After a long winter, spring is finally in the air as indicated by the warm (summer-like) temperatures last week. While your mind may be ready to play golf (and other outdoor activities), however, it is important to remember that without proper warmup and preparation, the risk of injury can increase substantially. PGA professionals benefit tremendously from sport science, physical therapy and fitness programs on tour year round. Amateur golfers in northern climates require diligence and planning to prepare for the game after 4-6 months off to avoid injury.
Muscle strains, ligament sprains, neck and LBP is prevalent in the early season for golfers, especially for the amateur. The reasons are many: general deconditioning after winter inactivity, poor golf swing mechanics, excessive practice, inadequate warm-up and poor flexibility and conditioning. The very nature of the golf swing can create great stress on the body, especially after time off.



NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM
Access all of Dr. Mackarey's articles at our Health and Exercise Forum
After a long winter, spring is finally in the air as indicated by the warm (summer-like) temperatures last week. While your mind may be ready to play golf (and other outdoor activities), however, it is important to remember that without proper warmup and preparation, the risk of injury can increase substantially. PGA professionals benefit tremendously from sport science, physical therapy and fitness programs on tour year round. Amateurs in northern climates require diligence and planning to prepare for the game after 4-6 months off to avoid injury.
Muscle strains, ligament sprains, neck and LBP is prevalent in the early season for golfers, especially for the amateur. The reasons are many: general deconditioning after winter inactivity, poor golf swing mechanics, excessive practice, inadequate warm-up and poor flexibility and conditioning. The very nature of the golf swing can create great stress on the body, especially after time off.
Get to the course early enough to make time to stretch before you play and hit a few balls at the range. Always start with low irons and work up to driver. Take a hot shower before an early morning round and use compression shorts and shirts on cool days. Do Not Bounce or Overstretch! Stretch slowly, holding for 10-20 seconds:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” Next Week: Part II - Preseason Golf Tips.

This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician.
For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles visit our Health and Exercise Forum
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), 32.2 million adults and children, 10.5% of the population in the United States, have diabetes. Unfortunately, one-third of these people are not aware that they have the disease. It will be the purpose of this column to raise the level of consciousness through education and offer recommendations for lowering blood sugar levels naturally.
Perhaps no goal is more important to a person with diabetes than maintaining a healthy blood sugar level. When managed over time, healthy blood sugar levels can slow the onset of complications associated with the disease. According to the ADA, pre-diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance, occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal (110 to 125mg/dl) but below type 2 diabetes levels (126mg/dl). 54 million Americans have pre-diabetes in addition to the 20.8 million with diabetes.
While medications are effective in maintaining blood sugar levels, for those who are borderline, there are effective ways to lower your blood sugar naturally. Your physician will determine which treatment is most appropriate for your problem. Also, maintaining your ideal body weight is always important.
**This column is based on information from local physicians Kenneth Rudolph, MD, Gregory Borowski, MD, the American Diabetes Association L (ADA), and Lifescript

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our Health and Exercise Forum
Pain is different than discomfort! Muscle soreness and “feeling the burn” can occur during a normal healthy exercise routine. However, you should never experience a sharp, deep, intense, or lingering pain during or after exercise. In fact, if the soreness lasts more than 24-48 hours, than you did more damage than benefit to your muscles and other tissues and it is time to scale back and take time off. If necessary, use RICE (rest, ice compression and elevation). It is important to get in tune with your body and learn the difference between muscle strain and fatigue discomfort and pain from soft tissue damage from overuse and overload. Find the proper amount of weight and repetitions and gradually increase over time.
There is no solid evidence that stretching alone before a sport or activity prevents injury. In fact, over stretching may be counterproductive before a sport as it may weaken the muscle. The current wisdom on the matter is; never stretch a cold muscle. Instead, warm up for 5-10 minutes by actively moving the extremities and light jogging or biking and THEN lightly stretch the arms, legs, back etc. More vigorous stretching should be performed to improve the flexibility of tight muscles (ie calf and hamstring muscles) and best done after your workout but not before a sporting activity (tennis, basketball, etc.).
