As most sports enthusiasts know, Aaron Rodgers, former Green Bay Packer quarterback and recent New York Jets QB (for just over a minute and half) suffered a season ending injury when he tore his Achilles tendon in the first game of the 2023/24 NFL season. Since then, I have been answering many questions from many about the nature of the injury and how to prevent it.
As the days continue to get shorter and temperatures begin a slow steady decline, athletes and exercise enthusiasts will work harder to “fit in” a warm-up before running or other activities during the winter months. But, no matter how limited time is, skipping the warm-up is risky. This time of year, one can expect to feel a little cold and stiff, especially if you are over 40, and therefore a little caution and preparation are in order to avoid muscle/tendon strain, or worse yet, muscle/tendon tears. The more commonly torn tendon is the Achilles tendon . Prevention of muscle tears, including the Achilles tendon includes; gradual introduction to new activities, good overall conditioning, sport specific training, pre-stretch warm-up, stretch, strengthening, proper shoes, clothing, and equipment for the sport and conditions.
A muscle contracts to move bones and joints in the body. The tendon is the fibrous tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Great force is transmitted across a tendon which, in the lower body, can be more than 5 times your body weight. Often, a tendon can become inflamed, irritated, strained or partially torn from improper mechanics or overuse. Although infrequent, occasionally tendons can also snap or rupture. A tendon is more vulnerable to a rupture for several reasons such as a history of repeated injections of steroids into a tendon and use of medications such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics. Certain diseases such as gout, arthritis, diabetes or hyperparathyroidism can contribute to tendon tears. Also, age, obesity and gender are significant risk factors as middle-aged, overweight males are more susceptible to tendon tears. Poor conditioning, improper warm-up and cold temperatures may also contribute to the problem.
Tendon rupture is very painful and debilitating and must not be left untreated. While conservative management is preferred, surgical management is usually required for complete tears. The purpose of this column is to present the signs, symptoms and management of Achilles tendon ruptures.
The Achilles tendon (also called the calcaneal tendon), is a large, strong cordlike band of fibrous tissue in the back of the ankle. The tendon (also called the heel cord) connects the powerful calf muscle to the heel bone (also called the calcaneus). When the calf muscle contracts, (as when you walk on the ball of your foot), the Achilles tendon is tightened, tension is created at the heel and the foot points down like pushing a gas pedal or walking on tip of your toes. This motion is essential for activities such as walking, running, and jumping. A partial tear of the tendon would make these activities weak and painful, while a full tear through the tendon would render these activities impossible.
With age, the Achilles tendon (and other tendons) gets weak, thin, and dehydrated, thus making it prone to inflammation, degeneration, partial tear or rupture. The middle-aged weekend warrior is at greatest risk. A full or complete tear (Achilles tendon rupture) usually occurs about 2 inches above the heel bone and is associated with a sudden burst of activity followed by a quick stop or a quick start or change in direction, as in tennis, racquet ball, and basketball.
In some instances, the tendon can be injured by a violent contraction of calf when you push off forcefully at the same time the knee is locked straight as in a sudden sprint. Other times, the tendon is injured when a sudden and unexpected force occurs as in a trip off a curb or sudden step into a hole or a quick attempt to break a fall.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog Next Week: Achilles tendon Part II of II.
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), 11.3% of the population in the United States or almost 37.3 million adults and children has diabetes. Unfortunately, the number keeps rising and one-third of these people are not aware that they have the disease. It will be the purpose of this column to raise the level of consciousness through education and offer recommendations for lowering blood sugar levels naturally.
Perhaps no goal is more important to a person with diabetes than maintaining a healthy blood sugar level. When managed over time, healthy blood sugar levels can slow the onset of complications associated with the disease. According to the ADA, pre-diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance, occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal (110 to 125mg/dl) but below type 2 diabetes levels (126mg/dl). 54 million Americans have pre-diabetes in addition to the 20.8 million with diabetes.
While medications are effective in maintaining blood sugar levels, for those who are borderline, there are effective ways to lower your blood sugar naturally. Your physician will determine which treatment is most appropriate for your problem. Also, maintaining your ideal body weight is always important.
