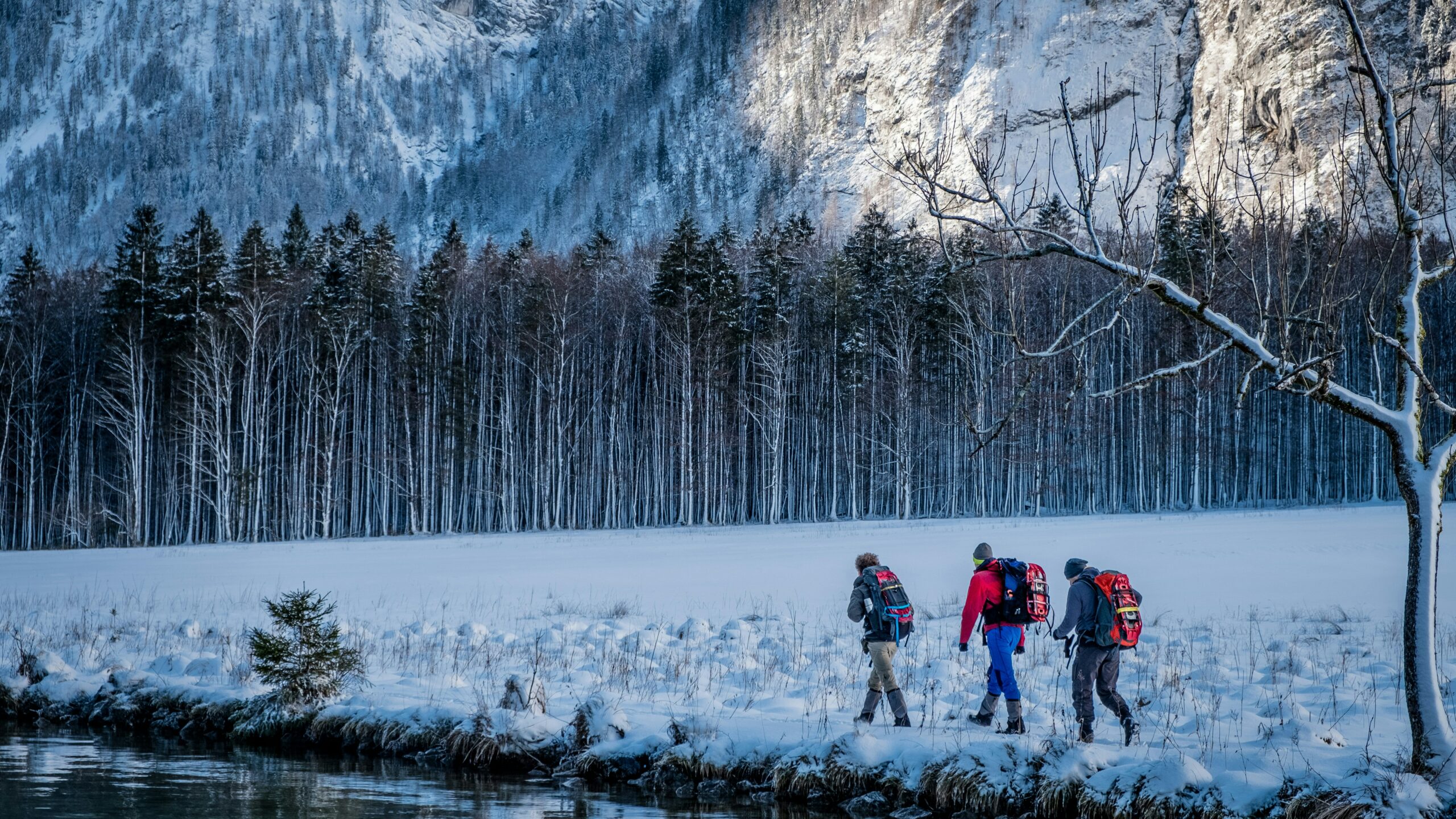
Last week, this column discussed the many benefits of snowshoeing as an option for those in NEPA to get outdoors and enjoy the winter. Today’s column will present another option for outdoor exercise when the weather is inclement…winter walking or running.
