April is National Stress and Anxiety Awareness Month! According to the National Institutes of Health, an estimated 19.1% of U.S. adults 18 and older had an anxiety disorder in the past year. Anxiety disorders were higher for females (23.4%) than for males (14.3%). An estimated 31.1% of U.S. adults experience an anxiety disorder at some time in their lives.
There are a wide variety of anxiety disorders and will vary by the objects or situations that induce them. However, the features of excessive anxiety and related behavioral disturbances are similar. Anxiety disorders can interfere with daily activities such as job performance, schoolwork, and relationships. Symptoms include: distress, nausea, shortness of breath, bowel pattern changes, excessive perspiration, frequent laughing or crying, restlessness, and is often associated with depression. While there are many types and degrees of anxiety and there is no substitute for medical and psychological care, there are some simple and basic tools to help manage the problem…daily exercise is one easy, affordable and accessible suggestion for most. Multiple studies have discussed the incidence of unhealthy self management of anxiety, including the use of alcohol and recreational drugs.
Last week, I presented coping tips for the management of anxiety. In this column, I will discuss one of the most understated benefits of exercise – mental health! Specifically, aerobic exercise (exercise that increases your heart rate for 30 minutes or more) such as walking, biking, running, swimming, hiking, elliptical & stepper machines to name a few, is the secret to “runner’s high.” This exercise euphoria is not limited to runners alone, but all who engage in aerobic exercise are more likely to experience high energy, positive attitude and mental wellness.
Physical activity, specifically aerobic exercise, is a scientifically proven useful tool for preventing and easing anxiety and depression symptoms. Studies in the British Journal of Medicine and the Journal of Exercise and Sports Science found that anxiety and depression scores were significantly reduced in groups that engaged in aerobic running, jogging or walking programs, 30-45 minutes 3-5 days per week for 10-12 weeks, when compared to a control group and a psychotherapy counseling group.
According to research reported in sports medicine journals, exercise reduces anxiety and depression in two ways, psychologically (mentally) and physiological (physically).
SOURCES: University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC); National Institutes of Health (NIH); The American Journal of Sports Medicine
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

As summer fads and cool fall nights are upon us, many of us will prepare to put away some of our warm weather toys…closing the pool, storing kayaks and boats and packing up the “slip and slide.” However, one activity that can last well into the fresh breeze of fall is cycling. In fact, many feel that fall is the best time of year to jump on a bike and enjoy the ride! If you are looking for a kick start to riding your bike this fall, consider the 20th and final Tour de Scranton on Sunday, April 15, 2024. It is a fun-filled, noncompetitive bike ride through Scranton and neighboring communities. Tom and Betty Moreken, with the help of dedicated friends and countless supporters have raised over $400,000.00 to benefit addiction treatment and prevention in honor of their daughter Erin, a victim of drug addiction. I have had the privilege to know Tom and Betty and have always admired their resilience and selflessness to turn a negative into a positive and do something good for others. They and their friends truly represent everything that is good about the people of NEPA!
So dust off your bikes and join the fun at Tour de Scranton. Hopefully, it will entice you to ride the many beautiful and well-maintained trails that are available at the Countryside Conservancy and other locations in the Abingtons and the Lackawanna Heritage Valley Authority.
Tour de Scranton is the official “kick off” to biking season in NEPA. This year, on Sunday, September 15th, the 20th annual and final Tour de Scranton will offer a selection of several routes and distances for the novice and experienced rider at its non-competitive bike ride for riders of every age and skill level. This event supports “The Erin Jessica Moreken Drug & Alcohol Treatment Fund” which provides charitable gifts to qualified local organizations or individuals struggling with the disease of addiction. For more information visit: www.tourdescranton.com.
There are many obvious reasons to bike…cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, improve leg strength and others. But, the real question is, “what are the advantages of biking over other forms of exercise?” Glad you asked…
Prevention is the best management of musculoskeletal problems associated with biking. First, many of the problems associated with biking such as knee pain, buttock soreness, and tendonitis can be prevented through proper fitting. Furthermore, it is important that your equipment be in good working order such as tires, chain, brakes and pedals. Next, be sure to maintain a fairly good fitness level in order to bike safely. If you are a beginner, start slowly. Warm up and slowly bike for 10 to 15 minutes and build up over time. Practice the coordination of stopping, starting, shifting and braking. Work on good strength and flexibility of the hamstrings, quadriceps, calves and gluteal muscles. All of these muscles are necessary to generate pedal force. Balance is also important to safety and can be practiced on and off the bike. Be aware that adaptive equipment can modify your bike for added comfort and safety such as soft handlebar tape, seat post and front fork shock absorbers, padded biking shorts, c-out and gel pad saddle seats, and wider tires.
