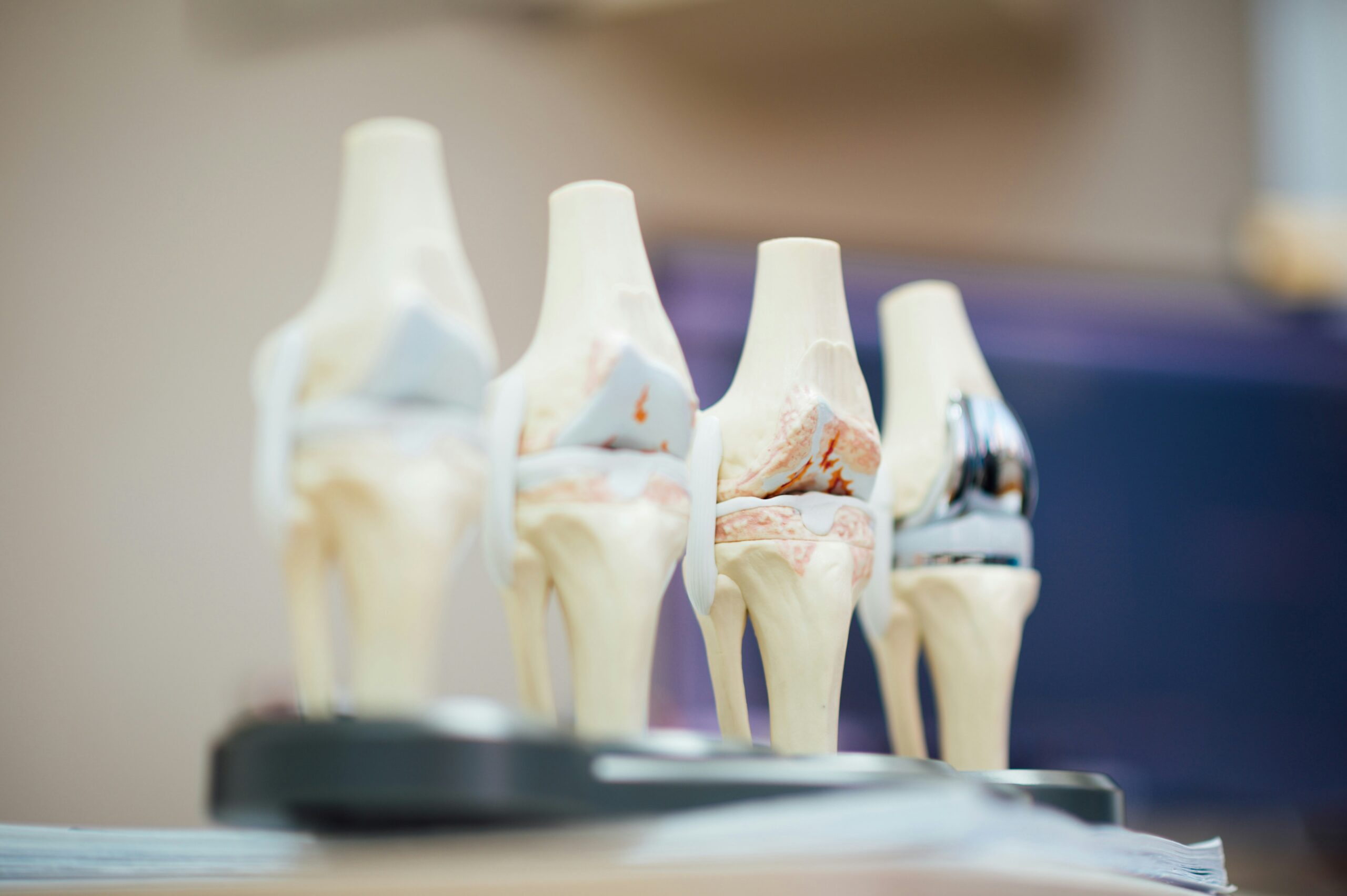
Patients often tell me that they would like to exercise but hesitate due to their knee or hip pain. They want to know what they should avoid, how to prevent and what is recommended to prevent or limit the progression of arthritis. Osteoarthritis (OA) is also known as degenerative arthritis. It is the most common form of arthritis in the knee. OA is usually a gradual, slow and progressive process of “wear and tear” to the cartilage in the joint which eventually wears down to the bony joint surface.