We live in such a beautiful environment. Each season brings its own unique beauty and winter is no different. Most will not have to abandon outdoor activities, but you must make some adjustments in equipment, clothing and food for each season and temperature changes that go with it. These tips are also appropriate for those who qualified for the Boston Marathon in the spring and will be training all winter, as well as those who enjoy walking and running throughout the winter for exercise. Consider the importance of making changes and adjustments in training as well as clothing and equipment, according to the weather and temperature.
There are running shoes specifically designed for use in wet, cold and sloppy winter conditions. These running shoes, which can also be used for walking, are considered “winterized” because they offer waterproofing, sealed seams, gaiter collars to keep out snow and slop, slip resistant fabric, anti-roll stability features, anti-microbial material and aggressive tread patterns for traction on slippery surfaces. Some shoe recommendations for both walkers and runners include:
Additionally, I am a strong proponent of walking with trekking poles for improved balance and safety when brisk walking in winter conditions. They are light weight, adjustable, and collapsible. Some examples are: Trekology Trek Z 2.0 – 45. and REI Co-op Trailmade $79.00. Also, an old pair of ski poles will work just fine.
Over the past several years great strides have been made on understanding the effects of extreme temperatures on performance. Current wisdom from the University of Otago in New Zealand has found:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

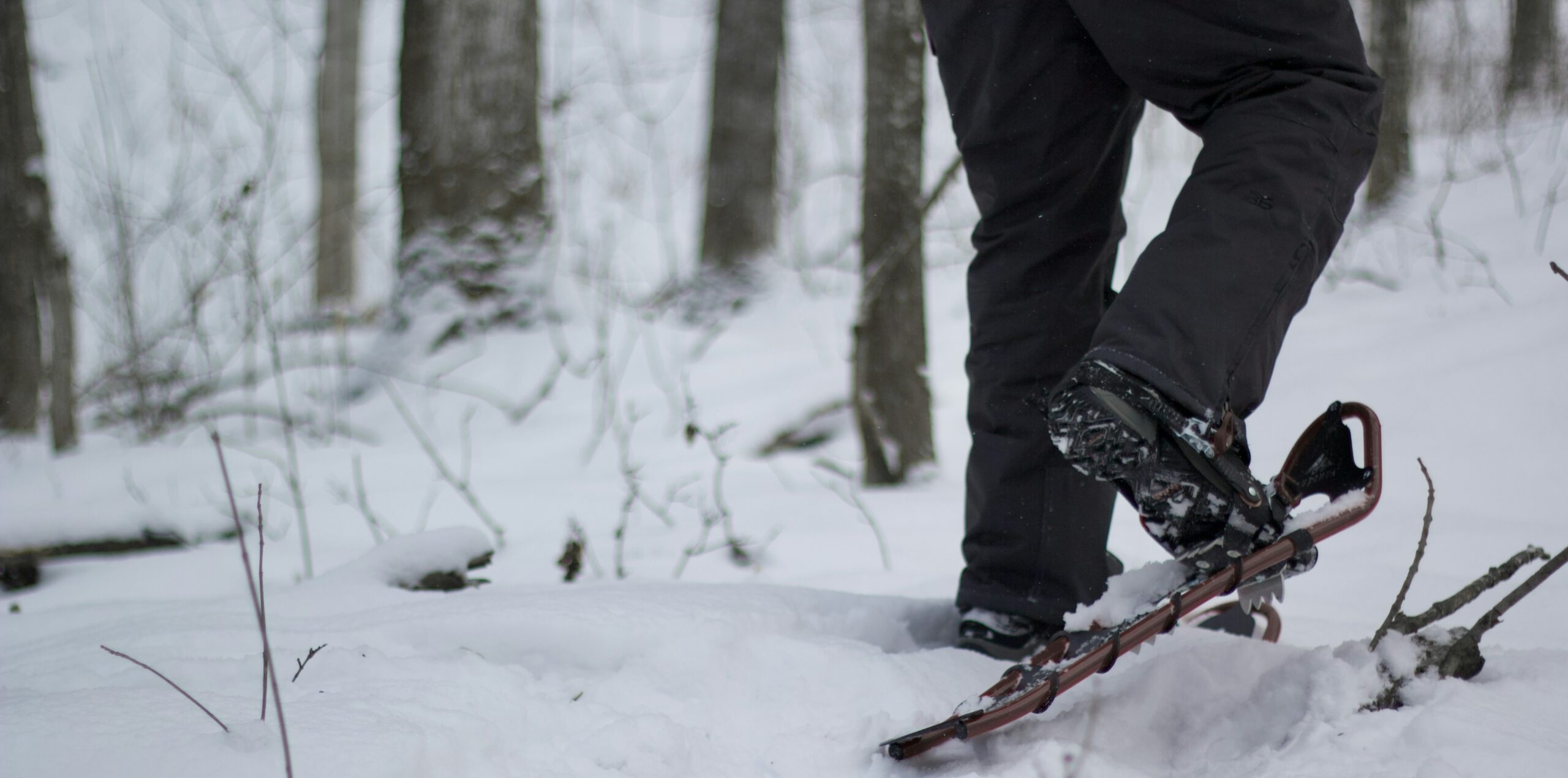
When I was a young boy growing up in NEPA, one of my favorite winter things was to walk in the freshly fallen snow. I loved the feel of fresh crisp air through my lungs, the mesmerizing sparkle of snow falling in the moonlight, the peaceful sound of silence as pedestrian and motor traffic came to a halt and only thing audible was the muffled sound of my boots as they crunched the snow beneath… for me, if it is sizzling hot in hell, it snows in heaven! Well, I am happy to share with you, as I struggle to hold on tightly to my “inner child,” I am as excited and inspired by a walk in the snow today, as I was 45 years ago. It is my hope, that this column will inspire my readers to consider a beautiful walk in the snow to rediscover their “inner child.”
While there are many options and opportunities available to enjoy winter in NEPA such as downhill skiing, cross country skiing, winter mountain biking, ice skating, and sled riding, none is as easy and natural as snowshoeing.