Be careful not to progress too quickly because inactivity to over activity in a short period of time can create problems. Overuse injuries such as tendonitis, can be avoided by cross training. Bike every other day and walk, run or swim on off days. Make sure to take time off to recover after a long ride. Use ice and massage to sore muscles and joints after riding.
Remember, cycling should be fun! Pain from improperly fitted and poorly maintained equipment is preventable. Excessive workouts and training rides should be kept to a minimum and consider cross-training in between.
EQUIPMENT: Helmets are a must! Also, keep your bike in good condition. Road bikes should have mirrors and reflectors. Use hand signals and obey traffic rules. Dress for weather and visibility. Have a first aid and tire patch kit, tire pump and tools. Seat comfort can be improved with gel cushion or split seat.
BE ALERT: for traffic, parked cars, pedestrians loose gravel and cracks in the road.
SOURCES: American Physical Therapy Association
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, and exercise regularly

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Like many of you, I have always enjoyed the outdoors...walking, running, biking, hiking etc. However, recently, I have been more concerned about my safety, (getting older and more cautious) when doing these activities on the side of the road.
Almost 15 percent of all motor vehicle injuries to people happened to those not in cars but while walking, running or hiking. In fact, over 4,000 walkers or runners were fatally hit by a motor vehicle according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). These statistics continue to increase as the number of distractions to drivers increases (phone calls, texts, etc). Consequently, walkers, runners and cyclists must be more aware than ever to prevent injury from motor vehicles.
Source: http://www.runnersworld.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician.
For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles visit: http://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/form
May is National Bike Month! In fact, Saturday, May 7, 2022 Lackawanna Heritage Valley’s Heritage Explorer Bike Tour is returning in person for the first time since 2019. For those who have a bike, now might be a good time to dust it off and enjoy the many beautiful and well-maintained trails that are available at the Countryside Conservancy at Lackawanna State Park, other locations in the Abingtons or the Lackawanna Heritage Valley Authority. For those who don’t have a bike, it might be a good time to get one!
There are many obvious reasons to bike…cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, improve leg strength and others. But, the real question is, “what are the advantages of biking over other forms of exercise?” Glad you asked…
Prevention is the best management of musculoskeletal problems associated with biking. First, many of the problems associated with biking such as knee pain, buttock soreness, and tendonitis can be prevented through proper fitting. Furthermore, it is important that your equipment be in good working order such as tires, chain, brakes and pedals. Next, be sure to maintain a fairly good fitness level in order to bike safely. If you are a beginner, start slowly. Warm up and slowly bike for 10 to 15 minutes and build up over time. Practice the coordination of stopping, starting, shifting and braking. Work on good strength and flexibility of the hamstrings, quadriceps, calves and gluteal muscles. All of these muscles are necessary to generate pedal force. Balance is also important to safety and can be practiced on and off the bike. Be aware that adaptive equipment can modify your bike for added comfort and safety such as soft handlebar tape, seat post and front fork shock absorbers, padded biking shorts, c-out and gel pad saddle seats, and wider tires.
Be careful not to progress too quickly because inactivity to over activity in a short period of time can create problems. Overuse injuries such as tendonitis, can be avoided by cross training. Bike every other day and walk, run or swim on off days. Make sure to take time off to recover after a long ride. Use ice and massage to sore muscles and joints after riding.
Remember, cycling should be fun! Pain from improperly fitted and poorly maintained equipment is preventable. Excessive workouts and training rides should be kept to a minimum and consider cross-training in between.
EQUIPMENT: Helmets are a must! Also, keep your bike in good condition. Road bikes should have mirrors and reflectors. Use hand signals and obey traffic rules. Dress for weather and visibility. Have a first aid and tire patch kit, tire pump and tools. Seat comfort can be improved with gel cushion or split seat.
BE ALERT: for traffic, parked cars, pedestrians loose gravel and cracks in the road.