SOURCES: The American Diabetes Association (ADA), CDC, NIH, and Lifescript
Visit your doctor reguLlarly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Studies have shown a recent escalation of joint replacements in a much younger and more active group than previously noted…the baby boomer! While the end result is mostly physical, the cause is often psychological. We all know the personality type: type A, hyperactive, goal-oriented, driven, possessed and highly organized – almost at all costs! Many of you have seen fitness enthusiasts running through the streets at 5:30 AM for 5-10-15 miles each day. Moreover, many of these runners have more activities planned later in the day: golf, tennis, ski, swim, play sports with their kids. Well, after 20 years of this behavior, many of these enthusiasts are now suffering the effects of long term multiple micro traumas. They are suffering from what orthopedic surgeons at the University of Pennsylvania call “Boomeritis! Boomeritis is inflammation of the baby boomer from overuse. Lower back pain, hip, groin, and knee pain is almost a daily event.
As baby boomers continue to enjoy sports with the same vigor and intensity as when they were younger, they are finding that their older bodies just can’t keep up. While these individuals often succeed in finding the balance of fitness and craziness, they have had times when they took it too far. Furthermore, nearly all compulsive exercisers suffer from over training syndrome. When take too far compulsive behavior is rationalized by insisting that if they didn’t work to extreme then their performance would suffer.
*Each sign is worth 1 point:
If you have two or more of the warning sings, consult your family physician to rule out potentially serious problems.
Avoid weight bearing exercises two days in a row. Run one day, walk, swim or bike the next.
Use the elliptical instead of the treadmill.
Avoid squatting…deep squatting is bad for your hips and knees. Even when gardening, use a kneeling pad instead of bending down and squatting.
Visit your family doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Fall is here, cross-country running season has begun and the 26th Steamtown Marathon is only a few weeks away! With that in mind, running injuries, some very specific to women, are on the increase…
While driving to or from work have you noticed more local running enthusiasts in the past few years? Moreover, have your noticed that most of the runners are women? Scranton Running Company has contributed to NEPA’s participation in a national trend; more women are engaged in running than men! Female runners account for 9.7 million runners (57%) while 7 million males run on a national level.
With this surge, the female runner has been subjected to a host of related injuries, including shin splints, which often lead to stress fractures. New research has found that stress fractures may be related to the loss of weight and body mass associated with the sport.
A recent study from Ohio State University found that female runners with a Body Mass Index (BMI) below 19 may have a higher risk of developing stress fractures than women with a BMI of 19 or above. Furthermore, the study also found that these women took longer to recover from these injuries.
According to Timothy Miller, MD, “When body mass index is very low and muscle mass is depleted, there is nowhere for the shock of running to be absorbed other than directly into the bones. Until some muscle mass is developed and BMI is optimized, runners remain at increased risk of developing a stress fracture,”
The study also found that female runners with a BMI of 19 or higher with severe stress fractures required 13 weeks to recover from their injuries and return to running. Runners with a BMI lower than 19, however, took more than 17 weeks to recover.
They concluded that women should know their BMI and consult with a medical professional to maintain a healthy number. Additionally, women should cross-train and include resistance training to improve the strength and muscle mass of the lower extremities to prevent injury.
The current BMI wisdom, according to the National Institutes of Health, is 19.8 for men and 24 for women, however, strong and competitive women tend to have a BMI of 26. A BMI of 18 is considered malnourished.
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight of adult men and women over 20 years of age, according to the National Institutes of Health.
BMI = (weight in pounds / height in inches squared) X 703)
Example 1: a person who weighs150 pounds and is 68 inches (5 feet 8 inches) tall has a BMI of 22.8
Example 2: a person who weighs 110 pounds and is 66 inches (5 feet 5 inches) tall has a BMI of 17.7
Underweight < 18.5%
Normal weight 18.5 to 24.9%
Overweight 25 to 29.9%
Obesity 30 and over
A stress fracture is fatigue damage to bone with partial or complete disruption of the cortex of the bone from repetitive loading. While standard x-rays may not reveal the problem, a bone scan, and MRI will. It usually occurs in the long bones of the leg, mostly the tibia (shin bone) but also the femur (thigh) and foot. Occasionally, it occurs in the arm.