It depends on your body type and hormones! It is very unlikely that women and prepubescent males will bulk up from lifting weights…especially light weights (blame or thank hormones). It will, however, increase metabolism and fat burning efficiency which can lead to weight loss and good muscle tone. Stick with low resistance and high repetitions for best results.
It is not possible to target an area of the body to burn more fat! It is very common for women to ask for a specific exercise to reduce the fat in their buttocks, thighs, and abdomen. Regretfully, it is not possible to target weight loss in these areas or other body parts. In fact, when you lose weight through diet and exercise, the caloric expenditure will be evenly distributed throughout the body. However, once the adipose tissue in a specific part of the body such as the abdomen is reduced from general weight loss, targeting the area with exercises specific to that muscle group will improve the tone and definition for a leaner look in that region.
Sure, it would be great to dedicate 60 minutes 5 -6 days a week for exercise. But for most of us who work and raise a family it is not practical. The good news is that the research supports 30 minutes of exercise 3-5 days a week. Moreover, evidence shows that 10 minutes, three times a day, 5 days per week will help you attain the 150 minutes a week supported in most exercise studies.
Most people with the most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, feel better when they are moving. That is not to say that they don’t have increased symptoms when they OVERDO it. An exercise program specifically designed for a person’s problem and limitations will improve their symptoms and function. For example, if an individual has arthritis in their knees, they should use an exercise bike (partial weight bearing) or swim (buoyancy effect of water) instead of walk or run (full weight bearing) for aerobic exercise.
Furthermore, they would do far better with light cuff weights in a sitting or lying position to strengthen their legs than performing squats or lunges. It is important to remember, the weight gain and joint weakness and stiffness associated with a sedentary lifestyle will do more harm to an arthritic joint than a proper exercise program.
Not unless you are planning a killer workout! The number one reason most of us exercise is to lose or control body weight. High calorie sports drinks are counterproductive and unnecessary. If you do not plan on exercising for more than 60 minutes, good old fashion H2O is more than adequate. However, if you plan to do a “killer” workout for more than 60 minutes and may incorporate a high intensity interval training (HIIT) program, than a sports drink with electrolytes and other nutrients, may be of value.
For most of us, effective resistance training is not about the equipment. It is safe to say, caveman was pretty fit and strong despite the fact that he never went to a gym and lifted weights. He did however, lift, push, pull, and carry heavy stones, timber, and animals for day-to-day survival. So too, it is for modern man, the body does not distinguish between the resistance provided by a elastic band, dumbbell, or cable with pulleys and weight stacks. As long as the basic principles of strength training are applied, (isolating a muscle or muscle group, loading the muscle with enough force to bring it to fatigue without causing tissue damage, and allowing for adequate rest and recover) than the muscle will gain strength regardless of the type of resistance.
First, let me confess that I love to run and up until recently, ran almost daily. However, now that I am over 60, I had to find new forms of aerobic exercise which would be kinder and gentler to my joints. So, I mix it up between biking (indoors and outdoors, recumbent and upright), brisk walking or hiking, elliptical and stepper and swimming laps. Again, like the caveman weightlifting example, the body (heart and lungs) does not know what is causing an increase in heart rate for 30, 45 or 60 minutes, it only knows that it must respond to allow the body to function under this stress. And, in the process it becomes conditioned to the point that it will work much more efficiently when not under stress with a lower heart and respiratory rate and blood pressure at rest.
Those over 50 would be well-advised to engage in low-impact aerobics on a regular basis. For example, if you want to run two to three days per week, do not run two days in a row and consider performing low impact exercise in between. Some examples of low impact aerobics are walking, treadmill walking, swimming, elliptical trainer, and an exercise or road bike.
Change is necessary with age! For many years, I have repeatedly preached about the value of engaging in an active lifestyle throughout life. It is especially important to be active as one gets older to maintain mobility and independence. However, many take this advice to an extreme and refuse to accept the inevitable changes that occur in the body with age. They run, jump, lift and throw like a teenager and often fail to modify their activity or exercise regimen appropriately for their age. Consequently, they suffer from multiple injuries, including muscle tears, tendonitis, bursitis, impingement, and advanced osteoarthritis.
