Fall has arrived in NEPA and walking is a great way to enjoy the fall foliage. Moreover, a new study has found that walking can reduce lower back pain. Researchers in Australia followed more than 700 adults who had a recent onset of lower back pain (and were able to bear full weight without associated leg symptoms) and enrolled them in a walking program under the supervision of a physical therapist. One group walked for 30 minutes, 3-5 times per week and the control group remained inactive. Both groups were followed for more than three years and discovered that the inactive control group was twice as likely to suffer from repeated flare-ups of lower back pain when compared to the walking group.
It is good news for those who enjoy walking, however, for many who have not maintained an active lifestyle or have health issues, it is challenging to know where to begin. Also, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program too aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning yourself into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
Walking to reduce or control lower back pain is only one of many important reasons to begin a program. According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen-minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
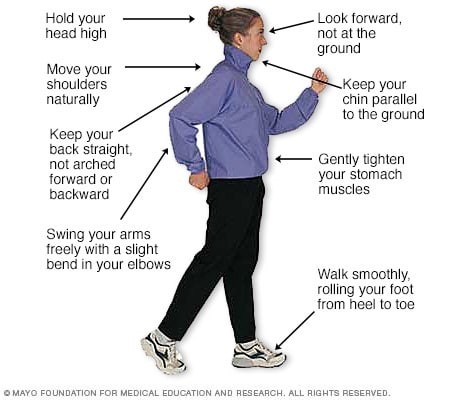
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic, “Health & Science New”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Congratulations to more than 1,000 courageous runners who finished the 27th Annual Steamtown Marathon today. Most, if not all of you are waking up this morning with a little less jump in your step than you had yesterday.
As active people by nature, many of you will resist the logic of rest, despite the pain and stiffness in your muscles and joints. Therefore, I would like to offer some words of wisdom, based on science, to encourage you to adequately rest and allow your body to recover.
With adequate rest and recovery, an elite runner can quickly regain full form in 3-4 weeks, while an average runner may require 4-6 weeks. Meb Keflezighi, an elite American runner and winner of the 2014 Boston Marathon, is an excellent example of the merits of rest and recovery. However, he discovered it by accident…following the 2012 New York City Marathon, Meb developed a foot infection which required three weeks rest. With the Olympic Trials just 70 days away, Meb quickly regained his pre-injury fitness level to win the 2012 US Olympic Marathon Trials and join the US Olympic Team in London. It may be that his injury was fortuitous and allowed him adequate recovery time, (that he might not have otherwise allowed), preparing him for intensive training leading up to the trials.
The Effects of Running 26.2 Miles on the Body:
(RunNow.com - Jim Peskett)
One of the most obvious effects of running a marathon is significant muscle and joint pain and stiffness. It will set in after you sit for a while and attempt to get up and move around. For most, it will be more pronounced the day after the marathon, as you get out of bed and limp to the bathroom. Studies show that the leg muscles, (especially the calf muscles) display significant inflammation and necrosis (dead tissue) in the fibers of the muscle. In other words, the trauma to the muscles is so severe that tissue damage causes muscle cells to die. Consequently, studies found that muscle strength, power and endurance is compromised and required significant time to recover… sometimes as long as 4-6 weeks!
Additionally, many runners report severe bone and joint pain following the race. Some studies report findings of microfractures or bone bruising from the repeated and prolonged pounding of the marathon. It is purported that the stress on the joints may be related to: weight and body type, running shoes, running style and mechanics. While not dangerous, again, it is important to respect the stress placed on the body and allow adequate healing…LISTEN TO YOUR BODY!
Creatine kinase is an enzyme found in the brain, skeletal muscles and heart. It is found in elevated levels in the presence of cellular damage to these tissues, for example, following a heart attack. Similarly, significantly elevated creatine kinase levels are found in the blood of runners up to 4 days post marathon, demonstrating extensive tissue damage at the cellular level. It is important to note, that these enzyme markers are present, even if a runner does not experience muscle soreness. So, adequate rest for healing and recovery is required, regardless of soreness.
It is not a coincidence that the runners are more likely to contract colds and flu after intensive training or running 26.2 miles. The immune system is severely compromised after a marathon and without adequate recovery; a runner can become ill and ultimately lose more training time or will underperform.
FALSE: As stated above, enzyme levels that indicate cellular damage to the tissues are present in the post-marathon runner, even in those without significant pain.
