Despite recent challenges for air travel due to increased volume, severe weather and a nationwide shortage of air traffic controllers, Americans report high levels of enthusiasm for air travel this summer, including travel abroad.
Confession; I recently was on a long trip that required sitting on an airplane for more than six hours…and I wore compression stockings … guess I’m getting older (and wiser)!
Have you noticed that being in a car or on an airplane for more than three hours leads to neck and back pain? Soreness, stiffness and swelling in your legs? With a little planning, preventing or limiting these problems on long trips is possible. Also, as people age and/or develop other health problems, they are more vulnerable to developing a more serious problem associated with long trips; deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or blood clots. But problems with long-distance travel can be avoided. The following tips, based on research and personal experience, can prevent neck, back and leg pain and stiffness and DVT.
A DVT is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein. The deep veins pass through the muscles and cannot be seen like the veins just under your skin. While it may occur in your arms, it is much more common in the legs, especially the calf muscle when traveling. When a blood clot forms in a leg vein it usually sticks to the vein wall. Often, pain and swelling lead you to the doctor and treatment is rendered before serious complications develop. However, there are two possible complications. One, a pulmonary embolus, occurs when a part of the clot logged in your deep vein of the calf breaks off and gets lodged in the lung. This is a very serious problem that can be fatal. Two, post-thrombotic syndrome, occurs when you have pain and swelling in your calf after a DVT.
The following risk factors for DVT significantly increase the potential for problems when traveling on long trips by air, more than 5 hours. Trains, cars and buses also create a risk, but air travel creates a greater risk for the following reasons: reduced cabin pressure, reduced cabin oxygen levels, dehydration and alcoholic drinks, which may increase dehydration and immobility.
Airplane seats are “C” shaped and force you to round your neck and back forwards. These exercises are designed to stretch and extend your back in the opposite direction. Please perform slowly, hold for 3-5 seconds and repeat 10 times each hour.
Sitting:
When sitting in an airplane seat, take the neck pillow in the overhead compartment and place it in the small of your lower back. While sitting or standing up, perform postural exercises every 30-45 minutes.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Happy Father’s Day! It is my hope that this information will be helpful to all the fathers who enjoy working in the yard! It is not too late to buy dad a new cart or kneeling pads for the yard. Last week, Health & Fitness Forum presented tips for gardeners for preventing hand and arm injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome. This week’s column is dedicated to prevention of lower back and lower body injuries when working in the yard and for gardeners with disabilities.
A relaxing and enjoyable activity for many, gardening can turn dangerous without proper precaution as repetitive stress injuries, back pain, muscle pulls, can stem from raking, weeding, digging and pruning, can turn into serious problems if not treated appropriately. Since prevention is the best approach, the US Dept of Agriculture promotes warm-up exercises and injury prevention tips to help all levels of gardeners avoid serious and long-term injuries while enjoying this popular outdoor activity.
People with various disabilities enjoy gardening at different levels. For example, those suffering from neurological diseases with muscle weakness, paralysis and poor balance as well as those with musculoskeletal problems such as neck and LBP or hip and knee arthritis can safely enjoy gardening at some level. This outdoor labor of love is very therapeutic.
Warm up and stretching is important. Don’t garden first thing in the morning before you have a chance to warm up. Get up, go for a short walk, have breakfast and maybe warm up with a hot shower before working in the garden. Some stretches include;
Note: These exercises should never be painful when completing them. You should only feel a gentle stretch. Hold the stretch10 seconds and repeat 5 times before you garden and every 2-3 hours while working. Should you experience pain, please consult your family physician or physical therapist.
The following guidelines to prevent injury and foster healthy gardening for those with and without disability:
Source: Karen Funkenbusch, MA; Willard Downs, PhD.: U. S. Department of Agriculture - Agricultural Engineering Extension

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Farmers and gardeners in NEPA always say that Memorial Day, the “kick off” day for planting without the fear of frost, however, this year we have had an unusually cold and wet spring… but it is not too late to start…not only for the beds but your body! While gardeners are anxious to work in their gardens and enjoy the fruits of their labor, a relaxing and enjoyable activity can turn dangerous quickly. Precautions are necessary as repetitive stress injuries such as shoulder and elbow tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome can stem from raking, weeding, digging and pruning. Additionally, simple scrapes, blisters, and bites can turn into serious problems if not treated appropriately. Since prevention is the best approach, the American Society of Hand Therapists (ASHT) promotes warm-up exercises and injury prevention tips to help all levels of gardeners avoid serious and long-term injuries while enjoying this popular outdoor activity.
ASHT recommends following these upper extremity warm-up exercises prior to gardening:
Note: These exercises should never be painful when completing them. You should only feel a gentle stretch. Hold 10 seconds and repeat 5 times. Should you experience pain, please consult a physician or hand therapist.
ASHT recommends the following guidelines to prevent injury and foster healthy gardening practices:
Professional Contributor: Nancy Naughton, OTD, CHT, is an occupational therapist and certified hand therapist practicing in NEPA.