It is most often found in middle-aged and older people and in weight bearing joints such as the hip, knee and ankle. It causes gradual onset of pain, swelling and stiffness in the joint involved, especially after increased activity. While diet and exercise help, some people are more likely to develop OA based on previous trauma or injury, labor intensive occupations and genetics. Either way, we all get OA to some degree but there are a few things you can do to limit wear and tear to your joints.
However, OA is not an excuse to avoid exercise, but it is important to be smart about it. Regular exercise is essential to maintain a normal lifestyle for those with OA. However, if you make poor lifestyle choices, do the wrong exercise, use poor technique, or are too aggressive, you could flare-up your joints and do more harm than good.
SOURCES: WebMD, University of Pennsylvania
Visit your family doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Every December, as we finish the last of the leftover turkey, patients begin to talk about the holiday season and gift shopping. This conversation invariably leads to suggestions for gift ideas related to health, exercise and fitness. The suggestions below offer a wide variety of fitness-related gifts, some expensive and frivolous and others reasonably priced and practical. I hope it makes your shopping a little easier.
These gifts can be purchased at most local sporting goods stores or on-line.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

It is one week away from the 28th Steamtown Marathon. This column is dedicated to all the runners preparing for the big day. One small piece of advice; start slowly, avoid the first mile adrenaline sprint downhill, and enjoy the journey! Remember, only one Olympic marathon winner (Juan Zabala, Argentina, 1932) was in the lead at the 5 mile mark. Lesson: The last miles matter more than the first!
Today, I hope to address some common questions for the novice marathon runner or for those coming from other locations to run in the race. What should you pack? How should I dress? What supplies will I need?
Elite runners are so experienced that they know exactly what to pack in preparation for the big day. However, those, running in marathon for the first or second time usually have lots of questions. First, what you need and what you can bring will depend on your support team. If you are running alone and will not have family or friends meeting you along the way, then you are limited to a fanny pack and a few supplies. If you have a support team, then they can carry a bag with supplies, meet you along the course and you can have a sense of security.
Remember; do not do anything different on race day. Try out special clothing, water with supplements and snacks on a practice run. Also, experiment with your best pre-race meal. You will be getting up at 5-6:00am to catch the bus from Scranton to Forest City. You may want to pack breakfast to eat in the high school gym such as; bagel, peanut butter, jelly, banana and coffee or Gatorade. Moving your bowels before the race is a must.
Columbus Day Weekend in NEPA could bring 30 to 40 degree temperatures when you catch the bus in Scranton and at the 8:00 am race starting time in Forest City.
If you don’t mind the little pack on your butt, a fanny pack can be valuable. In it, you will want supplies such as: small bandages, small roll of medical tape, ibuprofen, antacid tablets, small tube of lubricant, favorite running snack, and extra shoe laces. One might also consider packing a little money, credit card, ID, emergency contact numbers and medical insurance cards. A cell phone is optional.
Have your support team meet you at prearrange locations along the race route and bring your supply bag. In the bag, you might consider all of the above fanny pack items and: A change of clothes such as: extra running shoes, socks, shorts, shirt, water proof wind breaker, according to the weather, especially if rain is predicted. Towels, ace bandages, gauze pads and wrap, antibiotic cream, mole skin, sunscreen, petroleum jelly, safety pins, extra water and favorite sport drink, favorite sport snacks, extra ibuprofen, antacid, anti diarrhea medicine, chemical ice pack, mobile phone, money, credit cards, ID, medical insurance cards.
For those with allergic reactions, remember to pack: epinephrine, antihistamine, and other important medications.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

It is two weeks away from the 28th Steamtown Marathon. After training all spring and summer for the first seven Steamtown Marathons, not a Columbus Day Weekend goes by without my thoughts of this great event.
I would like to introduce this topic with some marathon history. In 490 B.C. Athens was under attack by the Persians and was outnumbered more than two to one. The Athenians fought bravely and defeated the enemy in the town of Marathon. The victory kept the intruders 26 miles away from Athens. To keep the anxious citizens of Athens calm, leaders immediately ordered a foot soldier, Phedippides, to run to the capital city to share the news. Phedippides ran, in full armor, for 26 miles from Marathon to Athens, delivered the message and died immediately. Now, people do the same thing of their own free will!
Each year at this time, dozens of runners preparing for the Steamtown Marathon come to my office with severe shin pain known as shin splints. Unfortunately, in many of these athletes, this problem can lead to a much more severe and advanced problem with shin splints called a stress fracture.