FEMALE RUNNERS WITH BMI LOWER THAN 19 – is a primary risk factor.
10-21% of all competitive athletes are at risk for stress fractures. Track, cross country and military recruits are at greatest risk. Females are twice as likely as males to have a stress fracture. Other athletes at risk are: sprinters, soccer and basketball players, jumpers, ballet dancers are at risk in the leg and foot. Gymnasts are also vulnerable in the spine while rowers, baseball pitchers, golfers and tennis players can experience the fracture with much less frequency in the ribs & arm.
The problem is much more prevalent in weight bearing repetitive, loading sports in which leanness is emphasized (ballet, cheerleading) or provides an advantage (distance running, gymnastics).
Stress fractures usually begin with a manageable, poorly localized pain with or immediately after activity such as a shin splint. Over time, pain becomes more localized and tender during activity and then progresses to pain with daily activity and at rest.
Source: Ohio State University, Science Daily
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy!
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Paul's Articles, visit our exercise forum!
Fall in NEPA is one of my favorite times of year. For outdoor enthusiasts, there is nothing more refreshing than activities in the bright sunshine and crisp, clean air. The hot humid summer weather can be a deterrent to outdoor activities and this time of year provides an opportunity to get fit by beginning a walking program. For many who have not maintained an active lifestyle or have health issues, it is challenging to know where to begin. Moreover, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program too aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, that our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
“There’s no question that increasing exercise, even moderately, reduces the risks of many diseases, including coronary heart disease, breast and colon cancer, and Type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Jennifer Joyce, MD, professor of family medicine at GCSOM. “Research has even shown that you could gain two hours of life for each hour that you exercise regularly.” According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
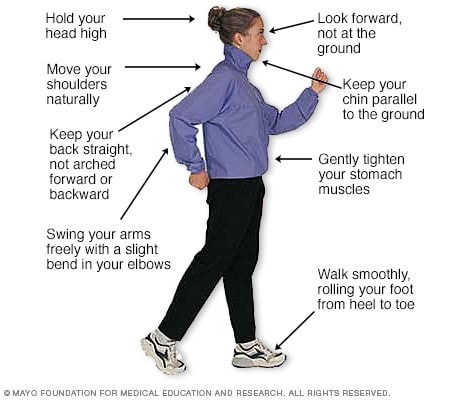
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic

NEXT MONDAY BLOG and in print in THE SUNDAY TIMES TRIBUNE – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Paul Mackarey's articles, check out our exercise forum!
Can you believe that the 4th of July holiday was more than one month ago? Do not despair! There is still plenty of time to be outdoors in NEPA and experience so many activities such as: biking, hiking, running, walking, swimming, boating, golfing, and playing tennis to name a few. Late summer and early fall tend to be beautiful and is also a wonderful opportunity to discover your inner child, mix it up and try something new! Below are some new and exciting ways to stay active and have fun in the sun:
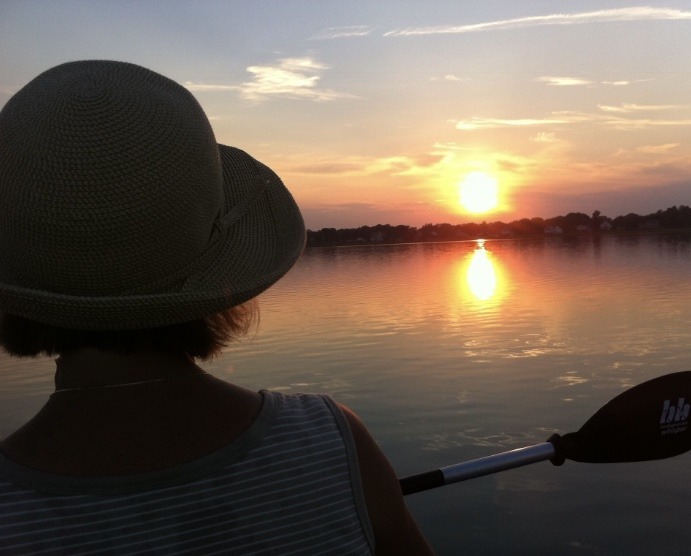

Spending time on any of the beautiful lakes in NEPA is time well spent. From an exercise standpoint, rowing, canoeing and kayaking offer a very special experience. Most kayaks are light weight, easy to use and maneuverable on a lake. Sitting low on the water offers a unique perspective as you feel yourself gliding across the lake. The Countryside Conservancy, in partnership with Lackawanna State Park, sponsors moonlight kayak events on the lake at the park. With a bright full moon, you can begin at 8 pm and return at 10 pm. Bring bug spray and headlights to enjoy the sunset and moon rise on the lake. You will feel like a kid breaking the rules of the park by being on the water after dark!