Next Week: “Prevention of Gardening Injuries” Part II of II.
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

The World Health Organization has classified obesity as a chronic disease and determined that it is reaching epidemic proportions, not only in the United States, but globally. Moreover, closer to home, the Pennsylvania Department of Health has determined that PA ranks 17th among all states in the country for percentage of obese residents. Childhood obesity is defined as having a body mass index (BMI) at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 and older.
People have theorized for many years that obesity must be genetic. Scientific research has validated this theory and more importantly, a recent study has shown that while there is an obesity gene that may predispose one to obesity, one can control the outcome with exercise. The fat mass and obesity gene (FTO) is linked to a high body mass index according to a new study in the Archives of Internal Medicine. More importantly, this study found that exercise can offset a genetic predisposition for obesity. Aerobic exercise 30-45 minutes 3-5 times per week coupled with mild weight training and other physical activities can overcome the FTO. With new knowledge, it becomes apparent that it is critical to promote a healthy lifestyle with exercise and physical activity at an early age to prevent childhood obesity.
Obesity increases with age and its prevalence among obese children will continue to be obese with age. Childhood obesity is the leading cause or is associated with: hypertension, Type II diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, lower extremity joint stress and pain, lower self-esteem and other psychological problems.
As with adult obesity, childhood obesity is most often caused by multiple problems including: nutritional, psychological, familial, and physiological.
Weight loss is not the primary role of a good childhood obesity program. The goal is to limit or stop weight gain so the child will eventually grow into their body weight over a period of many months or years. One study suggests that it requires 1 ½ years of body weight maintenance for every 20 percent excess in ideal body weight for a child to ultimately attain ideal body weight.
In conclusion, childhood obesity is a serious epidemic. It is physically and emotionally stressful for the child/adolescent and family. This problem requires a comprehensive team approach including: family, physician, educator, dietitian, psychologist, physical therapist and other health and exercise specialists. Lastly, to be successful, it must involve the entire family and be a lifetime lifestyle change 7 days a week regarding diet and exercise, not a 3-to-6-month fad. It must be a long-term program with a long-term goal!
Sources: World Health Organization (WHO), Archives of Physical Medicine, 2008, Vol 168, 1791 – 1797
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Recently, a young woman came to my office with complaints of severe middle and lower back pain. On her first visit, I noticed her beautiful pink purse (big bag) and asked her permission to weigh the bag and discovered that it weighed 8 pounds. While 8 pounds does not seem excessive, the woman weighed 120 pounds and based on the research, would be advised to carry a 2.5-to-3.5-pound bag, (2-3% of her body weight).
A recent study shows that the average weight of a woman’s purse has increased by 38% and now exceeds 6 pounds. Despite technological advances, women have not found a way to simplify their lives, or at least what they think they need in their lives. High tech gadgets have only added weight to a purse already filled to the brim.
On a whim, I decided to ask permission to examine the contents of some of my patient’s purses. A typical purse includes the following: hairbrush, cosmetic bag, mirror, feminine products, keys, and sunglasses, reading glasses, checkbook, wallet, coupons, water bottle, and medications. Additionally, I discovered heavy high-tech products such as cellular phones, tablets, digital Bluetooth earpieces, and rechargers. Lastly, some women add the weight of a book or Kindle to the bag. Studies also show that the larger the bag and stronger the straps, the more items are stuffed in, resulting in a very heavy purse.
It is a pervasive attitude that a woman should never be stranded without her purse full of essentials. So, where is the problem? The problem is that carrying a heavy bag, usually on one side of the body, forces the body to tilt forward and to the opposite direction to compensate. Over time, this change in posture leads to neck, middle and lower back pain.
Consider the following suggestions to promote healthy use of a purse and prevent injury:

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

NEPA has experienced more than its share of bitter cold temperatures this winter. And, as much as I enjoy skiing, ice skating and snowshoeing, I have noticed a few achy joints when the mercury plummets! Osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis, is often considered to be a normal part of aging. Usually by the age of forty our joints, especially those which are weight bearing (lower spine, hips, knees, ankles, feet) begin to show signs of wear and tear. The cartilage begins to thin, the joint surfaces are not as smooth, and fluid which lubricates the joint becomes diluted, dehydrated and less protective.
Consequently, these aging joints become stiff, sore, weak, and sometimes swollen. Most people with osteoarthritis report additional pain and stiffness in the winter and early spring due to cold, damp weather and NEPA has plenty of it! The cold, for example, restricts the flow of blood to the joints, leading to more pain and stiffness. While moving to a warmer and less humid climate is one solution, it is not practical for most. But all is not lost because there are other alternatives to protect and keep your joints healthier this winter and early spring.
SOURCES: www.apta.org; www.webmd.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