FALSE: In addition to rest, drink, drink, drink - 24 ounces of water for every 2 pounds you lose after the marathon. This is based on pre and post exercise weight. You just burned 2,600 calories so avoid diet soft drinks. You need the glucose (sugar) boost. Also, don’t drink alcohol and use minimal amounts of caffeine (the equivalent of 1-2 cups of coffee). First, drink plenty of water and sports drinks (Gatorade) to prevent a diuretic like caffeine from messing up your fluid balance.
FALSE: Studies clearly show that the VO2 Max, (the best measurement of a runner’s endurance and fitness), is unchanged after one week of inactivity. And, after two weeks, the loss is less than 6% and can be regained quickly. Moreover, it is important to remember, without adequate rest and recovery, performance is comprised, not by the loss of VO2 Max, but by muscle-skeletal tissue damage, which renders the leg muscles of the runner weaker. Remember Meb Keflezighi!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

It is one week away from the 27th Steamtown Marathon. This column is dedicated to all the runners preparing for the big day. One small piece of advice; start slowly, avoid the first mile adrenaline sprint downhill, and enjoy the journey! Remember, only one Olympic marathon winner (Juan Zabala, Argentina, 1932) was in the lead at the 5 mile mark. Lesson: The last miles matter more than the first!
Today, I hope to address some common questions for the novice marathon runner or for those coming from other locations to run in the race. What should you pack? How should I dress? What supplies will I need?
Elite runners are so experienced that they know exactly what to pack in preparation for the big marathon day. However, those, running in marathon for the first or second time usually have lots of questions. First, what you need and what you can bring will depend on your support team. If you are running alone and will not have family or friends meeting you along the way, then you are limited to a fanny pack and a few supplies. If you have a support team, then they can carry a bag with supplies, meet you along the course and you can have a sense of security.
Remember; do not do anything different on race day. Try out special clothing, water with supplements and snacks on a practice run. Also, experiment with your best pre-race meal. You will be getting up at 5-6:00am to catch the bus from Scranton to Forest City. You may want to pack breakfast to eat in the high school gym such as; bagel, peanut butter, jelly, banana and coffee or Gatorade. Moving your bowels before the race is a must.
Dress: Columbus Day Weekend in NEPA could bring 30 to 40 degree temperatures when you catch the bus in Scranton and at the 8:00 am race starting time in Forest City.
Clothing:
Accessories:
If you don’t mind the little pack on your butt, a fanny pack can be valuable. In it, you will want supplies such as: small bandages, small roll of medical tape, ibuprofen, antacid tablets, small tube of lubricant, favorite running snack, and extra shoe laces. One might also consider packing a little money, credit card, ID, emergency contact numbers and medical insurance cards. A cell phone is optional.
your supply bag. In the bag, you might consider all of the above fanny pack items and: A change of clothes such as: extra running shoes, socks, shorts, shirt, water proof wind breaker, according to the weather, especially if rain is predicted. Towels, ace bandages, gauze pads and wrap, antibiotic cream, mole skin, sunscreen, petroleum jelly, safety pins, extra water and favorite sport drink, favorite sport snacks, extra ibuprofen, antacid, anti diarrhea medicine, chemical ice pack, mobile phone, money, credit cards, ID, medical insurance cards.
For those with allergic reactions, remember to pack: epinephrine, antihistamine, and other important medications.
Map and directions to the bus or starting line, course map, race number, and get your timing chip.
Enjoy! Enjoy! Smell the roses, take in the fall foliage and chat with a fellow racer. Savor the moment enjoy the day…you are doing something very special!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Have you ever noticed high level athletes warming up before a game or competition walking or running backwards? You may also see fitness enthusiasts in gyms emulating these athletes to improve their fitness or performance. I found the concept of backward walking, (also called retro walking) interesting and decided to research the topic for more information and validation. Walking backward does have many therapeutic benefits, however, before you attempt this activity on a treadmill or elliptical, please consult your physician and physical therapist and have a spotter nearby.
At a recent meeting of The American College of Sports Medicine, several studies were presented on the topic of backward waking. Most of the research was conducted while moving backward on a treadmill and an elliptical machine. When comparing two groups recovering from knee injuries, the backward motion group showed significant improvement in strength in the quadriceps (front thigh) and hamstring (back thigh) muscles when compared to the traditional forward walking group. Furthermore, the muscles of the front (tibialis anterior) and back (gastro/achilles) of the shin/ankle also demonstrated an increase in strength and endurance with backward walking. One explanation is that forward motion is routine in daily living that it has become very efficient and does not tax or stress the muscles the body. While this efficiency prevents fatigue in daily activities, it may not stress the muscles enough to gain strength as quickly as an unfamiliar exercise.