Keep in mind, everyone ages differently. One person at 60 years of age may be the equivalent of another at 50. However, change with age is inevitable, so be kind to your body…it’s the only one you have! It is always prudent to consult your physician and physical therapist for a program designed specifically for your needs.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
Access all of Dr. Mackarey's articles in our Health Care Forum!
In 2000, President Bill Clinton dedicated March as National Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month. The purpose of this designation is to increase public awareness of the facts about colon cancer – a cancer that is preventable, treatable and has a high survival rate. Regular screening tests, expert medical care and a healthy lifestyle, which includes a proper diet and exercise, are essential for prevention. Several studies have demonstrated that exercise can also help prevent colon cancer.
The American Cancer Society estimates that there will be approximately 107,000 new cases of colorectal cancer in 2023. Of these, 52,550 men and women will succumb to the disease. It is the second-leading cause of U.S. cancer deaths for both men and women combined. The good news is incidence and mortality rates are dropping both nationally as well as in northeast Pennsylvania. The bad news is northeast Pennsylvania still has increased incidence and mortality rates when compared to the national average.
Studies show that prevention of this disease is multifaceted and includes: engaging in daily exercise, eating a low-fat diet with little red meat, avoiding smoking, drinking in moderation and having regular colonoscopy screenings.
Early detection is the key to survival. Death from colorectal cancer can be eliminated if caught at the earliest signs of disease. Colorectal cancer progresses very slowly, usually over years. It often begins as non-cancerous polyps in the lining of the colon. In some cases, these polyps can grow and become cancerous, often without any symptoms. Some symptoms that may develop are: blood in stool, changes in bowel movement, feeling bloated, unexplained weight loss, feeling tired easily, abdominal pain or cramps, and vomiting. Contact your physician if you have any of these symptoms.
The risk of colon cancer increases with age, as 90 percent of those diagnosed are older than age 50. A family history of colon cancer increases risk. Also, those with benign polyps, inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease are at greater risk and should be screened more frequently.
The intestine works like a sewage plant, recycling the food and liquid needed by your body. However, it also stores waste prior to disposal. The longer the wastes remain idle in your colon or rectum, the more time toxins have to be absorbed from you waste into the surrounding tissues. One method in which exercise may help prevent colon cancer is to get your body moving, including your intestines. Exercise stimulates muscular contraction called peristalsis to promote movement of waste through your colon.
Exercise to prevent colon cancer does not have to be extreme. A simple increase in daily activity for 15 minutes, two times per day or 30 minutes, once per day is adequate to improve the movement of waste through your colon. This can be simply accomplished by walking, swimming, biking or playing golf, tennis or basketball. For those interested in a more traditional exercise regimen, perform aerobic exercise for 30-45 minutes four to five days per week, with additional sports and activities for the remainder of the time. For those in poor physical condition, begin slowly. Start walking for five to 10 minutes, two to three times per day. Then, add one to two minutes each week until you attain a 30-45 minute goal.
Medical Contributor: Christopher A. Peters, M.D
Dr. Christopher Peters is a partner of Radiation Medicine Associates of Scranton (RAMAS) and serves as medical director of Northeast Radiation Oncology Centers (NROC). He is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. Sources: American Cancer Society/Northeast Regional Cancer Institute, and CA Cancer J Clin.

EVERY MONDAY - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey "Health & Exercise Forum!"
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's Articles, visit our Healthcare Forum!
PEOPLE WILL OFTEN ASK ME, “IS THERE SUCH A THING AS AN EXERCISE RUT?” THEY WANT TO KNOW WHY THEY DO NOT SEEM TO BE IMPROVING WITH THEIR EXERCISE PROGRAM…they exercise 3-4 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes and they feel frustrated and STUCK in a rut.
The purpose of this column will be to offer suggestions on how to improve or get more out of a “stale” exercise program. Last week’s column offered tips to improve a stale cardiovascular and strength program. This week we will discuss flexibility and functional training tips and include the components necessary for a healthy mind, body and spirit connection.