A stress fracture is fatigue damage to bone with partial or complete disruption of the cortex of the bone from repetitive loading. While standard x-rays may not reveal the problem, a bone scan, and MRI will. It usually occurs in the long bones of the leg, mostly the tibia but also the femur (thigh) and foot. Occasionally, it occurs in the arm.
10-21% of all competitive athletes are at risk for stress fractures. Track, cross country and military recruits are at greatest risk. Females are twice as likely as males to have a stress fracture. Other athletes at risk are: sprinters, soccer and basketball players, jumpers, ballet dancers are at risk in the leg and foot. Gymnasts are also vulnerable in the spine while rowers, baseball pitchers, golfers and tennis players can experience the fracture with much less frequency in the ribs & arm.
The problem is much more prevalent in weight bearing repetitive, loading sports in which leanness is emphasized (ballet, cheerleading) or provides an advantage (distance running, gymnastics).
Stress fractures usually begin with a manageable, poorly localized pain with or immediately after activity such as a shin splint. Over time, pain becomes more localized and tender during activity and then progresses to pain with daily activity and at rest.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

Read Health & Fitness Forum Next Monday/Sunday: Preparing Your First Aid Kit For the Steamtown Marathon
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Here are 10 most common exercise myths!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
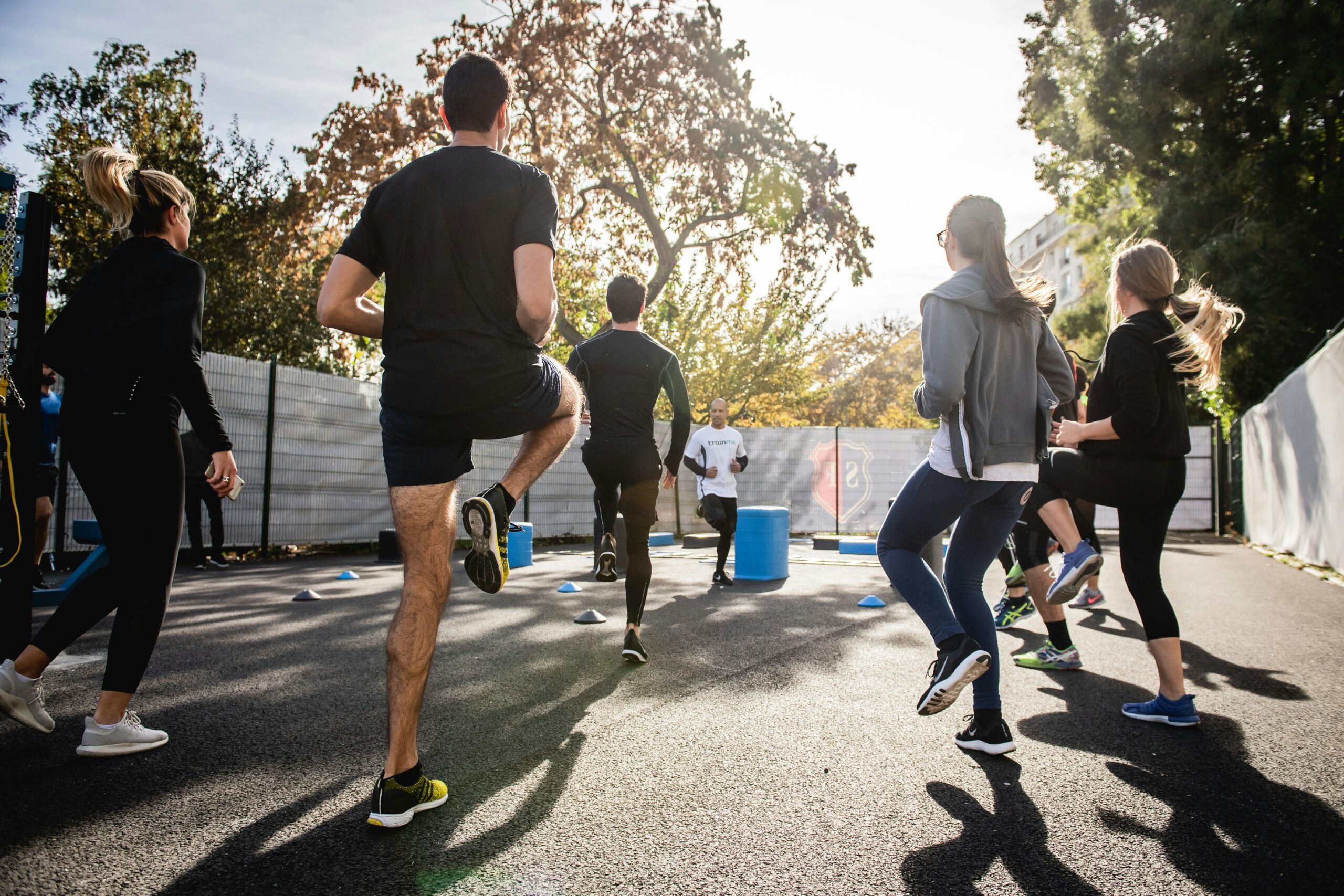

Happy Labor Day! There is little doubt that the workplace has been redefined since the pandemic as many employees continue to work from home. Sitting for many hours at a workstation that may not be optimal has also changed the way we define workplace health and safety. It may be more important than ever to pay close attention to designing an ergonomic workstation, changing position, and stretching regularly to prevent injury.