Due in great part to the increased strain of performing an unfamiliar exercise, backward walking on a treadmill or backward pedaling on an elliptical, offered a greater cardiovascular benefit and caloric expenditure than forward motion at all levels. Specifically, walking backward on a treadmill at 2.5 mph at grades of 5% - 10% has been found to significantly increase cardiovascular endurance than walking forward under the same conditions. This knowledge is useful for healthy individuals in need of greater cardio exercise. However, it may also serve as a precaution for those with cardio problems and should consult their physician prior to engaging in this activity.
A recent study in the International Journal of Obesity, found that those who performed new activities or increased the intensity of an activity, even if for a short duration (interval training) expended more energy and burned more calories than those who worked out at the same pace consistently for a longer duration. Moreover, when engaging in a new activity such as backward walking, even more calories were burned. This phenomenon may be due to the fact that routine activities such as forward walking are performed more efficiently and easily.
We challenge our body when we inefficiently perform a new motor skill such as backward walking and burn more calories. In other words, if you want to burn more calories without exercising for longer periods of time, than try a new activity and engage in higher intensity, intermittently, for part of the time. For example, walk backward on the treadmill for 30 minutes at 2.5 mph, but do so at a 5 – 10% incline for 1-2 minutes every 5 minutes.
Some studies show that using other muscle groups by performing different exercises not only prevents boredom, but also protects your muscles and tendons from overuse and joints from wear and tear. Specifically, the knee joint and the patella joint (the joint where the knee cap glides on the knee), benefits from backward walking due to less stress and compression forces on the joint. The thigh and ankle/foot muscles benefit from using a different form of contraction while lengthening the muscle. Some authors propose that this may also prevent strains and pulls and may be valuable to strengthen those with a history of shin splints and flat feet (pronation).
Mixing up your program prevents boredom. As a rule, those willing to change their exercise routine are more compliant and continue to exercise longer than those stuck in the same routine. A new challenge to improve distance, speed, and resistance while exercising in a different direction will be refreshing to your program.