Flexibility training involves the careful stretching of the muscles, tendons and joints to improve the range of motion in order to safely perform daily activities and sports without injuring or tearing soft tissues. It is probably the most neglected part of the fitness program. However, while the amount of inherent flexibility varies for each person, a minimal range is necessary as it relates to daily activities and sports. For example, as you age it is important to have enough flexibility in your back, hips and knees to wash your feet, put shoes and socks on. Flexibility exercises should always be performed after a warm –up activity and done slowly and gently.
There are two types of flexibility exercises; dynamic and static. Dynamic stretching is performed with movement such as pushing the ankle up and down like a gas pedal. Passive stretching is performed using an outside force such as using a towel to pull the ankle up in order to stretch the calf. Dynamic should be performed before an activity (before running or playing tennis) and static performed after the activity is over in order to increase range of motion for future activities.
In conclusion, it is easy for fitness enthusiasts to get so focused on maintaining a routine that they allow their program to become stale and ineffective. It is essential to reassess and update your program to prevent stagnation.
Make sure the routine has all three fundamental components of a well-balanced exercise program; cardiovascular, strength and flexibility training. Moreover, to be truly healthy, one must work toward a “Healthy Mind, Body, and Spirit. Therefore, in addition to traditional exercise one must incorporate the following: nutrition; meditation, relaxation techniques, yoga, core fitness; functional/sports specific training; leisure sports and activities
In order to prevent an exercise program from getting stale, one must incorporate all aspects of wellness…a healthy mind, body and spirit!
While each component offers its own specific benefit, the combination of all three cooperatively provides unique value. Too often, fitness enthusiasts concentrate on the exercises they LIKE or are good at more than the ones they NEED.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles our Health Care Forum
People will often ask me, "Is there such a thing as an exercise rut?" They want to know why they do not seem, to be improving with their exercise program?... they exercise 3-4 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes and they feel frustrated and STUCK in a rut. While initially responding favorably to exercise, after 6 -9 months or more, they do not notice progress in weight loss, strength, tone, endurance or daily function.
Here are a few suggestions on how to improve or get more out of a “stale” exercise program.
Step one is to build an exercise program that is grounded in the basics. Next, Step two, which begins after the basics have been mastered, includes the components necessary for a healthy mind, body and spirit connection and translates into functional activities of daily living including work and leisure sports.
Make sure your routine has all three fundamental components of a well-balanced exercise program:
While each component offers its own specific benefit, the combination of all three cooperatively provides unique value. Too often, fitness enthusiasts concentrate on the exercises they LIKE or are good at more than the ones they NEED. A well-balanced program includes what you like and need!
In fact, recent studies show that those performing all three components surpassed those performing one or any combination of two of the training types when tested for efficient:
Cardiovascular exercise is any activity that raises your heart rate and respiratory rate. This type of exercise strengthens the heart muscle and the muscles that assist in breathing. When these muscles are stronger, they in turn work more efficiently to deliver oxygen to your muscles and other parts of the body. Ultimately, these oxygenated muscles can work harder and longer to burn fat during exercise and at rest.
*Most experts recommend at least 30 minutes of sustained cardio, 3-4 days per week. However, recent studies support the notion of performing 10-15 minutes, twice daily, 4 days per week. For those “stuck” in a fitness rut, to advance your program, cardio should be performed 5-6 days per week for 45-60 minutes.
Strength training is an activity that provides any type of resistance to muscle contraction to build strength in the muscle. The resistance can be without movement against an immovable object such as pushing against a wall (isometric) or with movement such as lifting up or lowering a weight down against gravity (isotonic/dynamic). There are two types of isotonic muscle contraction; concentric, which involves raising the weight against gravity as the muscle shortens and eccentric which involves lowering a weight against gravity as the muscle lengthens.