The advantages are many:
As a result, the popularity of snowshoeing is growing rapidly. According to the Outdoor Industry Association, the number of snowshoe participants have increased by 7.5% to 4.1 million in 2011 and 40.7% overall since 2008.
History (Raquettes GV, Quebec, Canada info@gvsnowshoes.com)
While the advent of the wheel is estimated to have been approximately 3,500 BC, the snowshoe had already been established and developed by 6,000 BC according to Stone Age engravings found in Norway. The snowshoe was an instrumental tool used by early humans to cross the Bering Strait into North America.
Some historians feel the snowshoe developed, like many great inventions, as an imitation of nature. For example, animals such as the snowshoe hare use expansive feet to increase their surface area, limit sinking and move more efficiently through the deep snow. Hardwood frames with leather webbed lacing comprised the early snowshoes used by fur trappers, traders, and Native Americans. More recently, materials have advanced and light but durable aluminum frames comprise snowshoes that are used by park rangers and winter recreation enthusiasts.
Like all sporting equipment, you usually get what you pay for. Snowshoes range in cost from $50.00 to $300.00. Most people will be fine in a good pair for under $100.00. LL Bean and Dick’s Sporting Goods and Sierra Store offer several affordable options.
Some equipment examples are Tubbs Wayfinder Flat - $199 and Redfeather - $82.00. Ski poles are recommended for efficiency when snowshoeing. Traditional ski poles or adjustable hiking poles can be used. Warm and supportive winter boots or hiking shoes are essential.
Now you are ready to go! The next time a snow storm dumps 8 – 10 inches on NEPA, get outside BEFORE the streets are plowed. Put on you warm winter boots, strap them into the bindings of your new snowshoes and walk out your front door and explore your neighborhood as you have never seen it before...white, clean, glistening, crisp and quiet. Let your mind wander, enjoy winter and rediscover your inner child!
Next Week: Part II of II...Winter Walking and Running
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

The number one New Year’s Resolution in the United States is to lose weight. A close second is to gain control over one’s life. One of the best ways to lose weight is thought diet and exercise. It can also be a very effective method to begin taking control of one’s life. This is especially true for those suffering from stress, anxiety and depression. This year make your New Year’s Resolution to “Get a Runner’s High on Life!”
