The “first Thanksgiving” was in 1621 between the Pilgrims of Plymouth Colony and the Wampanoag tribe in present day Massachusetts to celebrate the harvest and other blessings of the previous year. In 1789, President George Washington, at the request of Congress, proclaimed Thursday, November 26, as a day of national thanksgiving. In 1863, Abraham Lincoln proclaimed the national holiday of Thanksgiving to be the last Thursday of November.
Americans and Canadians continue to celebrate this holiday as a time for family and friends to gather, feast, and reflect upon their many blessings. Like most, I am very grateful for the simple things; family, good friends, food, shelter, and health. It turns out that being grateful is, not only reflective and cleansing; it is also good for your health!
Grateful people are more likely to behave in a prosocial manner, even when it is not reciprocated. A study by the University of Kentucky found those ranking higher on gratitude scales were less likely to retaliate against others, even when others were less kind. Emmons and McCullough conducted one of the most detailed studies on thankfulness. They monitored the happiness of a group of people after they performed the following exercise:
There are many things in our lives, both large and small, that we might be grateful about. Think back over the past week and write down on the lines below up to five things in your life that you are grateful or thankful for.” The study showed that people who are encouraged to think of things they’re grateful for are approximately 10% happier than those who are not.
Amy Morin, psychotherapist, mental health trainer and bestselling author offers this advice: “Developing an “attitude of gratitude” is one of the simplest ways to improve your satisfaction with life. We all have the ability and opportunity to cultivate gratitude. Simply take a few moments to focus on all that you have, rather than complain about all the things you think you deserve.” So…be grateful and have a happy Thanksgiving!
Source: NIH, Forbes, Amy Morin “13 Things Mentally Strong People Don’t Do.”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
November is National Hospice Month! During this time, we celebrate the tireless work of the hospice professionals who assist patients and their families during the weeks and months that they journey with a serious or terminal illness.
However, in addition to the service of providing pain and symptom management, assisting with personal care, providing volunteer, counseling and social work services, there may be many other services that your local hospice program may be able to offer to patients, families and caregivers alike.
Please keep in mind that each hospice agency provides unique services to the community. Before you decide, it is important to reach out and ask which agency offers services that best meet your needs.
Some community support programs that are offered by hospice agencies that are routinely available include:
Bereavement Support ---Dealing with the death of a loved one can be a difficult and often lonely endeavor. All hospice agencies offer bereavement services to families of patients that have died. In addition, many hospices offer community support programming to help those who have suffered a loss. Some support programs are in groups, but often individualized help is available. Most times the bereavement services for the community are without charge.
Pet Bereavement Support---The death of a pet can often be quite traumatizing, especially when the pet has been a long-standing member of the family. Hospice agencies are offering bereavement counseling for those who suffered the loss of a pet. Call and reach out if you have suffered a loss and require support.
Dementia Support Groups--- Nancy Reagan always referred to the diagnosis of President Reagan as the ‘long goodbye’. Dealing with a loved one suffering with dementia is difficult---but you do not have to deal with this alone. Many hospices have dementia support groups that educate, support and guide.
Supporting Children through a Loss---Often it is difficult for children to understand or process the death of a parent, sibling, and grandparent or loved one. There are specialized programs for children to understand and live with the loss----developing a new normal. These programs are usually done in a series of 5 sessions so that proper education and guidance can be accomplished.
Community Education Series--- Not only are your local hospices taking the lead to advance end of life care, but many are helping to educate the professional and lay community alike. Ask about monthly seminars, educational programs and other topics of interest to you and your family/co-workers.
Memorial Services--- Hospice agencies routinely celebrate the lives of those patients who have died within the last 6 months or a year. Surrounding yourself with others who have suffered a loss can often be healing and certainly supportive. Call and ask your local hospice about planned memorial services that honor lives well lived through prayer and testimonials.
Volunteer opportunities---There can be no better way to give back to your community than through volunteering opportunities. Hospice offers a wide array of ways to volunteer ranging from direct patient contact to more administrative tasks. Whatever the job, the act of volunteering is what makes hospice care so special.
Mentoring Programs--- As hospice programs are traditionally interdisciplinary in approach; students working with hospice programs are provided an optimal environment to learn not only hospice care, but also the ever-important concept of team. Many hospice agencies work with students regularly from nursing schools, universities and our local medical college.