A standing biceps curl is an example that incorporates both concentric and eccentric contractions. A progressive strength training program includes all three types of muscle contraction. By using the classic bicep muscle curl these photos will demonstrate all three types of muscle contraction:
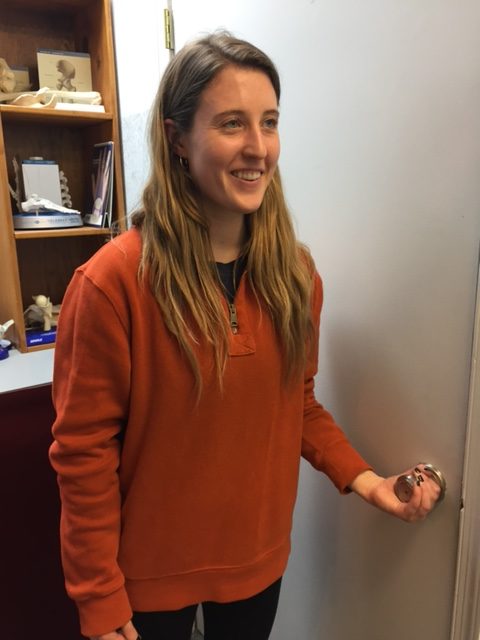
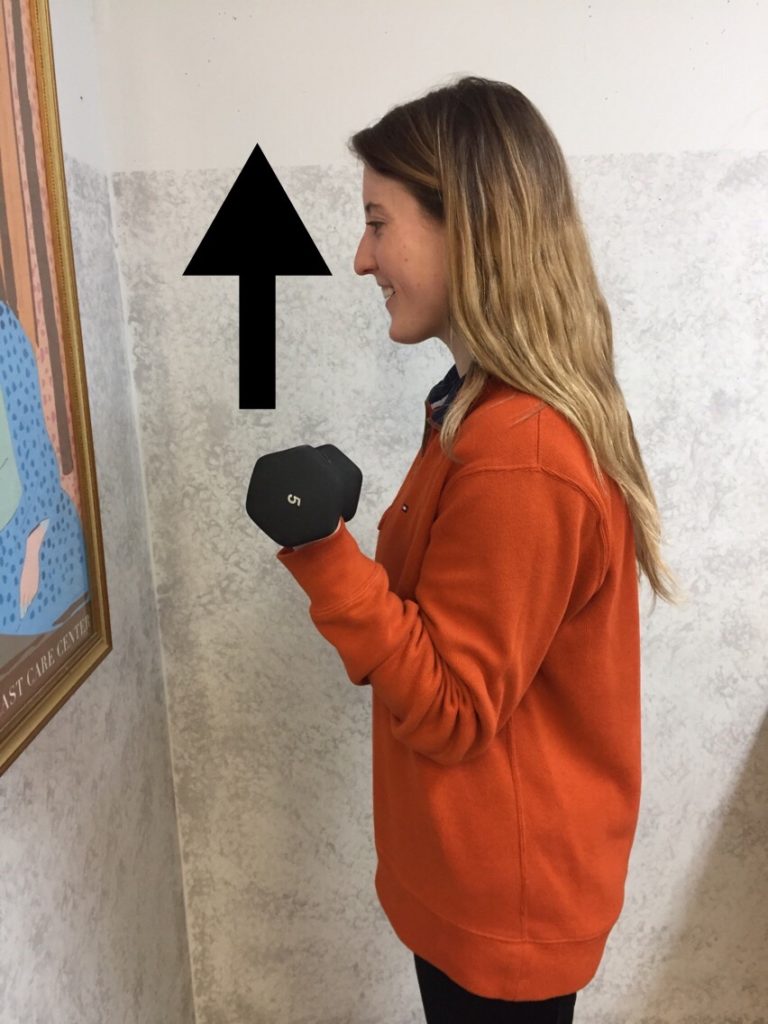


Sources: National Institutes of Health; American Council on Exercise
Model: Heather Holzman

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” Next Week: Read Stuck in an Exercise Rut…Part II of II!
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles visit: Mackarey's Health and Exercise Forum!
Tomorrow is Valentine’s Day! And, while you may wonder what that has to do with health and wellness, you might be surprised to learn that love can be good for your health! Studies show that it is in our DNA to seek out good relationships and that these solid relationships can lead to a happier, safer and healthier life. Conversely, infatuation and less committed, volatile relationships that are “on and off,” are very stressful and unhealthy. But those fortunate to participate in a stable and satisfying long-term relationship are the beneficiaries of many health benefits! Whether you have spouse, partner, or close friend, (love is love is love), feeling connected, respected, valued, and loved is critically important to your health and wellness!