Since 1894 Labor Day has been designated as the national holiday that pays tribute to the contributions and achievements of American workers. Research supports the notion that healthier employees are happier and more productive. When employers encourage healthy behavior and safety at work, they benefit in many ways.
For example, in addition to improving job satisfaction and productivity, healthy employees save money by using less sick time, worker’s compensation benefits and health benefits. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 75 percent of employers” health care costs are related to chronic medical problems such as obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Deconditioned, overweight employees are more likely to suffer from these preventable conditions and are at greater risk for injury. Employers, please consider using this holiday as an opportunity to start a health promotion program at your workplace…have a health fair, offer healthy snacks, encourage walking, smoking cessation, exercising at lunch, and offer fitness club stipends.
Lower back pain, one of the costliest illnesses to employers, is one example of a problem which can be prevented with a good health and safety program. It is widely accepted in the medical community that the best treatment for lower back pain (LBP) is prevention. Keeping fit, (flexible and strong), practicing good posture, and using proper body mechanics are essential in the prevention of LBP. At our clinic, significant time and effort is spent emphasizing the importance of these concepts to our patients, employees, and the businesses we work with through industrial medicine programs. A comprehensive approach can produce significant reductions in LBP injuries through an onsite safety program which promotes education, wellness, body mechanics, lifting techniques, postural and stretching exercises and ergonomics.
As little as 10 extra pounds puts great stress on your lower back. It also makes it more difficult to maintain good posture. Eat well, exercise regularly and don’t smoke. Smokers have a much higher incidence of LBP and failure from lower back surgery.
Good posture is critical for a healthy back. When sitting, standing or walking maintain a slight arch in your lower back, keep shoulders back, and head over your shoulders. In sitting, use a towel roll or small pillow in the small of the back. Also, consider sitting on a physio ball, which promotes proper posture for part of the day.
Perform postural exercises throughout the day. Most of the day we sit, stand, and reaching forward and bend our spine. These exercises are designed to stretch your back in the opposite direction of flexion. Please perform slowly, hold for 3-5 seconds and repeat 6 times each 6 times per day.
Chin Tuck: Tuck your chin back to bring your head over shoulders.
Shoulder Blade Pinch: Pinch your shoulder blades together.
Standing Extension: While standing, put your hands behind back and extend lower back 10-20 degrees.
Good Body Mechanics and ergonomics are also important in the prevention of LBP. When lifting, think twice. Think about the weight, shape and size of the object. Think about where the object is going and the surface resistance of the floor. Does it require two people to lift? Can I safely lift that high or bend that low?
When bending to lift an object think about safety:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is repeated every year at this time with the intent of raising the level of awareness to prevent death or serious illness from heat stroke in athletes and other active people in hot, humid weather.
It is early August, and we have managed to survive two “heat waves” in NEPA. While it is important to have fun in the sun, please be mindful of how your body reacts to high humidity and heat and take appropriate precautions. Athletes are particularly vulnerable this time of year due to daytime practice sessions. In response to this potential problem, the PIAA has established acclimatization guidelines for fall sports beginning in August. Visit www.piaa.org for more information. Keep in mind, you don’t have to be running a marathon or playing football in full uniform to suffer from heat stroke.