Prevention of falls by improvement in balance and coordination has received a great deal of attention in the past few years. This is not only valuable to the athlete but may be even more important to those over 50. With age, balance centers are slow to react to changes in inclination, elevation, rotation and lateral movements. This slow reaction time leads to falls that may cause fractures, head injuries and more. Working on this problem by challenging the vestibular and balance centers before it is seriously compromised is important and backward walking is one way for this to be effectively accomplished.
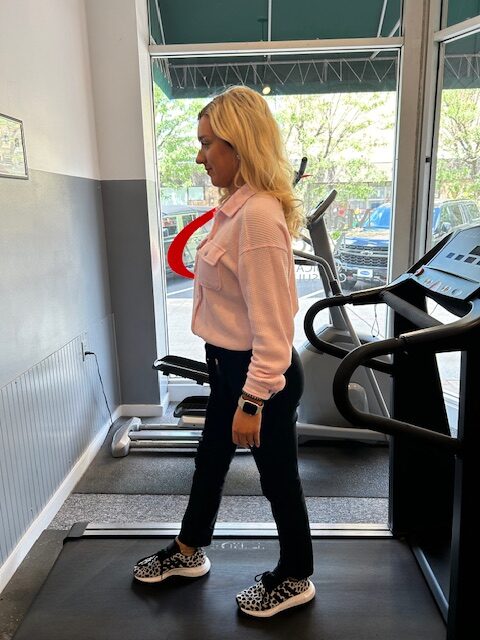

Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

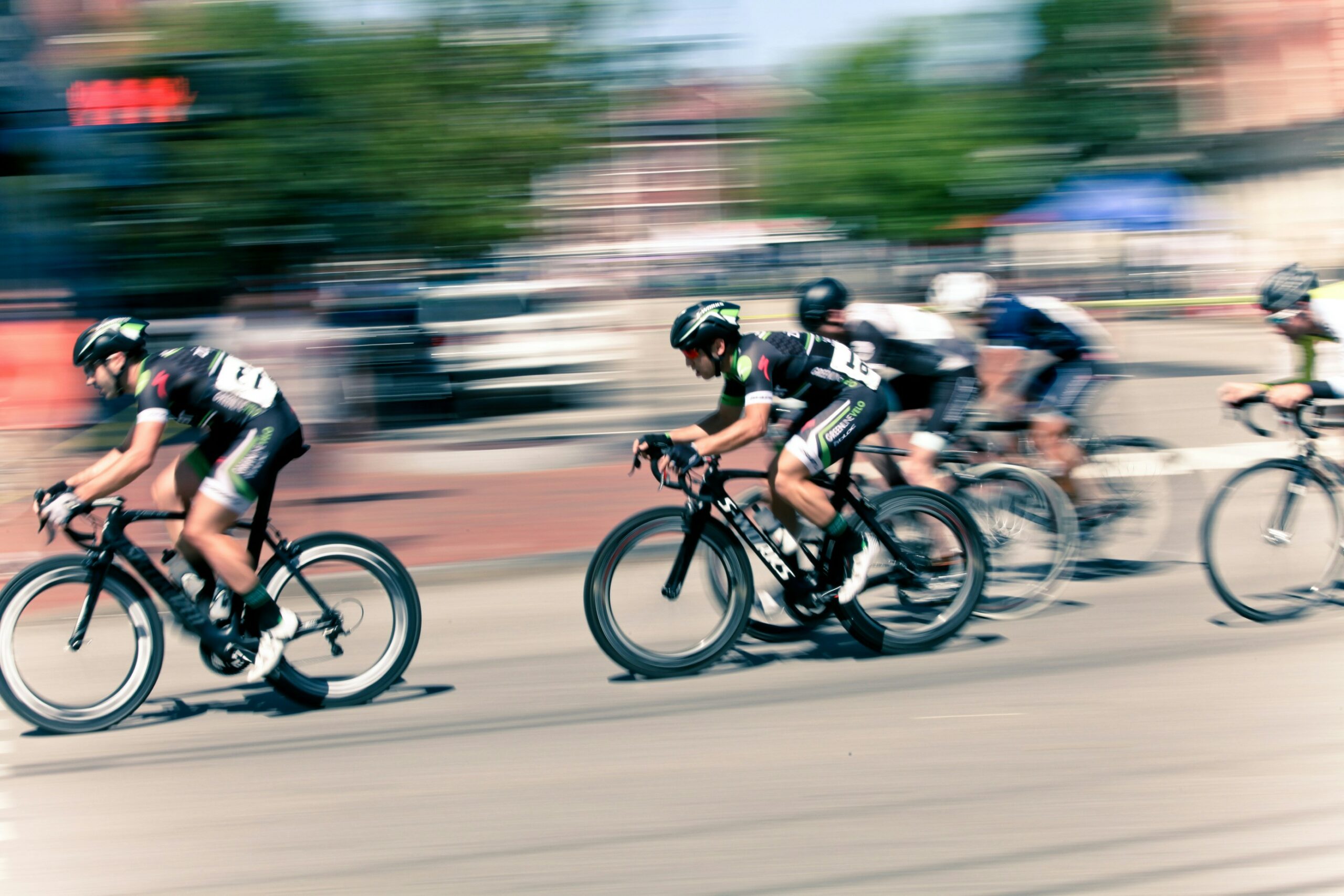
As summer fads and cool fall nights are upon us, many of us will prepare to put away some of our warm weather toys…closing the pool, storing kayaks and boats and packing up the “slip and slide.” However, one activity that can last well into the fresh breeze of fall is cycling. In fact, many feel that fall is the best time of year to jump on a bike and enjoy the ride! If you are looking for a kick start to riding your bike this fall, consider the 20th and final Tour de Scranton on Sunday, April 15, 2024. It is a fun-filled, noncompetitive bike ride through Scranton and neighboring communities. Tom and Betty Moreken, with the help of dedicated friends and countless supporters have raised over $400,000.00 to benefit addiction treatment and prevention in honor of their daughter Erin, a victim of drug addiction. I have had the privilege to know Tom and Betty and have always admired their resilience and selflessness to turn a negative into a positive and do something good for others. They and their friends truly represent everything that is good about the people of NEPA!
So dust off your bikes and join the fun at Tour de Scranton. Hopefully, it will entice you to ride the many beautiful and well-maintained trails that are available at the Countryside Conservancy and other locations in the Abingtons and the Lackawanna Heritage Valley Authority.
Tour de Scranton is the official “kick off” to biking season in NEPA. This year, on Sunday, September 15th, the 20th annual and final Tour de Scranton will offer a selection of several routes and distances for the novice and experienced rider at its non-competitive bike ride for riders of every age and skill level. This event supports “The Erin Jessica Moreken Drug & Alcohol Treatment Fund” which provides charitable gifts to qualified local organizations or individuals struggling with the disease of addiction. For more information visit: www.tourdescranton.com.