Specifically, aerobic exercise (exercise that increases your heart rate for 30 minutes or more) such as walking, biking, running, swimming, hiking, elliptical & stepper machines to name a few, is the secret to “runner’s high.” This exercise euphoria is not limited to runners alone, but all who engage in aerobic exercise are more likely to experience high energy, positive attitude, and mental wellness – not to mention burn calories.
Physical activity, specifically aerobic exercise, while well known for its importance to one’s physical well-being has also been scientifically proven valuable for preventing and easing stress, anxiety and depression. Studies have found improvement in mental health for groups that engaged in aerobic running, jogging or walking programs, 30-45 minutes 3-5 days per week for 10-12 weeks when compared to a control group and a group in counseling.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.comPaul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

According to American Association of Retired Persons (AARP), those 50 years old and older are seniors! By this definition, as hard as it is to admit, I am well into senior status and as one, I offer holiday health tips for seniors.
Overindulgence during the holidays causes many seniors to make New Year's resolutions related to diet and exercise. But, this year, I propose that seniors incorporate healthy habits during the holiday season, and you may find that your resolutions are not as hard to keep.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Happy Holidays! Despite political divisions and war in the Middle East and Ukraine, it is at this time of year that we celebrate life with great hope and faith. People of many faiths take time to reflect, respect, and resolve. Christians celebrate Christmas, the miraculous birth of Christ, the Son of God, and the Messiah. Jews celebrate Chanukah, the miraculous festival of lights, when one night’s oil provided enough light and safety for 8 nights. Both major faiths promote healthy lifestyles for the mind, body and spirit. These faiths are grounded in hope, faith, love and peace. It is no surprise that studies repeatedly demonstrate that faithful and spiritual people live longer and healthier lives! At this turbulent time in the world, it is important to note that people of all faiths benefited equally!
I purport, that to be truly healthy, one must have faith because complete health is multidimensional. Socrates preached this message to his students thousands of years before Christ. One must have a healthy mind, which requires intellectual stimulation with attainable goals related to education and intellect. One must have a healthy body by eating well, engaging in physical activity and having attainable goals related to his/her body. Likewise, one must have a healthy spirit with faith, hope, prayer and meditation, comrades and counsel, and set attainable spiritual goals.
How being religious or spiritual has been shown to benefit your mind, body and spirit…
1. Healthy Blood Pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) can lead to heart disease and stroke, which are the leading causes of death in the United States, according to the Centers of Disease Control (CDC). It affects 1 in every 3 adults and only half of these people have their blood pressure under control. Well, religion and spiritually may help …
The health benefits of religion or spirituality are well documented. One study conducted at Duke University Medical Center on 4,000 subjects, older adults who described themselves as religiously active were 40% less likely to have high blood pressure when compared to those less active. Moreover, they were surprised to find that those who described themselves as spiritual rather than religious also were less likely to develop high blood pressure.
2. Greater Sense of Satisfaction: Research also indicates that religious people are more satisfied with their lives than those without faith. A sociology study determined that high satisfaction among church goers may be due to the strong social bonds that are developed within a religious congregation. Regular church attendees see the same people weekly and often more often, when participating in rewarding and gratifying church-related volunteer work.
3. Greater Tolerance for Adversity: In an impressive study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers interviewed 345 late-stage cancer patients to assess their spirituality as it related to their illness. 88% stated that they were religious as it related to their coping mechanisms. It was determined that those using religion for coping demonstrated a 7.4% rate of resuscitation as compared to 1.8% for those not using religion as a coping mechanism.
4. Stronger Immune System: According to a Duke University study of 1,718 older adult participants, those described as “highly spiritual” were 50% less likely to have high levels of anti-inflammatory proteins that weaken the immune system and have been linked to some cancers, viral infections and autoimmune diseases. The outcome was similar for those who attend religious services at least once a week.