According to American Association of Retired Persons (AARP), those 50 years old and older are seniors! By this definition, as hard as it is to admit, I am well into senior status and as one, I offer holiday health tips for seniors.
Overindulgence during the holidays causes many seniors to make New Year's resolutions related to diet and exercise. But, this year, I propose that seniors incorporate healthy habits during the holiday season, and you may find that your resolutions are not as hard to keep.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Happy Holidays! Despite political divisions and war in the Middle East and Ukraine, it is at this time of year that we celebrate life with great hope and faith. People of many faiths take time to reflect, respect, and resolve. Christians celebrate Christmas, the miraculous birth of Christ, the Son of God, and the Messiah. Jews celebrate Chanukah, the miraculous festival of lights, when one night’s oil provided enough light and safety for 8 nights. Both major faiths promote healthy lifestyles for the mind, body and spirit. These faiths are grounded in hope, faith, love and peace. It is no surprise that studies repeatedly demonstrate that faithful and spiritual people live longer and healthier lives! At this turbulent time in the world, it is important to note that people of all faiths benefited equally!
I purport, that to be truly healthy, one must have faith because complete health is multidimensional. Socrates preached this message to his students thousands of years before Christ. One must have a healthy mind, which requires intellectual stimulation with attainable goals related to education and intellect. One must have a healthy body by eating well, engaging in physical activity and having attainable goals related to his/her body. Likewise, one must have a healthy spirit with faith, hope, prayer and meditation, comrades and counsel, and set attainable spiritual goals.
How being religious or spiritual has been shown to benefit your mind, body and spirit…
1. Healthy Blood Pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) can lead to heart disease and stroke, which are the leading causes of death in the United States, according to the Centers of Disease Control (CDC). It affects 1 in every 3 adults and only half of these people have their blood pressure under control. Well, religion and spiritually may help …
The health benefits of religion or spirituality are well documented. One study conducted at Duke University Medical Center on 4,000 subjects, older adults who described themselves as religiously active were 40% less likely to have high blood pressure when compared to those less active. Moreover, they were surprised to find that those who described themselves as spiritual rather than religious also were less likely to develop high blood pressure.
2. Greater Sense of Satisfaction: Research also indicates that religious people are more satisfied with their lives than those without faith. A sociology study determined that high satisfaction among church goers may be due to the strong social bonds that are developed within a religious congregation. Regular church attendees see the same people weekly and often more often, when participating in rewarding and gratifying church-related volunteer work.
3. Greater Tolerance for Adversity: In an impressive study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers interviewed 345 late-stage cancer patients to assess their spirituality as it related to their illness. 88% stated that they were religious as it related to their coping mechanisms. It was determined that those using religion for coping demonstrated a 7.4% rate of resuscitation as compared to 1.8% for those not using religion as a coping mechanism.
4. Stronger Immune System: According to a Duke University study of 1,718 older adult participants, those described as “highly spiritual” were 50% less likely to have high levels of anti-inflammatory proteins that weaken the immune system and have been linked to some cancers, viral infections and autoimmune diseases. The outcome was similar for those who attend religious services at least once a week.
5. Greater Longevity Those who attend religious services more than once per week are found to live and additional 7 years when compared to those who never attend services. Again, researchers feel that the social benefits of a belonging to a strong religious community may be a large part of the associated longevity. Additionally, the lifestyle of religious people is often healthier: members of these communities rarely engage in risky and unhealthy behaviors such as smoking, excessive drinking, indiscriminate sex, etc
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Holiday shopping is stressful for your body, causing backache, as well as your wallet. Even the “online shopper” is at risk when you consider the hours sitting with poor posture on your electronic device. But I do believe that “in person” shopping is worse for backache… driving from store to store, getting in and out of the car while bundled in a sweater and winter coat can add stress to your spine. Often, the expert shopper carries package after package from the store to the car, repeatedly. Six, eight, or ten hours later, the shopper arrives home exhausted with the backache slowly increasing, only to realize that 15 or 20 packages must be carried from the car into the house. This dilemma is compounded by the fact that the rain turned to sleet, and the sleet to snow. You are slipping and sliding all the way from the car to the house while carrying multiple packages of various sizes and shapes, fighting through the already developing backache. The shopping bags get wet and tear, forcing you to tilt your body as you carry the packages. Of course, no one is home to help you unload the car and you make the trip several times alone. You get into the house exhausted and crash onto the couch because your backache is too much to do anymore at this point. You fall asleep slouched and slumped in an overstuffed pillow chair. Hours later you wake up with a stiff neck and lower back pain. You wonder what happened to your neck and back.
Plan Ahead: It is very stressful on your spirit, wallet and back to do all of your shopping in the three weeks available after Thanksgiving. Even though we dislike “rushing” past Thanksgiving to the next holiday, try to begin holiday shopping in before
Use the Internet: Supporting local businesses is important. However, Internet shopping can save you lots of wear and tear. Sometimes, you can even get a gift wrapped.
Gift Certificates: While gift certificates may be impersonal, they are easy, convenient and can also be purchased over the internet.
Perform Stretching Exercises: Stretch intermittently throughout the shopping day…try the three exercises below, gently, slowly, hold 3 seconds and relax, repeat 5 times.
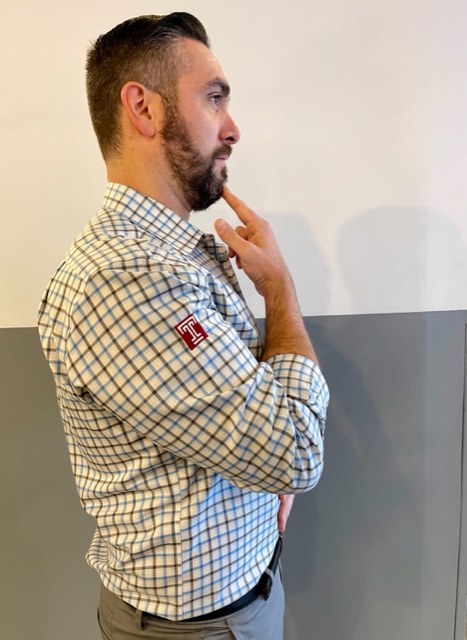
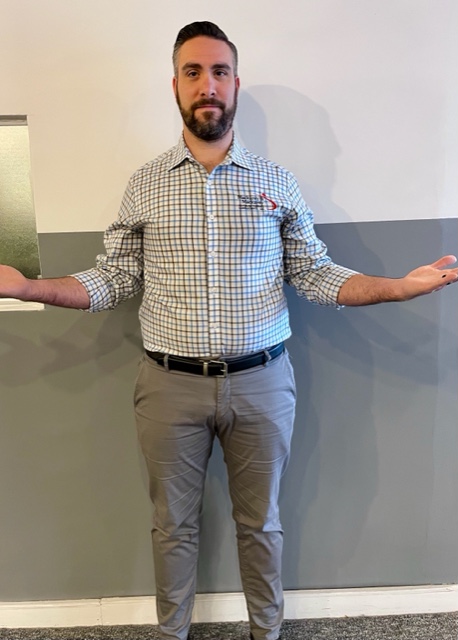