There are many obvious reasons to bike…cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, improve leg strength and others. But, the real question is, “what are the advantages of biking over other forms of exercise?” Glad you asked…
Prevention is the best management of musculoskeletal problems associated with biking. First, many of the problems associated with biking such as knee pain, buttock soreness, and tendonitis can be prevented through proper fitting. Furthermore, it is important that your equipment be in good working order such as tires, chain, brakes and pedals. Next, be sure to maintain a fairly good fitness level in order to bike safely. If you are a beginner, start slowly. Warm up and slowly bike for 10 to 15 minutes and build up over time. Practice the coordination of stopping, starting, shifting and braking. Work on good strength and flexibility of the hamstrings, quadriceps, calves and gluteal muscles. All of these muscles are necessary to generate pedal force. Balance is also important to safety and can be practiced on and off the bike. Be aware that adaptive equipment can modify your bike for added comfort and safety such as soft handlebar tape, seat post and front fork shock absorbers, padded biking shorts, c-out and gel pad saddle seats, and wider tires.
Be careful not to progress too quickly because inactivity to over activity in a short period of time can create problems. Overuse injuries such as tendonitis, can be avoided by cross training. Bike every other day and walk, run or swim on off days. Make sure to take time off to recover after a long ride. Use ice and massage to sore muscles and joints after riding.
Remember, cycling should be fun! Pain from improperly fitted and poorly maintained equipment is preventable. Excessive workouts and training rides should be kept to a minimum and consider cross-training in between.
EQUIPMENT: Helmets are a must! Also, keep your bike in good condition. Road bikes should have mirrors and reflectors. Use hand signals and obey traffic rules. Dress for weather and visibility. Have a first aid and tire patch kit, tire pump and tools. Seat comfort can be improved with gel cushion or split seat.
BE ALERT: for traffic, parked cars, pedestrians loose gravel and cracks in the road.
SOURCES: American Physical Therapy Association
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, and exercise regularly

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Patients often tell me that they would like to exercise but hesitate due to their knee or hip pain. They want to know what type of exercise is best for those suffering from osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis is also known as degenerative arthritis. It is the most common form of arthritis in the knee. It is usually a gradual, slow and progressive process of “wear and tear” to the cartilage in the joint which eventually wears down to the bony joint surface. It is most often found in middle-aged and older people and in weight bearing joints such as the hip, knee and ankle. It causes gradual onset of pain, swelling and stiffness in the involved joint, especially after increased activity and weakness with loss of function due to disuse.
However, OA is not an excuse to avoid exercise but it is important to be smart about it. Regular exercise is essential to maintain a normal lifestyle for those with OA. However, if you do the wrong exercise, use poor technique, or are too aggressive, you could flare-up your joints and do more harm than good.
When performed correctly, exercise for those with OA has many benefits:
Pain Control
Exercise controls OA pain by releasing natural pain control chemicals in the body called endorphins. It also controls pain by assisting in weight loss and improving range of motion.
Weight Control
We all know how well exercise burns calories and that increased body weight creates increase stress on the joints.
Prevention of Joint Stiffness
Exercise will help maintain joint range of motion. A stiff joint is a painful joint.
Prevention of Muscle Weakness
Exercise will help maintain muscle strength. Weak muscles will allow or increase in joint wear and tear.
Maintain Lifestyle
If a joint is stiff and weak, then they become painful which negatively impacts your lifestyle. Exercise can prevent this problem.
Start Slowly
Wean into exercise because if you advance too quickly, you will flare up the joint and have increased pain. For example, walk for 5-10 minutes the first session. If you do not have pain, add 1-2 minutes each session.
Lose Weight
Every pound lost equates to less stress on your joints. For example, a loss of 5 pounds of body weight translates to 20-30 pounds of stress through the knee, according to David Borenstein, MD, President of the American College of Rheumatology. Also, body weight has a direct impact on daily activities. For example, walking upstairs creates stress through the knee equal to 4 times body weight and seven times body weight going downstairs. Therefore, less body weight equals less stress.
Low Impact Workouts
Low impact exercise creates less stress on the joints while strengthening leg muscles and those who those who maintain leg muscle strength have less stress on their joints. It is even important not to load your arms with heavy objects when walking or using stairs to limit joint stress.
Some examples of low-impact exercises are: walking, swimming, elliptical trainer, and biking. Strength training is also low-impact and should be performed with low weight and high repetitions. Water therapy is great for those with OA, especially in a heated pool. It is a great low-impact exercise with less gravity and stress on the joints. Walk, swim and do mild resistance exercises in the water. Use a snorkel and mask for swimming to limit excessive neck turning and back extension.
Walking is a great form of exercise; however, walking softly is important for those with OA. Wear good running shoes and orthotics if necessary. Discuss this with your physical therapist or podiatrist. When possible, use soft surfaces like cinder, mulch or rubber. Avoid grass and soft stand due to instability and torsion that may irritate your joints.