5. Greater Longevity Those who attend religious services more than once per week are found to live and additional 7 years when compared to those who never attend services. Again, researchers feel that the social benefits of a belonging to a strong religious community may be a large part of the associated longevity. Additionally, the lifestyle of religious people is often healthier: members of these communities rarely engage in risky and unhealthy behaviors such as smoking, excessive drinking, indiscriminate sex, etc
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

The “first Thanksgiving” was in 1621 between the Pilgrims of Plymouth Colony and the Wampanoag tribe in present day Massachusetts to celebrate the harvest and other blessings of the previous year. In 1789, President George Washington, at the request of Congress, proclaimed Thursday, November 26, as a day of national thanksgiving. In 1863, Abraham Lincoln proclaimed the national holiday of Thanksgiving to be the last Thursday of November.
Americans and Canadians continue to celebrate this holiday as a time for family and friends to gather, feast, and reflect upon their many blessings. Like most, I am very grateful for the simple things; family, good friends, food, shelter, and health. It turns out that being grateful is, not only reflective and cleansing; it is also good for your health!
Grateful people are more likely to behave in a prosocial manner, even when it is not reciprocated. A study by the University of Kentucky found those ranking higher on gratitude scales were less likely to retaliate against others, even when others were less kind. Emmons and McCullough conducted one of the most detailed studies on thankfulness. They monitored the happiness of a group of people after they performed the following exercise:
There are many things in our lives, both large and small, that we might be grateful about. Think back over the past week and write down on the lines below up to five things in your life that you are grateful or thankful for.” The study showed that people who are encouraged to think of things they’re grateful for are approximately 10% happier than those who are not.
Amy Morin, psychotherapist, mental health trainer and bestselling author offers this advice: “Developing an “attitude of gratitude” is one of the simplest ways to improve your satisfaction with life. We all have the ability and opportunity to cultivate gratitude. Simply take a few moments to focus on all that you have, rather than complain about all the things you think you deserve.” So…be grateful and have a happy Thanksgiving!
Source: NIH, Forbes, Amy Morin “13 Things Mentally Strong People Don’t Do.”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Fall has arrived in NEPA and walking is a great way to enjoy the fall foliage. Moreover, a new study has found that walking can reduce lower back pain. Researchers in Australia followed more than 700 adults who had a recent onset of lower back pain (and were able to bear full weight without associated leg symptoms) and enrolled them in a walking program under the supervision of a physical therapist. One group walked for 30 minutes, 3-5 times per week and the control group remained inactive. Both groups were followed for more than three years and discovered that the inactive control group was twice as likely to suffer from repeated flare-ups of lower back pain when compared to the walking group.
It is good news for those who enjoy walking, however, for many who have not maintained an active lifestyle or have health issues, it is challenging to know where to begin. Also, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program too aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning yourself into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
Walking to reduce or control lower back pain is only one of many important reasons to begin a program. According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen-minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
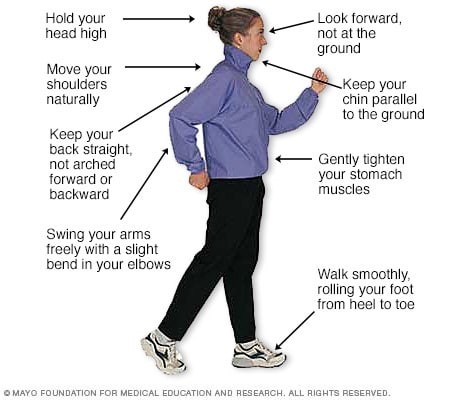
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic, “Health & Science New”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

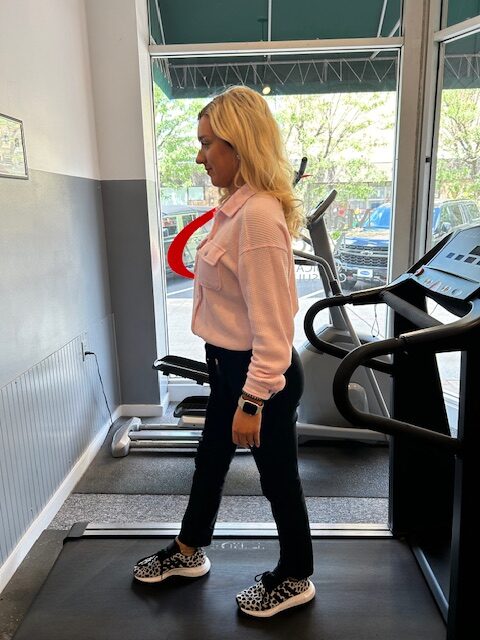
Have you ever noticed high level athletes warming up before a game or competition walking or running backwards? You may also see fitness enthusiasts in gyms emulating these athletes to improve their fitness or performance. I found the concept of backward walking, (also called retro walking) interesting and decided to research the topic for more information and validation. Walking backward does have many therapeutic benefits, however, before you attempt this activity on a treadmill or elliptical, please consult your physician and physical therapist and have a spotter nearby.