NOTE: Try kayaking in the daytime first and then advance to sunset trips before staying on the water for the moonlight. Rentals are available at the park.
Website: www.countrysideconservancy.org; www.dcnr.state.pa.us/stateparks.org
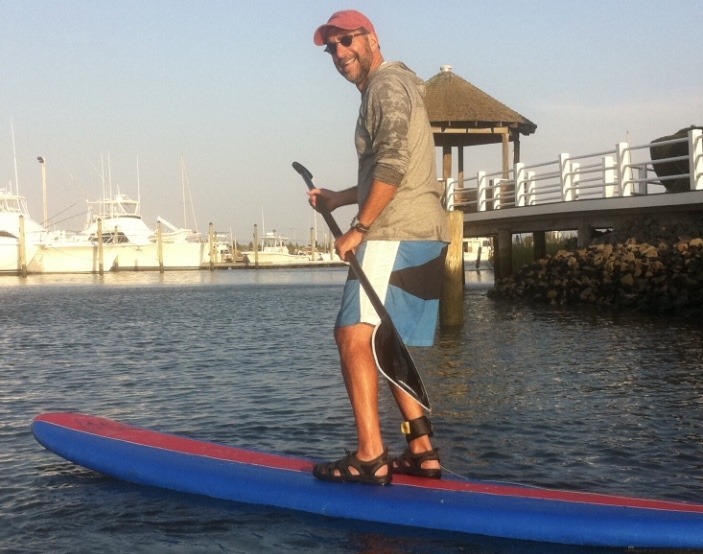

Stand up paddle boarding (SUP) is becoming a fast-growing sport among water enthusiasts. It is a fun way to exercise your core, improve balance, and tone your upper body. It requires minimal equipment; a board that is essentially a long and wide surfboard and a long paddle to use while standing on the board. It can be done in the ocean surf, bay, lakes, or rivers; however, beginners would be wise to stay in calm water. Rentals are available at most beaches.
Check out the video for more information: REI paddleboard basics
What is it? Imagine a standup paddle board with a handlebar and pedals like a exercise stepper machine. Instead of using a paddle, you step up and down on the pedals and fins under the board propel you through the water. Check it out…Hobie Mirage Eclipse Stand Up Peddle Board; Dick’s Sporting Goods
Zumba is a very popular form of dance aerobics spiced up with Latin music. When adding water and sun to this already cool activity, you are assured to have fun while exercising. As with any aquatic exercise, the added resistance from the water gives arm rows and leg kicks more challenge. Female participants report an additional benefit; they are uninhibited to “shake that thing” to the music under the cover of the water. So, beat the heat, let loose and get some fun in the sun while you exercise.
NOTE: Consider trying regular Zumba first to get the hang of it. Amy Sekol is a local certified Zumba instructor and also offers Aqua Zumba. (amys.zumba.com)
Website: www.zumba.com
I love this idea…why didn’t I think of it first! In the gym I enjoy the elliptical machine because it simulates running without the impact on my joints but of course, I would rather be outdoors. Well, this is the answer to my prayers…an elliptical machine that is attached to a bike with handle bars and brakes included. I think it will probably be difficult on steep hills but it is something I MUST TRY!