Warm-Up
Warming up your body is critical to prevent injury to the muscles and tendons. This can be done by marching in place or using aerobic equipment such as a bike for 5 to 10 minutes before exercise. Always perform the warm-up activity at ½ your normal pace.
Balance & Relaxation Techniques
Tai Chi and ballroom dancing are two good examples of activities which promote balance and relaxation. Studies showed that those with OA who participated in Tia Chi two times a week for eight weeks reported less pain, increased range of motion and improved daily activities and function. They also noted less low back pain and better sleeping.
Proper Clothing
Stay warm in winter and consider wearing compression shorts. Be cool in the summer months with DrytechR type material.
Pre/Post Exercise First Aid
If you are sore for longer than 12 to 24 hours after exercise, then you overdid it and must make adjustments next time. Otherwise, use hot packs, bath or shower before you exercise to loosen up and apply ice to your joints after exercise, especially if they are sore.
Post Exercise Stretch
Gentle, active range of motion stretches after exercise is important to maintain mobility. Do not bounce or cause pain. For example: Low Back – knees to chest; Arms – row –the – boat, arms behind head, arms behind back; Legs – wall lean calf stretch, bend and extend knees, open and close hips.
SOURCES: Rothman Institute, Philadelphia, PA and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons; www.lifescript.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is repeated every year at this time with the intent of raising the level of awareness to prevent death or serious illness from heat stroke in athletes and other active people in hot, humid weather.
It is the end of July and we have managed to survive two “heat waves” in NEPA. While it is important to have fun in the sun, please be mindful of how your body reacts to high humidity and heat and take appropriate precautions. Athletes are particularly vulnerable this time of year due to daytime practice sessions. (August 5 & 6, 2024, first day of acclimatization and August 12, 2024, first day of practice for fall sports according to PIAA). Visit www.piaa.org for more information. Keep in mind, you don’t have to be running a marathon or playing football in full uniform to suffer from heat stroke.
Heat stroke, one of the most serious heat-related illnesses, is the result of long term exposure to the sun to the point which a person cannot sweat enough to lower the body temperature. The elderly and infants are most susceptible and it can be fatal if not managed properly and immediately. Believe it or not, the exact cause of heatstroke is unclear. Prevention is the best treatment because it can strike suddenly and without warning. It can also occur in non athletes at outdoor concerts, outdoor carnivals, or backyard activities.
Some “old school” folks think that wearing extra clothing and “breaking a good sweat” is an optimal goal for exercise. However, it may be potentially very dangerous in hot and humid conditions. When exercising in hot weather, the body is under additional stress. As the activity and the hot air increases your core temperature your body will to deliver more blood to your skin to cool it down. In doing so, your heart rate is increased and less blood is available for your muscles, which leads to cramping and other more serious problems. In humid conditions, problems are magnified as sweat cannot be evaporated from the skin to assist in cooling the body.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and The American College of Sports Medicine has the following recommendations which are appropriate for both the competitive athlete and weekend warrior:

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Several years ago, while hiking to the bottom of the Grand Canyon with my family, my wife Esther developed “canyon knee,” also known as “hiker’s knee” or in medical terms, “patellar tendonitis.” Regardless of the term, the end result was that she had severe pain in the tendon below her knee cap and was unable to walk up the trail to get out of the canyon. In addition to ice, rest, bracing, and non-steroidal anti inflammatory medications, the National Park Ranger insisted that she use two trekking poles on her ascent to the rim.
Prior to that experience, I always thought that “walking, hiking sticks or trekking poles” were for show or those in need of a walking aide. Well, I could not have been more incorrect. Needless to say, Esther made it out of the canyon safely and, with the use of our life saving trekking poles; we have lived “happily ever after!” Now, 15 years later, I rarely walk more than 5 miles without my poles.
As a result of this experience, I have been recommending walking or trekking poles to my patients. These poles are an essential part of hiking or distance walking gear, for the novice and expert alike. Specifically, for those over 50 who have degenerative arthritis and pain in their lower back, hips, knees, ankles or feet, these simple devices have been shown to improve the efficiency of the exercise and lessen the impact on the spine and lower extremities. Additionally, using poles reduces the likelihood of ankle sprains and falls during walking. Trekking poles are also a safe option for those with compromised balance. If you want to walk distances for exercise and need a little stability but don’t want the stigma of a cane, trekking poles are for you.