Model: Paul Mackarey, PT, DPT, Clinic Director, Mackarey PT
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Fall has arrived in NEPA and walking is a great way to enjoy the fall foliage. Moreover, a new study has found that walking can reduce lower back pain. Researchers in Australia followed more than 700 adults who had a recent onset of lower back pain (and were able to bear full weight without associated leg symptoms) and enrolled them in a walking program under the supervision of a physical therapist. One group walked for 30 minutes, 3-5 times per week and the control group remained inactive. Both groups were followed for more than three years and discovered that the inactive control group was twice as likely to suffer from repeated flare-ups of lower back pain when compared to the walking group.
It is good news for those who enjoy walking, however, for many who have not maintained an active lifestyle or have health issues, it is challenging to know where to begin. Also, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program too aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning yourself into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
Walking to reduce or control lower back pain is only one of many important reasons to begin a program. According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen-minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
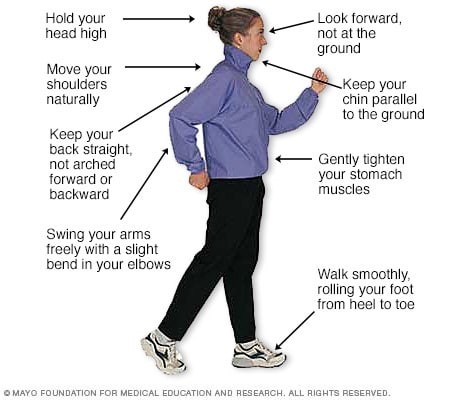
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic, “Health & Science New”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