Website: www.elliptigo.com; www.mywingflyer.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's Articles, check out our exercise forum!
According to the National Institutes of Health, an estimated 19.1% of U.S. adults 18 and older had an anxiety disorder in the past year. Anxiety disorders were higher for females (23.4%) than for males (14.3%). An estimated 31.1% of U.S. adults experience an anxiety disorder at some time in their lives.
There are a wide variety of anxiety disorders and will vary by the objects or situations that induce them. However, the features of excessive anxiety and related behavioral disturbances are similar. Anxiety disorders can interfere with daily activities such as job performance, school work, and relationships. Symptoms include: distress, nausea, shortness of breath, bowel pattern changes, excessive perspiration, frequent laughing or crying, restlessness, and is often associated with depression. While there are many types and degrees of anxiety and there is no substitute for medical and psychological care, there are some simple and basic tools to help manage the problem…daily exercise is one easy, affordable and accessible suggestion for most. Multiple studies have discussed the incidence of unhealthy self management of anxiety, including the use of alcohol and recreational drugs.
Last week, I presented coping tips for the management of anxiety. In this column, I will discuss one of the most understated benefits of exercise – mental health! Specifically, aerobic exercise (exercise that increases your heart rate for 30 minutes or more) such as walking, biking, running, swimming, hiking, elliptical & stepper machines to name a few, is the secret to “runner’s high.” This exercise euphoria is not limited to runners alone, but all who engage in aerobic exercise are more likely to experience high energy, positive attitude and mental wellness.
Physical activity, specifically aerobic exercise, is a scientifically proven useful tool for preventing and easing anxiety and depression symptoms. Studies in the British Journal of Medicine and the Journal of Exercise and Sports Science found that anxiety and depression scores were significantly reduced in groups that engaged in aerobic running, jogging or walking programs, 30-45 minutes 3-5 days per week for 10-12 weeks, when compared to a control group and a psychotherapy counseling group.
According to research reported in sports medicine journals, exercise reduces anxiety and depression in two ways, psychologically (mentally) and physiological (physically).
Psychological or Mental Benefits of Exercise on Anxiety and Depression:
Physiological or Physical Benefits of Exercise on Anxiety and Depression:
Work hard to recognize and overcome these symptoms to begin an exercise program. An aerobic exercise routine should eventually lessen these symptoms.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
SOURCES: University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC); National Institutes of Health (NIH); The American Journal of Sports Medicine

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Paul's articles, check out our exercise forum!
According to the National Institutes of Health, an estimated 19.1% of U.S. adults 18 and older had an anxiety disorder in the past year. Anxiety disorders were higher for females (23.4%) than for males (14.3%). An estimated 31.1% of U.S. adults experience an anxiety disorder at some time in their lives.
There are a wide variety of anxiety disorders and will vary by the objects or situations that induce them. However, the features of excessive anxiety and related behavioral disturbances are similar. Anxiety disorders can interfere with daily activities such as job performance, school work, and relationships. Symptoms include: distress, nausea, shortness of breath, bowel pattern changes, excessive perspiration, frequent laughing or crying, restlessness, and is often associated with depression. While there are many types and degrees of anxiety and there is no substitute for medical and psychological care, there are some simple and basic tools to help manage the problem…daily exercise is one easy, affordable and accessible suggestion for most.
Multiple studies have discussed the incidence of unhealthy self management of anxiety, including the use of alcohol and recreational drugs. The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) recommends the following healthy tips for coping with anxiety:
1. Get Enough Sleep
Adequate sleep is critical for mental health. Unfortunately, anxiety can lead to sleeping problems and, according to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) inadequate sleep can worsen anxiety.
Seven to nine hours of sleep each night is recommended for most adults. The National Sleep Foundation recommends maintaining a regular schedule that includes going to bed at the same time each night and waking up at the same time each morning.
2. Practice Mindfulness Meditation
Incorporating meditation into your life can help you cope with anxiety, according to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health.