At a recent meeting of The American College of Sports Medicine, several studies were presented on the topic of backward waking. Most of the research was conducted while moving backward on a treadmill and an elliptical machine. When comparing two groups recovering from knee injuries, the backward motion group showed significant improvement in strength in the quadriceps (front thigh) and hamstring (back thigh) muscles when compared to the traditional forward walking group. Furthermore, the muscles of the front (tibialis anterior) and back (gastro/achilles) of the shin/ankle also demonstrated an increase in strength and endurance with backward walking. One explanation is that forward motion is routine in daily living that it has become very efficient and does not tax or stress the muscles the body. While this efficiency prevents fatigue in daily activities, it may not stress the muscles enough to gain strength as quickly as an unfamiliar exercise.
Due in great part to the increased strain of performing an unfamiliar exercise, backward walking on a treadmill or backward pedaling on an elliptical, offered a greater cardiovascular benefit and caloric expenditure than forward motion at all levels. Specifically, walking backward on a treadmill at 2.5 mph at grades of 5% - 10% has been found to significantly increase cardiovascular endurance than walking forward under the same conditions. This knowledge is useful for healthy individuals in need of greater cardio exercise. However, it may also serve as a precaution for those with cardio problems and should consult their physician prior to engaging in this activity.
A recent study in the International Journal of Obesity, found that those who performed new activities or increased the intensity of an activity, even if for a short duration (interval training) expended more energy and burned more calories than those who worked out at the same pace consistently for a longer duration. Moreover, when engaging in a new activity such as backward walking, even more calories were burned. This phenomenon may be due to the fact that routine activities such as forward walking are performed more efficiently and easily.
We challenge our body when we inefficiently perform a new motor skill such as backward walking and burn more calories. In other words, if you want to burn more calories without exercising for longer periods of time, than try a new activity and engage in higher intensity, intermittently, for part of the time. For example, walk backward on the treadmill for 30 minutes at 2.5 mph, but do so at a 5 – 10% incline for 1-2 minutes every 5 minutes.
Some studies show that using other muscle groups by performing different exercises not only prevents boredom, but also protects your muscles and tendons from overuse and joints from wear and tear. Specifically, the knee joint and the patella joint (the joint where the knee cap glides on the knee), benefits from backward walking due to less stress and compression forces on the joint. The thigh and ankle/foot muscles benefit from using a different form of contraction while lengthening the muscle. Some authors propose that this may also prevent strains and pulls and may be valuable to strengthen those with a history of shin splints and flat feet (pronation).
Mixing up your program prevents boredom. As a rule, those willing to change their exercise routine are more compliant and continue to exercise longer than those stuck in the same routine. A new challenge to improve distance, speed, and resistance while exercising in a different direction will be refreshing to your program.
Prevention of falls by improvement in balance and coordination has received a great deal of attention in the past few years. This is not only valuable to the athlete but may be even more important to those over 50. With age, balance centers are slow to react to changes in inclination, elevation, rotation and lateral movements. This slow reaction time leads to falls that may cause fractures, head injuries and more. Working on this problem by challenging the vestibular and balance centers before it is seriously compromised is important and backward walking is one way for this to be effectively accomplished.

Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

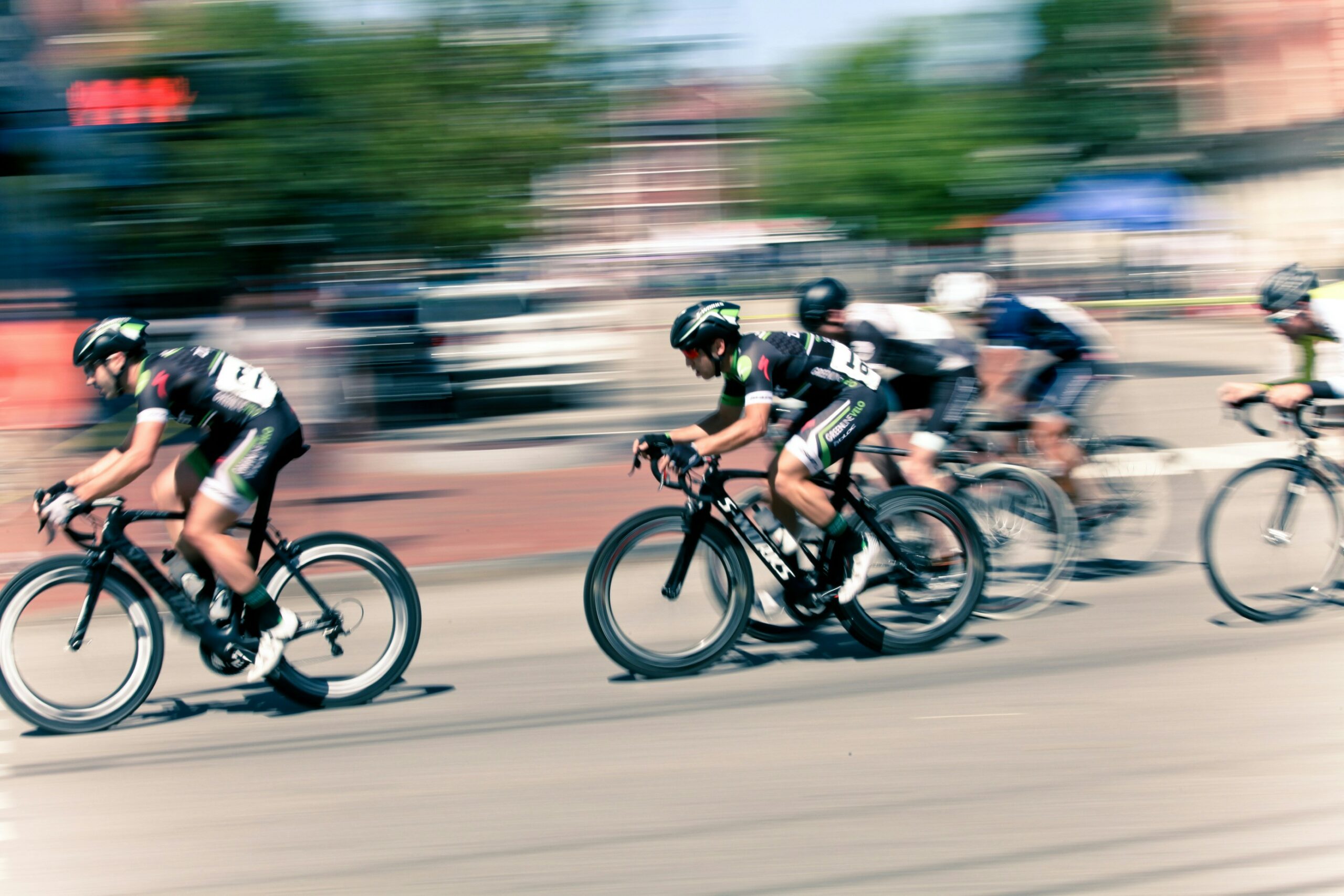
As summer fads and cool fall nights are upon us, many of us will prepare to put away some of our warm weather toys…closing the pool, storing kayaks and boats and packing up the “slip and slide.” However, one activity that can last well into the fresh breeze of fall is cycling. In fact, many feel that fall is the best time of year to jump on a bike and enjoy the ride! If you are looking for a kick start to riding your bike this fall, consider the 20th and final Tour de Scranton on Sunday, April 15, 2024. It is a fun-filled, noncompetitive bike ride through Scranton and neighboring communities. Tom and Betty Moreken, with the help of dedicated friends and countless supporters have raised over $400,000.00 to benefit addiction treatment and prevention in honor of their daughter Erin, a victim of drug addiction. I have had the privilege to know Tom and Betty and have always admired their resilience and selflessness to turn a negative into a positive and do something good for others. They and their friends truly represent everything that is good about the people of NEPA!