SOURCES: American Physical Therapy Association
According to the New York Times, there is a shortage and backorder of bicycles this summer due to COVID-19, especially in the cities where public transportation is discouraged. Fortunately, in NEPA, the problem is not so extreme. For those who have a bike, now might be a good time to dust them off and enjoy the many beautiful and well-maintained trails are available at the Countryside Conservancy at Lackawanna State Park, other locations in the Abingtons or the Lackawanna Heritage Valley Authority.
However, whether you head out for 5 or 50 miles, ensuring a proper bike fit should be on your checklist. Riding a bicycle that is properly fit to your style and body will not only help to prevent injury, but allow for a more comfortable riding experience. There are many things to take into consideration when checking your bike fit. First and foremost you must choose a bike that fits your style of riding.
For the sake of simplicity 3 basic styles of bikes include Road bikes, Hybrid bikes and Mountain bikes. Road bikes are designed for long distance riders, hybrid bicycles can be used for longer distance riders, but usually accommodates a recreational cyclist, and mountain bikes are designed for dirt or gravel and technical trails. The next component of ensuring a proper bike fit is making sure that you have a good foundation by choosing the right sized frame. To find the right sized frame you can use the following guidelines as a way to start or simply ask the local bike shop or bike fit consultant of your choice for help.
Road bikes: When straddling the bike you should have about 1” of clearance between your body and the top tube if the bike has a straight top tube (which runs parallel to the ground). When lifting the bike you should have 1” clearance between the tires and the ground. If the bike has a sloping top tube (semi-compact design) you should have a clearance of 2” or more.
Mountain bikes: When straddling the bike lift the bike off the ground and you should have a minimum of 2” clearance between the ground and the tires. With full suspension bikes you will want 1”-2” standover clearance because when you sit on the bike the frame will become lower from compressing the suspension. More aggressive riders will likely have 3”-5” of clearance.
Comfort bikes: Standing over a comfort bike to chose the right sized frame is not necessary. They are commonly designed with a steep sloping top tube and allow the rider to put feet firmly on the ground when the rider comes to a stop.
Now that you have right size for your bike you should adjust the components of the bike to allow for a more comfortable riding experience. Please use the diagram as a point of reference for the following tips. Also be sure to reexamine your bike fit after any bad falls. Keep in mind these measurements are meant to be used as a simple guideline and if you have any pre existing injuries or concerns please be sure to consult your local Physical Therapist or bike fit consultant.
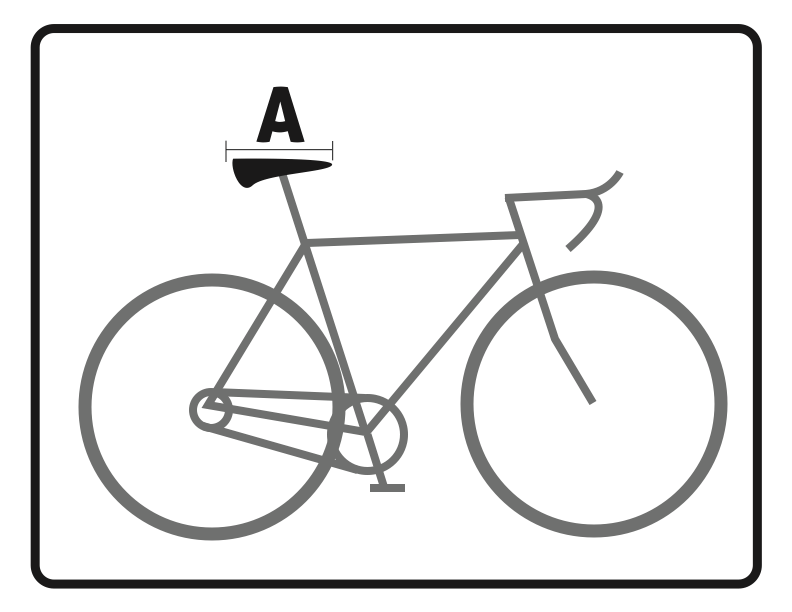
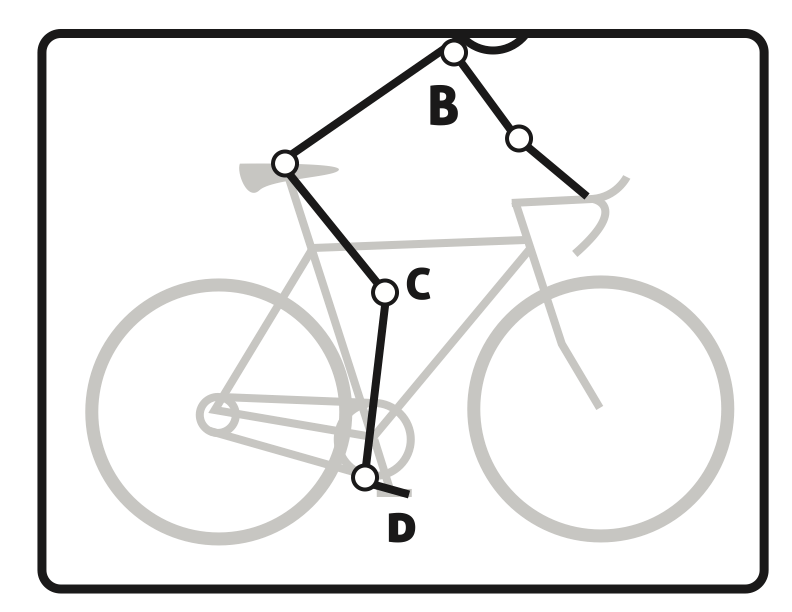
Handlebars (HB)
Knee to Pedal
Foot to Pedal
If you are a recreational cyclist it’s a good idea to take all the proper steps in preventing injury. This article can be used as a reference point to help to prevent common cycling injuries, enhance your comfort and improve your riding efficiency. If you have any further questions about enhancing your bike fit please contact your local physical therapist or bike fit consultant.
Sources: REI.com APTA.org