Heat stroke, one of the most serious heat-related illnesses, is the result of long term exposure to the sun to the point which a person cannot sweat enough to lower the body temperature. The elderly and infants are most susceptible and it can be fatal if not managed properly and immediately. Believe it or not, the exact cause of heatstroke is unclear. Prevention is the best treatment because it can strike suddenly and without warning. It can also occur in non athletes at outdoor concerts, outdoor carnivals, or backyard activities.
Some “old school” folks think that wearing extra clothing and “breaking a good sweat” is an optimal goal for exercise. However, it may be potentially very dangerous in hot and humid conditions. When exercising in hot weather, the body is under additional stress. As the activity and the hot air increases your core temperature your body will to deliver more blood to your skin to cool it down. In doing so, your heart rate is increased and less blood is available for your muscles, which leads to cramping and other more serious problems. In humid conditions, problems are magnified as sweat cannot be evaporated from the skin to assist in cooling the body.
The American Academy of Pediatrics and The American College of Sports Medicine has the following recommendations which are appropriate for both the competitive athlete and weekend warrior:

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

While I fully expect to be at the “butt end” of many comments for this column, I feel compelled to address this topic at the request of several patients. It seems that many geriatric physical therapists commonly encounter patients that suffer from constipation which limits their participation in rehabilitation. Ironically, research demonstrates that exercise and activity actually help relieve constipation.
The National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC) reports that 3.1 million people in the United States suffer from constipation. The NDDIC further reports that this problem leads to almost 400,000 hospitalizations, 1.4 million visits to emergency rooms, 1 million prescriptions and 121 deaths each year. Constipation is defined by the Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine as three or less bowel movements per week. It is also estimated that more than 27 percent of the elderly are affected.
Severe constipation can result in immediate medical attention in some cases due to intestinal obstruction. In addition to infrequent bowel movements, some symptoms include: feeling poorly, weight loss, loss of appetite, abdominal distention and/or pain, and vomiting.
Healthy people must continue to keep active. Get into good exercise habits at a young age and continue through life. Maintaining a consistent schedule of eating and exercise is also helpful. Some simple suggestions for beginning an exercise program for prevention of constipation in the healthy population are:
Depending on your general health and ambulatory status, these endurance exercises may be appropriate for you. Therefore, consider one or two of the following as a good starting point:
IN CONCLUSION: KEEP MOVING YOUR BODY AND YOU WILL KEEP MOVING YOUR BOWELS!
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

After such a long, cold and wet spring, we are all grateful that the 4th of July holiday weekend is here! There is still plenty of time to be outdoors in NEPA and experience so many activities such as: biking, hiking, running, walking, swimming, boating, golfing, and playing tennis to name a few. It is a wonderful opportunity to discover your inner child, mix it up and try something new! Below are some new and exciting ways to stay active and have fun in the sun:
Spending time on any of the beautiful lakes in NEPA is time well spent. From an exercise standpoint, rowing, canoeing and kayaking offer a very special experience. Most kayaks are light weight, easy to use and maneuverable on a lake. Sitting low on the water offers a unique perspective as you feel yourself gliding across the lake. The Countryside Conservancy, in partnership with Lackawanna State Park, sponsors moonlight kayak events on the lake at the park. With a bright full moon, you can begin at 8 pm and return at 10 pm. Bring bug spray and headlights to enjoy the sunset and moon rise on the lake. You will feel like a kid breaking the rules of the park by being on the water after dark!
NOTE: Try kayaking in the daytime first and then advance to sunset trips before staying on the water for the moonlight. Rentals are available at the park.
Website: www.countrysideconservancy.org; www.dcnr.state.pa.us/stateparks.org
Stand up paddleboarding (SUP) is becoming a fast-growing sport among water enthusiasts. It is a fun way to exercise your core, improve balance, and tone your upper body. Stand Up Paddleboarding requires minimal equipment; a board that is essentially a long and wide surfboard and a long paddle to use while standing on the board. It can be done in the ocean surf, bay, lakes, or rivers; however, beginners would be wise to stay in calm water. Rentals are available at most beaches.
Check out the video for more information: REI paddleboard basics
What is it? Imagine a standup paddleboard with a handlebar and pedals like a exercise stepper machine. Instead of using a paddle, you step up and down on the pedals and fins under the board propel you through the water.