Transitions Program--- Often patients are referred for hospice services, but do not meet eligibility requirements for this level of care. However, many hospice agencies offer a transitions program, which is a volunteer supported program to monitor the frail elderly in the community and reporting changes back to the physician for advice and guidance. These programs are free of charge, volunteer supported and a valuable asset for the independent senior who may need that extra set of eyes and ears of a skilled volunteer.
So, in honor of National Hospice Month, we say, thank you to all the hospice professionals, volunteers and families who work so diligently to care for those in our community with a serious or terminal illness. But remember too, that your local hospice agency can be a wonderful resource for education, mentoring, dementia support and grief counseling. Ask questions, attend a seminar, inquire about memorial services or look for support when caring for a loved one with dementia. Help, support, guidance and education are available----just make the call to your local hospice agency.
To find out which hospices serve your community, call NHPCO’s HelpLine at 1-800-658-8898 or visit www.caringinfo.org/findahospice.
Medical Contributor: Ralph DeMario, MD, Former CMO, Hospice of the Sacred Heart

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

November is National Hospice Month! Each November, the community of hospice and palliative care professionals celebrates National Hospice Month. Although, at first glance, spotlighting the concept of death and dying may seem a bit gloomy. It’s actually the concept of quality of life and the focus on living that is truly being celebrated.
It is true that hospice serves those patients and their families who are on the journey of a serious or terminal illness. But as any hospice professional from the nurse to the social worker to the volunteer to the pastoral counselor will attest------our focus is ALWAYS on the value of life being maintained and the quality of living for each and every one of our patients.
Placing the focal point of hospice care on living, instead of dying, enables the patient and family to focus on:
Remember that your hospice team will make suggestions to improve your pain and symptoms, all with the ultimate goal of allowing you to live your life as fully and functionally as possible. Pain alleviation will allow for improved activities, help with personal care will conserve energy for visiting with family and friends, and allowing a volunteer into your home will give caregivers much needed time for rest and relaxation.
There are a number of myths surrounding hospice care----and this is good a time as ever to help dispel them…
Myth #1--- Hospice is for patients in the last days of their lives.
Actually, hospice care was designed to care for patients and their families for the last 6 months of their lives----the longer patients are under the care of hospice professionals, the better their symptoms are controlled and the better their quality of living.
Myth #2--- Pain medications are given in large doses to sedate the patient and hasten death…..
Pain medications are used in small of doses as required to control pain, and to maintain patients’ alertness, always focusing on living life to the fullest. Medications are never given to hasten death, only to control pain and maintain quality of life.
Myth #3--- Once patients start hospice services, death will come soon….
The statistics on this issue are interesting. In a major study, patients who received hospice care for congestive heart failure actually lived 29 days longer!!! Also, on average 15% of patients are actually discharged from hospice services because of significant improvement in symptoms.
Myth #4--- Patients receiving hospice services cannot leave the home or travel….
The truth is that patients receiving hospice care can drive, travel as able, go to bingo/hairdresser/casino----actually come and go as they are able. So the goal is to improve symptoms so that patients can enjoy their lives as fully as possible while on the journey of a serious illness.
Although the topic of death and dying has been rather taboo in the US, hospice professionals celebrate the living potential that their patients still have. The focus is on quality of relationships, maintaining a functional lifestyle and living the life they were meant to live. Hospice professionals also celebrate the many lives they have improved, all the lives they have touched and the fact that they were chosen to dedicate their professional lives to helping others live more fully……
To find out which hospices serve your community, call NHPCO’s HelpLine at 1-800-658-8898 or visit www.caringinfo.org/findahospice
Medical Contributor: Ralph DeMario, MD, Former CMO, Hospice of the Sacred Heart

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.comPaul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Recently, two patients asked me when I thought it would be safe for them to return to their exercise programs after abdominal surgery. She stated that she was not sure how to properly and safely implement or return to her program.
This column will attempt to ensure a safe return to activity and exercise following general surgery such as gall bladder, appendix, hernia, etc. The post-operative patient has many questions: When is it safe to begin an exercise program? How do I begin? What is the best exercise? Which exercises are best? How do I know if the activity is too intense or not intense enough? Are there safe guidelines?