Research shows mindfulness meditation programs are effective in reducing anxiety and depression. UPMC offers a Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction Course and a Beginners Guide to Meditation that have been proven to be very effective. Another option for reduction of anxiety and stress is Progressive Muscle Relaxation. This mind-body technique can be found in 5, 10, 15 or 20 minute videos.
3. Spend Time in Nature
How you deal with anxiety should include a walk in the forest or even a tree-lined park. In NEPA we are very fortunate to have access to beautiful walking and biking trails and state parks. Make time to enjoy them.
Research shows that “forest bathing,” long, slow walks in nature for health purposes, can lower blood pressure and relieve anxiety. A review of clinical trials published in the International Journal of Biometeorology found that salivary cortisol levels, biomarkers for stress, were significantly lower in groups who participated in forest bathing versus the control group.
4. Take up Yoga or Tai Chi
Yoga does more than increase your flexibility. It incorporates exercise, deep breathing, and meditation. Yoga is an all-in-one anti-anxiety activity, as shown in a review of body-centered interventions published in Frontiers in Psychology. Tai chi, a mix of meditation and martial arts, works much the same way.
5. Dance Therapy
That same research found that dance therapy, also known as movement therapy, reduces anxiety by engaging the body’s nervous system, which regulates how the body reacts to stress. In addition, dance/movement therapy increases production of serotonin, a chemical produced by the cells that’s responsible for mood.
6. Breathe Through It
When you begin to feel anxiety or a panic attack with symptoms such as: sweating, trembling, dizziness, rapid heartbeat and nausea, start to come on, “take a deep breath.” Research shows that slow deep breaths can calm you down and lower your heart rate while quick, shallow breaths can induce or worsen anxiety.
One breathing technique shown to reduce anxiety is diaphragmatic breathing. Using your diaphragm for deep breathing requires you to fill your lungs to capacity.
Breathe in slowly through your nose so that your stomach rises. Then, tighten the stomach muscles and exhale slowly through pursed lips. Repeat several times.
7. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Too much caffeine restricts blood vessels, which can increase blood pressure and contribute to anxiety. Coping with anxiety also doesn’t mean masking it with alcohol. Studies show that there is a complex relationship between alcohol and anxiety. While some may use alcohol and recreational drugs to mask the symptoms of anxiety (often leading to substance abuse disorder), some studies show that alcohol can interfere with the neurotransmitters that manage anxiety and prevent you from getting a good night’s sleep. Drinking to cope creates a sort of feedback loop, which makes the anxiety worse and can lead to alcohol dependence.
8. Check Your Medicine
Certain medicines, such as corticosteroids, asthma drugs, and others, can cause anxiety. Ask your doctor if any medicines you take may be a contributing factor.
9. Eat Healthy Foods
Keeping the body nourished is essential for all functions of life. New research shows that a healthy diet may affect more than just weight and energy levels. One example is a Mediterranean Diet, with lots of vegetables, fruits, beans, lentils, nuts, whole grains, extra virgin olive oil and a moderate amount of fish (especially those rich in omega-3 fatty acids), with limited use of red meat.
10. Keep a Journal
Keeping a journal can be a great way to keep track of your progress with anxiety and how your body responds to such situations. Tracing the triggers of anxiety can help you develop the skills to properly respond when put in anxious conditions.
11. Exercise Regularly
Exercise promotes the release of endorphins. These brain chemicals reduce the body’s reaction to pain and stress. They also produce a feeling of euphoria, or happiness, that’s comparable to morphine. Just five minutes of aerobic exercise can kick start these anti-anxiety effects, according to some studies. Next week in “Health & Exercise Forum” specific details about exercise for anxiety will be presented.
Talk to a Mental Health Professional
Chronic anxiety also can point to an underlying mental health issue. When your anxiety causes extreme distress or interrupts your ability to function on a daily basis, or when panic attacks are frequent and debilitating, it’s important to talk to your physician and ask for a referral to a mental health professional. They can provide a treatment plan, which may include specialized anti-anxiety medicine, psychotherapy, or both.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
SOURCES: University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC); National Institutes of Health (NIH);

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” Next week: Coping with Anxiety Part II This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Paul's articles, check out our exercise forum!