The US Department of Human Services found that couples in a committed long-term relationship are less likely to require sick visits to their physician. And, when hospitalized, these “love birds,” have shorter hospital stays. One theory for this health benefit is that couples in good relationships watch after each other to ensure regular healthy visits for routine care and testing. Consequently, they are less likely to have unexpected serious illnesses.
Experts feel that social isolation is associated with unhealthy behavior and depression. Happy, loving and committed couples are far less likely to suffer from depression. Furthermore, these couples are less likely to engage in risky and unhealthy behaviors such as excessive drinking and drug abuse.
Researchers have found a strong relationship between marital status and blood pressure. Happily married couples have the lowest, while unhappily married couples have the highest. Happy singles scored somewhere in between. It is also interesting to note that non married committed couples and well-adjusted singles with strong support groups had lower blood pressure.
Studies show that long-term committed couples have far less anxiety than new romance. MRI brain scans found both groups showed high activation in areas of the brain related to romance, but only new couples had activation of the area of the brain associated with anxiety.
A CDC report on pain included a study of more than 127,000 adults and found that married people were less likely to complain of headaches and lower back pain. In fact, one study showed, when a happily married couple held hands, pain thresholds improved and, the happier the marriage, the greater the effect
Similar to the findings on pain, there is a strong link between happy and committed couples and stress management. The support and love from a strong and healthy relationship provides good coping methods to help overcome adversity…job loss, illness etc.
Solid loving relationships can boost your immune system. In fact, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University found that people who exhibit positive emotions are less likely to get sick after exposure to cold or flu viruses.
It may be that a wound from “Cupid’s Arrow” will heal faster when you are in a loving relationship. Researchers at Ohio State University Medical Center gave married couples superficial wounds and followed their healing time. The wounds healed nearly twice as fast in spouses who interacted warmly compared with those who behaved with hostility.
Strong research indicates that married people live longer. Researchers found that people who had never been married were 58% more likely to die than married people. Some reasons purported were mutual financial, emotional and physical support and assistance from children. One common denominator for a short life span is loneliness and those in a healthy relationship may live longer because they feel loved and connected.
A study in the Journal of Family Psychology showed that happiness depends more on the quality of family relationships than on the level of income. So, according to the research, when it comes to a long, happy and healthy life…love is more important than money!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles visit our "Health and Exercise Forum"
We are more than one month into the New Year and many people are still talking about their health and fitness goals. As you probably know, losing weight and getting fit are the most popular resolutions, however, for many who have not maintained an active lifestyle in years, it is challenging to know where to begin. Moreover, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program to aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, that our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
“There’s no question that increasing exercise, even moderately, reduces the risks of many diseases, including coronary heart disease, breast and colon cancer, and Type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Jennifer Joyce, MD, professor of family medicine at GCSOM. “Research has even shown that you could gain two hours of life for each hour that you exercise regularly.”
According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
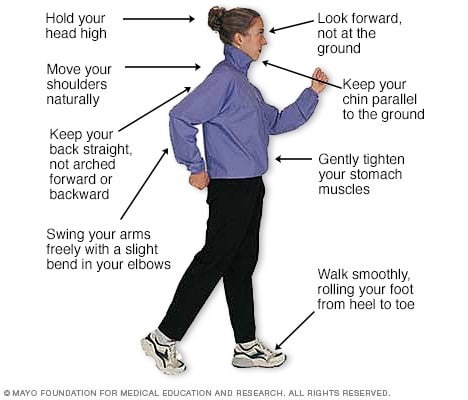
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic
* Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles: Visit our Healthcare Forum!
There is a very good chance that the cold temps and snow will return soon! Winter in NEPA can be the perfect opportunity to try something new. For example, for those who enjoy running or walking you can continue to do so in the winter, with a few adjustments. Equipment, such as treaded sneakers, allows you to run or walk in the snow. Snow shoes are a great way to hike and walk in the snow while cross country skiing simulates running in the snow. But, in the last few years, another outdoor activity has become a winter sport; mountain biking in the snow has become popular.