Before you begin, discuss your intention to exercise with your surgeon and primary care physician. Get medical clearance to make sure you can exercise safely. With the exception of short daily walks, don’t be disappointed if your surgeon requires you to wait at least until your 6 week post-op check-up to begin exercise.
While a 60 minute workout would be the long term goal, begin slowly at 15-20-30 minutes and add a few minutes each week. Make time to warm up and cool down.
Warm-up 5-10 minutes
Strength Training 10-15-20 minutes
Aerobic 10-15-20 minutes
Cool down 5-10 minutes
How to Monitor Your Exercise Program:
First, determine your resting heart rate by taking your HR (pulse) using your index finger on the thumb side of your wrist for 30 seconds and multiply it by two. 80 beats per minute is considered a normal HR but it varies. This is a good baseline to use as a goal to return to upon completion of your workout. For example, your HR may increase to 150 during exercise, but you want to return to your pre exercise HR (80) within 3-5 minutes after you complete the workout.
For those who are healthy, calculating your target heart rate (HR) is an easy and useful tool to monitor exercise intensity.
220 – Your Age = Maximum Heart Rate
EXAMPLE for a 45 year old: 220 – 45 = 175 beats per minute should not be exceeded during exercise.
For those concerned about calories expended during exercise.
NOTE: Keep the level at a light/moderate level for the first four to six weeks and advance to the moderate/heavy at week six. The Very Heavy Level may not be appropriate for 12 weeks post op is for those who have a reasonable fitness level and exercise 4-5 days per week.
Example of Data Found on Fitness Equipment
Remember, this is only accurate if you program your correct height, weight and age.
Level kCal/min MET
Light 2 - 4.9 1.6 – 3.9
Moderate 5 - 7.4 4 – 5.9
Heavy 7.5 - 9.9 6 - 7.9
Very Heavy 10 - 12.4 8 – 9.9
Always secure physician approval before engaging in an exercise program.
If the patient is on beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol, etc), it is important to use the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale (RPE) scale to determine safe exercise stress since exercise will not increase HR as expected:
0 - Nothing at all
1 - Very light
2 - Light
3 - Moderate
4 - Somewhat intense
5 - Intense (heavy)
6
7 - Very intense
8
9 - Very, very intense
10 - Maximum Intensity
NOTE: Keep the RPE at 2-3 the first 6 weeks post op and advance to level 3-4 at 8-12 weeks post op. Levels 5-6-7 are for those with a reasonable fitness level and exercise 4-5 days per week. The advanced levels should not be attained until 2-3 months of exercise and 3-4 months post op.
MEDICAL CONTRIBUTOR: Timothy Farrell, MD, is a general surgeon at GCMC.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Osteochondritis dissecans, also called OCD, is the most common cause of a loose body or fragment in the knee and is usually found in young males between the ages of ten and twenty. While this word sounds like a mouth full, breaking down its Latin derivation to its simplest terms makes it understandable: “osteo” means bone, “chondro” means cartilage, “itis” means inflammation, and “dissecans” means dissect or separate. In OCD, a flap of cartilage with a thin layer of bone separates from the end of the bone. As the flap floats loosely in the joint, it becomes inflamed, painful and disrupts the normal function of the joint.
Typically, OCD is found in the knee joint of active young men who participate in sports which involve jumping or full contact. Although less common, it is also found in other joints such as the elbow.
Often, the exact cause of OCD is unknown. For a variety of reasons, blood flow to the small segment at the end of the bone lessens and the weak tissue breaks away and becomes a source of pain in the joint. Long term, OCD can increase the risk of osteoarthritis in the involved joint.
To properly diagnose OCD a physician will consider onset, related activities, symptoms, medical history, and examine the joint involved for pain, tenderness, loss of strength and limited range of motion. Often, a referral to a specialist such as an orthopedic surgeon for further examination is necessary. Special tests specifically detect a defect in the bone or cartilage of the joint such as:
Radiograph (X-ray) may be performed to assess the bones.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may be performed to assess bones and other soft tissues such as cartilage, ligaments, muscles and tendons.
The primary goal of treatment for OCD is to relieve pain, control swelling, and restore the complete function (strength and range of motion) of the joint. The age of the patient and severity of the injury determine the treatment methods. For example, medications assist with pain and inflammation reduction.