Early explorers, Europeans and Native Americans have been using walking sticks for centuries. More recently, in the 1968 classic hiker’s bible, “The Complete Walker,” Colin Fletcher praised his “walking staff” for its multipurpose use: for balance and assistance with walking and climbing, protection from rattlesnakes, and for use as a fishing rod. Today, these sticks are now versatile poles made from light-weight materials.
Trekking poles are made of light-weight aluminum and vary in cost and quality. But, like most things, “you get what you pay for!” These hollow tubes can telescope to fit any person and collapse to pack in luggage for travel. Better poles offer multiple removable tips for various uses, conditions and terrains. For example, abasket to prevent sinking too deeply in snow, mud or sand; a blunt rubber tip for hard surfaces like asphalt or concrete, or the pointed metal tip to grip ice or hard dirt/gravel. Better quality poles offer an ergonomic hand grip and strap and a spring system to absorb shock through your hands, wrists and arms upon impact.
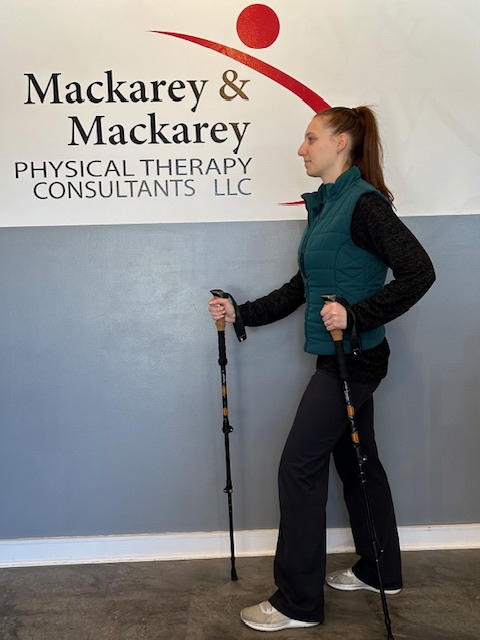
The poles should be properly adjusted to fit each individual. When your hand is griping the handle the elbow should be at a 90 degree angle. Proper use is simple; just walk with a normal gait pattern of opposite arm and leg swing. For example, left leg and right arm/pole swings forward to plant while the left arm/pole remain behind with the right leg .
This pattern is reciprocated with as normal gait advances (opposite arm and leg). I have been very pleased with my moderately priced poles (Cascade Mountain Tech from Dick’s Sporting Goods ($34.99 per pole). Prices range from $19.99 to 79.95 per pole. dickssportinggoods.com; montem.com; leki.com; rei.com. However, if you travel frequently to hike the State and National Parks, you may want to purchase more expensive poles that collapse and retighten more efficiently. (montem.com; leki.com;)
Montem Trekking Poles - with close-up of easy adjustable locking clasp.

There are numerous studies to support the use of trekking poles, especially research that supports their use for health and safety. One study compared hikers in 3 different conditions; no backpack, a pack with 15% body weight and a pack with 30% body weight. Biomechanical analysis was performed blindly on the three groups and a significant reduction in forces on lower extremity joints (hip, knee, and ankle) was noted for all three groups when using poles compared to those not using poles.
Another study confirmed that trekking poles reduced the incidence of ankle fractures through improved balance and stability. Additional studies support the theory that trekking poles reduce exercise induced muscle soreness from hiking or walking steep terrain and another study found that while less energy is expended in the lower body muscles using poles, increase energy is used in the upper body; therefore, the net caloric expenditure is equal as it is simply transferred from the legs to the arms.
In conclusion, it is important to remember that trekking poles for hiking or distance walking are much more than a style statement. They are proven to be an invaluable tool for health, safety and wellness by reducing lower extremity joint stress, improving stability and balance, and enhancing efficiency for muscle recovery.
Sources: Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. The Complete Walker, by Colin Fletcher
Model: Andrea Molitoris, PT, DPT at Mackarey Physical Therapy

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Seasonal allergies affect 30 % of adults and 40% of children in the United States. Avoiding the outdoors is often not an option…especially if you enjoy outdoor activities and sports. Not long ago, it was unthinkable that an athlete with serious seasonal allergies could compete at a high level, such as the Olympics. Now, in great part due to advanced research, medications and proper management, an Olympic gold medal for those suffering from seasonal allergies is a reality. Recently, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease at the National Institutes of Health have published research on this topic to provide a better understanding and make recommendations.