Many mountain biking enthusiasts in NEPA enjoy 7-8 months of trail riding at our beautiful state parks. Now, with a few modifications, mountain bikers can continue year round. In fact, the adventure in the snow may be an exciting new experience. If winter biking is not your thing, maybe winter walking, running, snow shoeing or cross-country skiing will suit you better.
The physical and psychological benefits of outdoor activities are many: each season brings its own unique beauty, and winter is no different. Most will not have to abandon outdoor activities, but some adjustments in equipment, clothing, and food are necessary for each season and the temperature changes that it brings.
While recommended, it is not necessary to purchase a bike specifically for mountain biking in the snow. With a few simple modifications and adjustments, you can prepare a regular mountain bike for winter use.
In addition to rocks and stumps, winter biking offers the challenges of snow banks and ice chunks. The air pressure in your shock system will be affected by temperature. Additional air pressure will be required to improve shock absorption and in extreme cases, using less viscous oil will be required.
Pressure - lower the air pressure in the tires 5-10 psi lower than normally used in the summer to improve traction.
Treads – Just as with winter car tires, a larger tire with more volume and large, widely space knobs will improve traction. Some special winter tires offer studs for improved performance on the ice.
Disc Brakes – that are self-cleaning and mounted away from the snow are best for winter biking. However, brakes should be examined and cleaned intermittently for snow and ice accumulation.
Platform Pedals – allow the rider to quickly plant the foot for balance when sliding.
It is important to layer clothing. Use DryTech or UnderArmor type materials (headgear, gloves, shirts and pants) to allow sweat to breath away from the skin to the next layer of clothing. Use a facemask to cover your mouth and nose to prevent frost bite and warm air before it enters the lungs. Chemical hand and toe warmers are great. Try winter running or walking shoes as described below.
There are running shoes specifically designed for use in wet, cold and sloppy winter conditions. These “winterized” running shoes, which can also be used for walking, offer waterproofing, sealed seams, gaiter collars to keep out snow and slop, slip resistant fabric, anti-roll stability features, anti-microbal material and aggressive tread patterns for traction on slippery surfaces. Some shoe recommendations for both winter walkers and runners include:
. Some shoe recommendations for winter runners and walkers from The Runner’s World Magazine include:
For winter walkers, walking or trekking poles will improve balance and safety when briskly walking in winter conditions. I am a strong proponent of using these tools. They are lightweight, adjustable, and collapsible. Some examples are: Black DiamondR Trail Explorer 3 Trekking Poles - $59.99 andMountainsmithR FX Lite Trekking Poles - $35.09. For an inexpensive alternative, an old pair of ski poles will work just fine.
These activities should also be considered as a viable option for the winter walker and runner. These are great cross-training alternatives with tremendous aerobic benefits.
Snowshoes work by distributing your weight over a larger surface area so your foot does not sink completely into the snow. Commonly used by fur traders, trappers and forest rangers, snow shoeing has become very popular among many outdoor exercise enthusiasts. It is relatively safe and inexpensive. Some snowshoes include the Tubbs Flex TRK - $169. (REI) and Redfeather Hike - $149.00 (Cabelas).Boots and poles are also required, but ski or trekking poles along with hiking boots or winter running shoes can be used.
Cross country skiing has also gained tremendous popularity among winter outdoor exercise enthusiasts. It is a cross between running and skiing in which the participant propels through a snow-covered trail by pushing and gliding with a running or fast-walking motion. Some examples of equipment packages that include boots, pole, bindings and skis are Alpina Sports Tour – no wax for $229.00 and Rossignol XT from LL Bean at $224.00.
Many of the area’s state parks, such as Lackawanna and Promised Land, offer wonderful trails for winter walking, hiking, running, snow shoeing, cross-country skiing and biking.
For the more casual walker in need of protection from the snow and ice, it may be treacherous just to walk the dog or go to the bank, post-office or grocery store. Consider traction devices that easily slip on and off your shoes or boots such as StabilicersR (cleats-type device) or YaktraxR (chain-type device).
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum” every Monday.
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles: visit our healthcare forum