Young patients who are still growing have a good chance of healing with conservative treatment. Rest and physical therapy are the conservative treatments of choice. Rest entails avoiding any activity that compresses the joint such as jumping, running, twisting, squatting, etc. In some cases, using a splint, brace and crutches to protect the joint and eliminate full weight bearing, may be necessary for a few weeks. Physical therapy, either as a conservative or post operative treatment, involves restoring the range of motion with stretching exercises and improving the strength and stability of the joint through strengthening exercises. Modalities for pain and swelling such as heat, cold, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, compression devices assist with treatment depending on the age of the patient and severity of the problem.
Conservative treatment can often require 3 to 6 months to be effective. However, if it fails, arthroscopic surgery stimulates healing or reattaches the loose fragment of cartilage and bone. In some cases if the defect is small, surgery involves filling in the defect with small bundles of cartilage. In other cases, the fragment is reattached directly to the defect using a small screw or bioabsorbable device. More recently, surgeons are using the bone marrow of the patient to repair the deficit by stimulating the growth of new tissue (bone marrow stimulation).
In other cases, a plug of healthy tissue from the non-weight bearing surface of a patient's knee relocated to the defect to stimulate healing (osteochondral autograft transplantation OATS). While there are many surgical options for OCD, an orthopedic surgeon will help the patient decide the most appropriate procedure based on age, size of defect, and other factors.
While prevention is not always possible, some measures can be taken to limit risk. For example, if a child playing sports has a father and older brother who had OCD, then it would be wise to consider the following: Avoid or make modifications for sports requiring constant jumping. Cross-train for a sport to avoid daily trauma (run one day and bike the next). Also, do not play the sport all year round (basketball in the fall/winter and baseball in the spring/summer). Seek the advice from an orthopedic or sports physical therapist to learn proper strength and conditioning techniques. Learn proper biomechanics of lifting, throwing, squatting, running, jumping and landing.
Sources: Mayo Clinic

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Fall has arrived in NEPA and walking is a great way to enjoy the fall foliage. Moreover, a new study has found that walking can reduce lower back pain. Researchers in Australia followed more than 700 adults who had a recent onset of lower back pain (and were able to bear full weight without associated leg symptoms) and enrolled them in a walking program under the supervision of a physical therapist. One group walked for 30 minutes, 3-5 times per week and the control group remained inactive. Both groups were followed for more than three years and discovered that the inactive control group was twice as likely to suffer from repeated flare-ups of lower back pain when compared to the walking group.
It is good news for those who enjoy walking, however, for many who have not maintained an active lifestyle or have health issues, it is challenging to know where to begin. Also, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program too aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning yourself into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
Walking to reduce or control lower back pain is only one of many important reasons to begin a program. According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen-minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
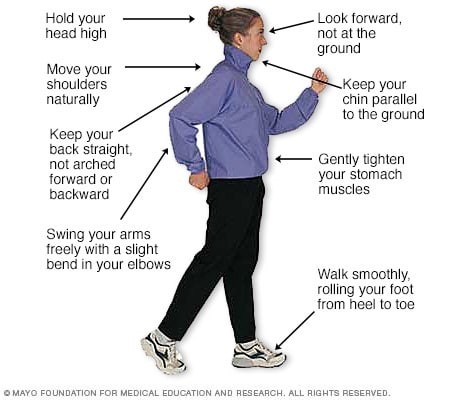
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic, “Health & Science New”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Age-related changes to your body are normal and expected. For example, loss of muscle tone, stiffness in joints, and loss of balance. With effort, some of these changes can be retarded and managed with stretching, strengthening and balance exercises. The brain is no different…it can slow down and lead to memory lapses. However, for most of us, it too can be managed and with a little effort, be kept sharp and clear.
Many experts feel that exercise is the best method to maintain not only physical health but mental health. Regular exercise can prevent the things that contribute to memory loss with age such as; diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity and stroke.
