with an instructor – if it makes you more comfortable, make time to talk to an instructor before enrolling in a class.
Dress for success – wear loose-fitting clothes that allow for range of motion and comfortable shoes for balance and support.
Track your progress – use an app or keep a journal of your progress. Heart rate, blood pressure and endurance (the time you can hold a pose or tolerate a class) are easy to monitor.
Model: Lily Smith, University of Scranton Physical Therapy Student and PT aide at Mackarey Physical Therapy.
Sources: HarvardHealthPublishing; New Atlas; China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (CACMS); National Institutes of Health
Local Tai Chi Classes: Steamtown Yoga, Scranton, PA; Mission Yoga, Scranton, PA;Dragon’s Heart Tai Chi & Kung Fu, Clarks Summit, PA; Rothrocks Kung Fu & Tai Chi, Duryea, PA
For more information: HarvardHealth; www.taichihealth.com; www.treeoflifetaichi.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Seasonal allergies affect 30 % of adults and 40% of children in the United States. Avoiding the outdoors is often not an option…especially if you enjoy outdoor activities and sports. Not long ago, it was unthinkable that an athlete with serious seasonal allergies could compete at a high level, such as the Olympics. Now, in great part due to advanced research, medications and proper management, an Olympic gold medal for those suffering from seasonal allergies is a reality. Recently, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease at the National Institutes of Health have published research on this topic to provide a better understanding and make recommendations.
The most common allergic reactions which athletes suffer from are sneezing, itchy and watery eyes, runny nose and coughing. Moreover, 67% of those with these symptoms also suffer from asthma. The athlete in NEPA is particularly vulnerable when the pollen count is high during spring and fall for several reasons. One, after being indoors all winter, one might develop a heightened sensitivity to allergens. Also, increased rapid and deep breathing during exercise makes athletes more susceptible to significant symptoms when exposed to allergens such as tree, grass and weed pollens.
Allergy skin testing can be performed to determine the allergens to which you are susceptible. Once determined, allergy shots are effective in building up tolerance to these allergens. If appropriate, you may be able to use allergy drops, administered under the tongue and conveniently used at home.
Asthma suffers should use their inhaler BEFORE symptoms occur. A recent study found that pretreatment using a short-acting bronchodilator inhaler within 15 minutes before exercise is very effective in preventing asthma symptoms for more than four hours. It is important to keep a bronchodilator available. If you fail to benefit from this, see your physician for other methods to control your exercise-induced symptoms.
Whether you have allergic respiratory problems from rhinitis or asthma, you many benefit from conditioning your airways with a 10 to 15 minute warm-up before and cool-down after the activity. This may serve to gradually prepare your lungs for an increased demand.
In addition to preventing dehydration on hot and humid days, constant hydration is very important for the athlete with allergies to prevent dry airways in athletes.
Know the signs and symptoms of asthma (coughing, wheezing, tightness in chest, shortness of breath).
Some schools have a file on each student athlete with a allergic or asthmatic problem which requires medication. The file includes information such as medical doctor release and instruction, emergency contacts and medications. Students must have their medications on hand before they can enter the field. The National Athletic Trainers Association recommends using a peak flow meter to monitor at risk players and can determine when a player can return to the field.
If possible, find an alternate practice facility with climate control for athletes at risk. Plan practices for these athletes when the pollen count is low. Check the newspaper or internet for pollen counts in your area. Training by the water, (ocean) where there is a breeze and less pollen is helpful.
Shower and change clothing immediately after being outdoors
During a flare up, do less aerobic exercise to limit stress on respiratory system. Try strength training indoors instead.
When pollen count is high, keep windows shut at home and in your car….use air-conditioning.
Keep pets out of your bedroom…especially when sleeping
Dry clothing in dryer…do not hang on clothesline outdoors
Sources: American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. National Athletic Trainers Association.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is dedicated to the memory of John R. O’Brien, Esq., who recently passed due to medical complications associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). John was a source of joy and inspiration for those fortunate to have known him. Twenty years ago, John hesitantly agreed to contribute to my column on MS with two requirements: one, if the column would be valuable to those affected by MS and two, he would remain anonymous. When speaking with his dedicated wife, Sally, it became very apparent that any discussion of John’s life would be diminished if it was defined by the disease because he was committed to turning his “DISABILITY INTO AN ABILITY!”
With the help of his loving wife, family, friends, and devices such as an electric scooter and adaptive car, John not only lived but thrived! He was a skilled lawyer, a respected member of the Bar, and an active member of the community. John served on the executive committee of the Lackawanna Bar Association. In addition, the Lackawanna Pro Bono honored him recently. He also taught business law and healthcare law and coached Prep’s mock trial team.
John shared his thoughts with me about the challenges of redefining life… from Golf Club Champion to living with a physically disabling disease. Anyone who knew him would agree that he succeeded in doing so through his keen intellect and sharp wit and humor…his heart and brain overcompensated for his body! In addition to reading books in Latin and Greek, he had his crossword puzzles published in The New York Times and Los Angeles Times. In September 2023, John conducted an interview with presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin before a full house at the Scranton Cultural Center. Ms. Goodwin later reported that John was the most knowledgeable, effective and enjoyable interviewer she’s encountered.
John’s absence will be deeply felt and his legacy will continue to shape our community for years to come!
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic disease. While it may lay dormant and stable for a period of time, living a healthy lifestyle will make a positive contribution toward how you and your family live with Multiple Sclerosis. Studies show that a life of family, love, and support are essential to maintain a positive attitude with a chronic illness. This combined with a healthy diet and proper exercise can contribute greatly toward taking control and living a relatively normal life with MS.
As I have mentioned in many other columns, studies show that people with good attitudes and great faith live longer than others. This is especially helpful when living with chronic disease like Multiple Sclerosis. The Cleveland Clinic offers some suggestions how to maintain a positive attitude:
Many sources, including the Cleveland Clinic suggest that exercise, when performed properly, can have a positive impact on Multiple Sclerosis symptoms both physically and psychologically. However, because you have a chronic illness, you should consult with you family physician and physical therapist before beginning an exercise program. They will advise you on the proper type and amount of exercise.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!