“The woods are lovely, dark, and deep,
But I have promises to keep,
And miles to go before I sleep,
And miles to go before I sleep.” Robert Frost
The purpose of this column is to present an alternative to traditional running that will allow training on more interesting and less stressful surfaces such as those used when hiking, mountain biking and horse riding trails in the beautiful woods of Northeast Pennsylvania…”trail running!”
I remember my trail running days with fondness. One day, when the temperatures soared above 90 and my wife pleaded with me to avoid running in the heat (she was wise), as a typical runner, I needed hit the road. As I set out on State Road 348 just on the periphery of Lackawanna State Park in Dalton, the sun was beating down on me. I happened to see a sign that read, “Orchard Trail, Bull Hill Trail, Tree Line Trail.” I thought it might be a good idea to find some shade and decided to run on this path normally used for hiking, mountain biking and horseback riding. It turned out to be a great decision. While I was forced to run 25% slower due to the uneven terrain (rocks, tree roots, stumps), I was able to practice “light running” techniques by running with short strides on the balls of my feet. I felt much more refreshed as I avoided the direct sunlight under the cover of the trees.
Furthermore, I enjoyed the up close view of nature as I ran by cool streams and wet mossy rocks. I saw beautiful flowers, rhododendron, and mountain laurel. I observed deer, chipmunks and birds. In my quest to avoid the hot sun, I discovered the beautiful underworld of “trail running” – a growing trend in today’s running community. If you, like me, enjoyed pounding the pavement for many years, trail running can help you rediscover why you love to run. It is beautiful, peaceful, natural and unique. It is fun to get in touch with your inner child as you run in the woods and get muddy. Trail running makes running fun…and it’s good for your joints!
The trail running community purports that trail running is popular because it satisfies a primal need for man to move through nature, derived from hunter/gatherer days. Others who promote trail running feel the popularity is due to the many advantages it offers. One, trail running prevents impact injuries due to soft surfaces. Two, the training style of running with shorter strides on the ball of the foot, lessens impact. Three, this type of running will develop stronger ankles and trunk core muscles while improving balance, coordination and proprioception from running on uneven surfaces. Lastly, the ability to release copious amounts of endorphins while breathing fresh air instead of roadside fumes is invaluable.
Sources: American Trail Running Association, Trailspace.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Paul's articles. check out our exercise forum!
Since 1949 May has been designated as National Mental Health Month for the purpose of eliminating the stigma associated with mental illness by raising awareness. One of the most common mental health conditions is depression. New research from Boston University School of Public Health has found that depression has been increasing in the United States and life with COVID for more than two years has accelerated it rapidly. In 2021 the number of people suffering from depression increased more than 32 percent, affecting 1 in every 3 American adults. However, research also has good news to offer: one of the most understated benefits of exercise is mental health! Specifically, aerobic exercise (exercise that increases your heart rate for 30 minutes or more) such as walking, biking, running, swimming, hiking, elliptical & stepper machines to name a few, is the secret to “runner’s high.” This exercise euphoria is not limited to runners alone, but all who engage in aerobic exercise are more likely to experience high energy, positive attitude, and mental wellness.
Physical activity, specifically aerobic exercise, is a scientifically proven useful tool for preventing and easing depression symptoms. Studies in the British Journal of Medicine and the Journal of Exercise and Sports Science found that depression scores were significantly reduced in groups that engaged in aerobic running, jogging or walking programs, 30-45 minutes 3-5 days per week for 10-12 weeks when compared to a control group and a psychotherapy counseling group.
Depression is the most common mental disorder and is twice as common among women as in men. Symptoms include: fatigue, sleeplessness, decreased appetite, decreased sexual interest, weight change, and constipation. Many of these symptoms are likely to bring an individual to their family physician.
According to research, exercise reduces depression in two ways, psychologically (mentally) and physiological (physically).
Psychological or Mental Benefits of Exercise on Depression:
Physiological or Physical Benefits of Exercise on Depression:

NEXT MONDAY - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey’s "Health & Exercise Forum"!
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's Articles, check out our Health and Exercise Forum!