Check it out…Hobie Mirage Eclipse Stand Up Pedalboard; Dick’s Sporting Goods
Zumba is a very popular form of dance aerobics spiced up with Latin music. When adding water and sun to this already cool activity, you are assured to have fun while exercising. As with any aquatic exercise, the added resistance from the water gives arm rows and leg kicks more challenge. Female participants report an additional benefit; they are uninhibited to “shake that thing” to the music under the cover of the water. So, beat the heat, let loose and get some fun in the sun while you exercise.
NOTE: Consider trying regular Zumba first to get the hang of it. Amy Sekol is a local certified Zumba instructor and also offers Aqua Zumba. (amys.zumba.com)
Website: www.zumba.com
I love this idea…why didn’t I think of it first! In the gym I enjoy the elliptical machine because it simulates running without the impact on my joints but of course, I would rather be outdoors. Well, this is the answer to my prayers…an elliptical machine that is attached to a bike with handle bars and brakes included. I think it will probably be difficult on steep hills but it is something I MUST TRY!
Website: www.elliptigo.com; www.mywingflyer.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

As most sports enthusiasts know, in 2021 Tiger Woods ruptured his Achilles tendon while training at home and in 2023 Aaron Rodgers, a former Green Bay Packer quarterback, did the same in the first game of the 2023/24 NFL season with the New York Jets. As with many sports injuries, it is painful and devastating and best managed by PREVENTION!
Spring is here and as the days continue to get longer and temperatures begin a slow steady rise, athletes and weekend warriors are eager to get outdoors to play and exercise. However, be mindful of the weather (damp and rainy), temperature (cool mornings and evenings) and winter “dust” on your muscles and tendons. Many overjealous fitness enthusiasts will rush to pound the pavement and barely “fit in” a warm-up before participating. But, no matter how limited time is, skipping the warm-up is risky.
This time of year, one can expect to feel a little cold and stiff, especially if you are over 40, and therefore a little caution and preparation are in order to avoid muscle/tendon strain, or worse yet, muscle/tendon tears. The Achilles tendon is one of the more common tendons torn. Prevention of muscle tears, including the Achilles tendon includes; gradual introduction to new activities, good overall conditioning, sport specific training, pre-stretch warm-up, stretch, strengthening, proper shoes, clothing, and equipment for the sport and conditions.
A muscle contracts to move bones and joints in the body. The tendon is the fibrous tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Great force is transmitted across a tendon which, in the lower body, can be more than 5 times your body weight. Often, a tendon can become inflamed, irritated, strained or partially torn from improper mechanics or overuse. Although infrequent, occasionally tendons can also snap or rupture. A tendon is more vulnerable to a rupture for several reasons such as a history of repeated injections of steroids into a tendon and use of medications such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics. Certain diseases such as gout, arthritis, diabetes or hyperparathyroidism can contribute to tendon tears. Also, age, obesity and gender are significant risk factors as middle-aged, overweight males are more susceptible to tendon tears. Poor conditioning, improper warm-up and cold temperatures may also contribute to the problem.
Tendon rupture is very painful and debilitating and must not be left untreated. While conservative management is preferred, surgical management is usually required for complete tears. The purpose of this column is to present the signs, symptoms and management of Achilles tendon ruptures.
The Achilles tendon (also called the calcaneal tendon), is a large, strong cordlike band of fibrous tissue in the back of the ankle. The tendon (also called the heel cord) connects the powerful calf muscle to the heel bone (also called the calcaneus). When the calf muscle contracts, (as when you walk on the ball of your foot), the Achilles tendon is tightened, tension is created at the heel and the foot points down like pushing a gas pedal or walking on tip of your toes. This motion is essential for activities such as walking, running, and jumping. A partial tear of the tendon would make these activities weak and painful, while a full tear through the tendon would render these activities impossible.
With age, the Achilles tendon (and other tendons) gets weak, thin, and dehydrated, thus making it prone to inflammation, degeneration, partial tear or rupture. The middle-aged weekend warrior is at greatest risk. A full or complete tear (Achilles tendon rupture) usually occurs about 2 inches above the heel bone and is associated with a sudden burst of activity followed by a quick stop or a quick start or change in direction, as in tennis, racquet ball, and basketball.
In some instances, the tendon can be injured by a violent contraction of calf when you push off forcefully at the same time the knee is locked straight as in a sudden sprint. Other times, the tendon is injured when a sudden and unexpected force occurs as in a trip off a curb or sudden step into a hole or a quick attempt to break a fall.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
Next Week: Achilles tendon Part II of II
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