The most common allergic reactions which athletes suffer from are sneezing, itchy and watery eyes, runny nose and coughing. Moreover, 67% of those with these symptoms also suffer from asthma. The athlete in NEPA is particularly vulnerable when the pollen count is high during spring and fall for several reasons. One, after being indoors all winter, one might develop a heightened sensitivity to allergens. Also, increased rapid and deep breathing during exercise makes athletes more susceptible to significant symptoms when exposed to allergens such as tree, grass and weed pollens.
Allergy skin testing can be performed to determine the allergens to which you are susceptible. Once determined, allergy shots are effective in building up tolerance to these allergens. If appropriate, you may be able to use allergy drops, administered under the tongue and conveniently used at home.
Asthma suffers should use their inhaler BEFORE symptoms occur. A recent study found that pretreatment using a short-acting bronchodilator inhaler within 15 minutes before exercise is very effective in preventing asthma symptoms for more than four hours. It is important to keep a bronchodilator available. If you fail to benefit from this, see your physician for other methods to control your exercise-induced symptoms.
Whether you have allergic respiratory problems from rhinitis or asthma, you many benefit from conditioning your airways with a 10 to 15 minute warm-up before and cool-down after the activity. This may serve to gradually prepare your lungs for an increased demand.
In addition to preventing dehydration on hot and humid days, constant hydration is very important for the athlete with allergies to prevent dry airways in athletes.
Know the signs and symptoms of asthma (coughing, wheezing, tightness in chest, shortness of breath).
Some schools have a file on each student athlete with a allergic or asthmatic problem which requires medication. The file includes information such as medical doctor release and instruction, emergency contacts and medications. Students must have their medications on hand before they can enter the field. The National Athletic Trainers Association recommends using a peak flow meter to monitor at risk players and can determine when a player can return to the field.
If possible, find an alternate practice facility with climate control for athletes at risk. Plan practices for these athletes when the pollen count is low. Check the newspaper or internet for pollen counts in your area. Training by the water, (ocean) where there is a breeze and less pollen is helpful.
Shower and change clothing immediately after being outdoors
During a flare up, do less aerobic exercise to limit stress on respiratory system. Try strength training indoors instead.
When pollen count is high, keep windows shut at home and in your car….use air-conditioning.
Keep pets out of your bedroom…especially when sleeping
Dry clothing in dryer…do not hang on clothesline outdoors
Sources: American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. National Athletic Trainers Association.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is dedicated to the memory of John R. O’Brien, Esq., who recently passed due to medical complications associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). John was a source of joy and inspiration for those fortunate to have known him. Twenty years ago, John hesitantly agreed to contribute to my column on MS with two requirements: one, if the column would be valuable to those affected by MS and two, he would remain anonymous. When speaking with his dedicated wife, Sally, it became very apparent that any discussion of John’s life would be diminished if it was defined by the disease because he was committed to turning his “DISABILITY INTO AN ABILITY!”
With the help of his loving wife, family, friends, and devices such as an electric scooter and adaptive car, John not only lived but thrived! He was a skilled lawyer, a respected member of the Bar, and an active member of the community. John served on the executive committee of the Lackawanna Bar Association. In addition, the Lackawanna Pro Bono honored him recently. He also taught business law and healthcare law and coached Prep’s mock trial team.
John shared his thoughts with me about the challenges of redefining life… from Golf Club Champion to living with a physically disabling disease. Anyone who knew him would agree that he succeeded in doing so through his keen intellect and sharp wit and humor…his heart and brain overcompensated for his body! In addition to reading books in Latin and Greek, he had his crossword puzzles published in The New York Times and Los Angeles Times. In September 2023, John conducted an interview with presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin before a full house at the Scranton Cultural Center. Ms. Goodwin later reported that John was the most knowledgeable, effective and enjoyable interviewer she’s encountered.
John’s absence will be deeply felt and his legacy will continue to shape our community for years to come!
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic disease. While it may lay dormant and stable for a period of time, living a healthy lifestyle will make a positive contribution toward how you and your family live with Multiple Sclerosis. Studies show that a life of family, love, and support are essential to maintain a positive attitude with a chronic illness. This combined with a healthy diet and proper exercise can contribute greatly toward taking control and living a relatively normal life with MS.
As I have mentioned in many other columns, studies show that people with good attitudes and great faith live longer than others. This is especially helpful when living with chronic disease like Multiple Sclerosis. The Cleveland Clinic offers some suggestions how to maintain a positive attitude:
Many sources, including the Cleveland Clinic suggest that exercise, when performed properly, can have a positive impact on Multiple Sclerosis symptoms both physically and psychologically. However, because you have a chronic illness, you should consult with you family physician and physical therapist before beginning an exercise program. They will advise you on the proper type and amount of exercise.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!