Specifically, aerobic exercise may be most beneficial. Aerobic exercise is any type of sustained exercise that strengthens the heart and lungs to improve the body’s use of oxygen. This may include running/jogging, brisk walking, cycling, swimming, rowing, and the use of a treadmill, elliptical, stepper or similar device, at light to moderate intensity which requires the use of oxygen to adequately meet the oxygen demands of the body for an extended period of time. The generally accepted time and frequency is at least 30 minute sessions performed three or more times per week. Two 15 minute or three 10 minute sessions are also valuable. For those with back, hip, knee and other lower body pain, consider low-impact or partial weight-bearing activities such as a recumbent bike or stepper or upright bike instead of a treadmill.
The benefits of a healthy diet are well-documented. Specifically, a Mediterranean-style diet comes highly recommended. It focuses on plenty of fruits and vegetables with fish instead of red meat and olive oil instead of butter. Researchers found people who closely adhered to a Mediterranean diet were nearly 20% less likely to have thinking and memory problems.
Exercise your brain just as you do your body. Make time each day to challenge your brain. Learn something new to keep your mind sharp. Play cards, read a book, do crossword puzzles or other word games, take a class or learn play a musical instrument.
Human beings are social animals and in the right setting, we stimulate and challenge each other. Join a book club, fitness center, or a community center. Consider volunteering, taking an art or photography class. Social interaction can prevent isolation which can lead to depression and depression is associated with dementia.
Without adequate sleep, attention and concentration is compromised. Studies show that those who have normal restful sleep outperform those who are restless and sleep deprived. Some tips for better sleep are: avoid big meals before bed, keep a consistent sleep and wake up time, avoid nicotine, caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime. “
Consider an afternoon “power nap!” Recent studies show that an afternoon nap was rejuvenating to the mind and body. Participants improved on mental skills such as memory, calculation, orientation and attention.
Cortisol is the hormone associated with stress. Recent studies have found that elevated cortisol levels were associated with poorer overall cognitive functioning, including memory, language, and processing speed.
Try yoga, massage, breathing techniques to relax. Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) techniques can be very effective…try it on YouTube!
Smoking is clearly one of the worst things you can do to your body AND MIND! Smoking can lead to early memory lose in part due to small strokes in the brain. Do whatever it takes to quit; nicotine replacement, medication, or counseling.