So dust off your bikes and join the fun at Tour de Scranton. Hopefully, it will entice you to ride the many beautiful and well-maintained trails that are available at the Countryside Conservancy and other locations in the Abingtons and the Lackawanna Heritage Valley Authority.
Tour de Scranton is the official “kick off” to biking season in NEPA. This year, on Sunday, September 15th, the 20th annual and final Tour de Scranton will offer a selection of several routes and distances for the novice and experienced rider at its non-competitive bike ride for riders of every age and skill level. This event supports “The Erin Jessica Moreken Drug & Alcohol Treatment Fund” which provides charitable gifts to qualified local organizations or individuals struggling with the disease of addiction. For more information visit: www.tourdescranton.com.
There are many obvious reasons to bike…cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, improve leg strength and others. But, the real question is, “what are the advantages of biking over other forms of exercise?” Glad you asked…
Prevention is the best management of musculoskeletal problems associated with biking. First, many of the problems associated with biking such as knee pain, buttock soreness, and tendonitis can be prevented through proper fitting. Furthermore, it is important that your equipment be in good working order such as tires, chain, brakes and pedals. Next, be sure to maintain a fairly good fitness level in order to bike safely. If you are a beginner, start slowly. Warm up and slowly bike for 10 to 15 minutes and build up over time. Practice the coordination of stopping, starting, shifting and braking. Work on good strength and flexibility of the hamstrings, quadriceps, calves and gluteal muscles. All of these muscles are necessary to generate pedal force. Balance is also important to safety and can be practiced on and off the bike. Be aware that adaptive equipment can modify your bike for added comfort and safety such as soft handlebar tape, seat post and front fork shock absorbers, padded biking shorts, c-out and gel pad saddle seats, and wider tires.
Be careful not to progress too quickly because inactivity to over activity in a short period of time can create problems. Overuse injuries such as tendonitis, can be avoided by cross training. Bike every other day and walk, run or swim on off days. Make sure to take time off to recover after a long ride. Use ice and massage to sore muscles and joints after riding.
Remember, cycling should be fun! Pain from improperly fitted and poorly maintained equipment is preventable. Excessive workouts and training rides should be kept to a minimum and consider cross-training in between.
EQUIPMENT: Helmets are a must! Also, keep your bike in good condition. Road bikes should have mirrors and reflectors. Use hand signals and obey traffic rules. Dress for weather and visibility. Have a first aid and tire patch kit, tire pump and tools. Seat comfort can be improved with gel cushion or split seat.
BE ALERT: for traffic, parked cars, pedestrians loose gravel and cracks in the road.
SOURCES: American Physical Therapy Association
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, and exercise regularly

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

There is plenty of summer remaining … so make time to get to the water! Research shows that spending time outdoors has many positive effects on your health. Moreover, new research has found that being near a body of water makes us calmer and healthier. You know that special feeling you get when you drive to the lake or the beach and jump out of the car and smell the fresh air and hear the sound of splashing in the lake or the waves of the ocean? Well, it is not just because you’re on vacation…the water makes your muscles relax and breath deeper. Your brainwaves slow down to simulate the gentle roll of the water…lake or ocean! These “blue environments,” not to be confused with “blue zones” are the subject of extensive research at the University of Exeter Medical School in the UK.
Time spent near water promotes physical activity, general fitness and well-being. In addition, noted for reducing the incidence of diabetes and other diseases associated with obesity. Additionally, time near the water slows down our heart rate, reduces stress hormones and improves mental health. In fact, the study also found that subconsciously, people consistently preferred pictures of natural environments (rivers, lakes, oceans) even when compared to attractive urban landscapes. In fact, urban landscapes with water (rivers, fountains etc) were far more popular than those without. Also, health disparities between coastal and inland communities are more noticeable for low-income individuals who do not have the means to venture to the coast. This may be one of the reasons that four out of the five “Blue Zones” discovered by Dan Buettner are islands.
Sources: NIH, Global News, Plume, L, University of Exeter Medical School in the UK.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!