CoAuthor: Sarah Singer, PTA is a physical therapist assistant at Mackarey Physical Therapy, specializing in orthopedic and sports rehab.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” at https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum/
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com. Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice in downtown Scranton and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
According to the New York Times, there is a shortage and backorder of bicycles this summer due to COVID-19, especially in the cities where public transportation is discouraged. Fortunately, in NEPA, the problem is not so extreme. For those who have a bike, now might be a good time to dust them off and enjoy the many beautiful and well-maintained trails are available at the Countryside Conservancy at Lackawanna State Park, other locations in the Abingtons or the Lackawanna Heritage Valley Authority.
There are many obvious reasons to bike…cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, improve leg strength and others. But, the real question is, “what are the advantages of biking over other forms of exercise?” Glad you asked…
Prevention is the best management of musculoskeletal problems associated with biking. First, many of the problems associated with biking such as knee pain, buttock soreness, and tendonitis can be prevented through proper fitting. Furthermore, it is important that your equipment be in good working order such as tires, chain, brakes and pedals. Next, be sure to maintain a fairly good fitness level in order to bike safely. If you are a beginner, start slowly. Warm up and slowly bike for 10 to 15 minutes and build up over time. Practice the coordination of stopping, starting, shifting and braking. Work on good strength and flexibility of the hamstrings, quadriceps, calves and gluteal muscles. All of these muscles are necessary to generate pedal force. Balance is also important to safety and can be practiced on and off the bike. Be aware that adaptive equipment can modify your bike for added comfort and safety such as soft handlebar tape, seat post and front fork shock absorbers, padded biking shorts, c-out and gel pad saddle seats, and wider tires.
Be careful not to progress too quickly because inactivity to over activity in a short period of time can create problems. Overuse injuries such as tendonitis, can be avoided by cross training. Bike every other day and walk, run or swim on off days. Make sure to take time off to recover after a long ride. Use ice and massage to sore muscles and joints after riding.
Remember, cycling should be fun! Pain from improperly fitted and poorly maintained equipment is preventable. Excessive workouts and training rides should be kept to a minimum and consider cross-training in between.
EQUIPMENT: Helmets are a must! Also, keep your bike in good condition. Road bikes should have mirrors and reflectors. Use hand signals and obey traffic rules. Dress for weather and visibility. Have a first aid and tire patch kit, tire pump and tools. Seat comfort can be improved with gel cushion or split seat.
BE ALERT: for traffic, parked cars, pedestrians loose gravel and cracks in the road.
SOURCES: American Physical Therapy Association
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, and exercise regularly

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” at https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/forum/ or visit our website at https://mackareyphysicaltherapy.com/
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice in downtown Scranton and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.