There are many medical conditions and medications associated with memory loss. Regular medical check-ups can prevent, diagnose and treat some of these conditions such as; depression, diabetes, thyroid disease, vitamin deficiencies, and drug interactions or side effects. For example, sleep aid and anxiety drugs associate with memory loss.
In addition to common tricks such as word association, sticky notes, use your smart phone for appointments and reminders. If you don’t know how to use a smart phone, it is time to learn something new…and that is a healthy brain activity!
SOURCES: WebMD; Harvard Health

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

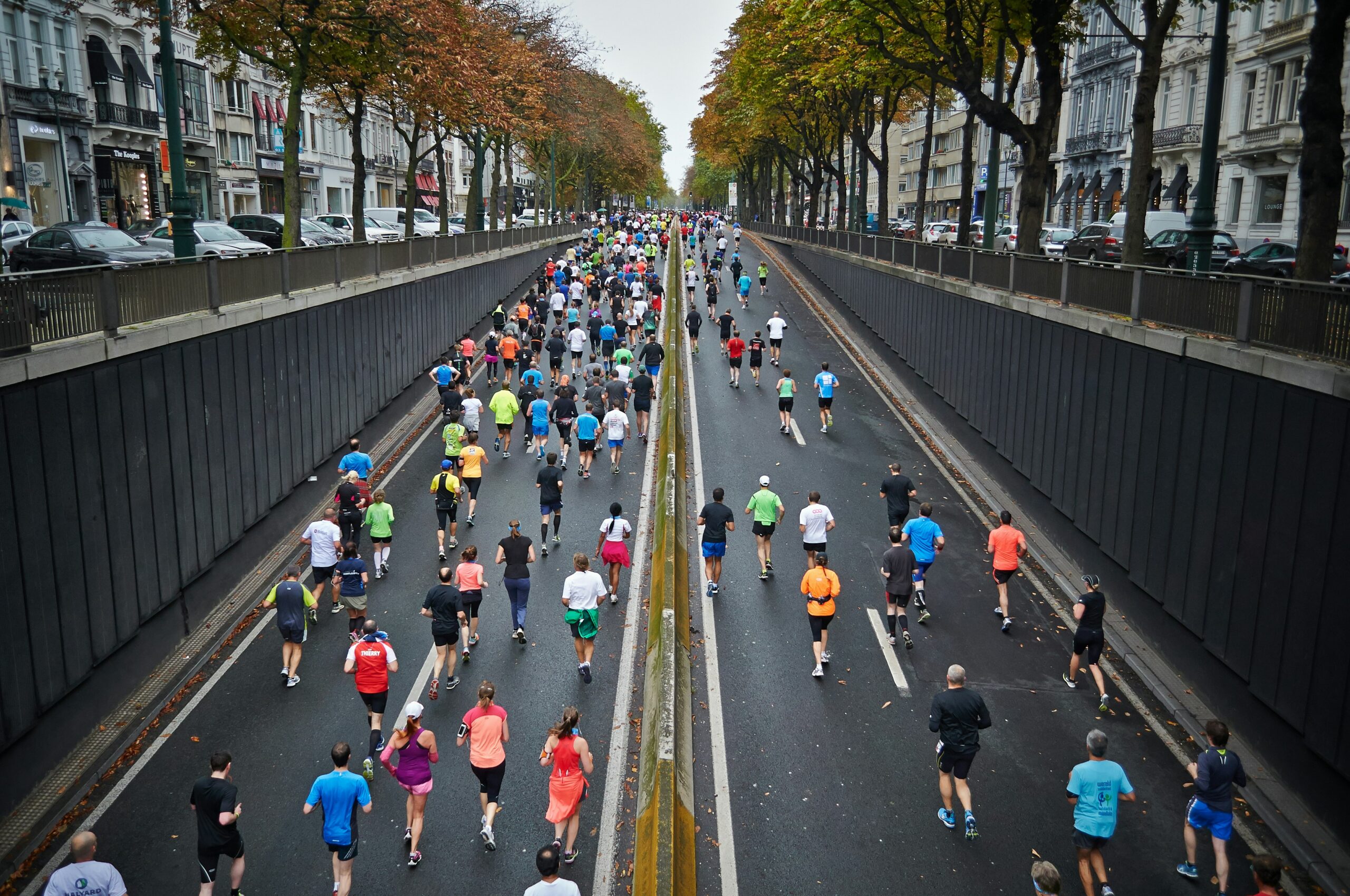
Congratulations to more than 1,000 courageous runners who finished the 27th Annual Steamtown Marathon today. Most, if not all of you are waking up this morning with a little less jump in your step than you had yesterday.
As active people by nature, many of you will resist the logic of rest, despite the pain and stiffness in your muscles and joints. Therefore, I would like to offer some words of wisdom, based on science, to encourage you to adequately rest and allow your body to recover.
With adequate rest and recovery, an elite runner can quickly regain full form in 3-4 weeks, while an average runner may require 4-6 weeks. Meb Keflezighi, an elite American runner and winner of the 2014 Boston Marathon, is an excellent example of the merits of rest and recovery. However, he discovered it by accident…following the 2012 New York City Marathon, Meb developed a foot infection which required three weeks rest. With the Olympic Trials just 70 days away, Meb quickly regained his pre-injury fitness level to win the 2012 US Olympic Marathon Trials and join the US Olympic Team in London. It may be that his injury was fortuitous and allowed him adequate recovery time, (that he might not have otherwise allowed), preparing him for intensive training leading up to the trials.
The Effects of Running 26.2 Miles on the Body:
(RunNow.com - Jim Peskett)
One of the most obvious effects of running a marathon is significant muscle and joint pain and stiffness. It will set in after you sit for a while and attempt to get up and move around. For most, it will be more pronounced the day after the marathon, as you get out of bed and limp to the bathroom. Studies show that the leg muscles, (especially the calf muscles) display significant inflammation and necrosis (dead tissue) in the fibers of the muscle. In other words, the trauma to the muscles is so severe that tissue damage causes muscle cells to die. Consequently, studies found that muscle strength, power and endurance is compromised and required significant time to recover… sometimes as long as 4-6 weeks!
Additionally, many runners report severe bone and joint pain following the race. Some studies report findings of microfractures or bone bruising from the repeated and prolonged pounding of the marathon. It is purported that the stress on the joints may be related to: weight and body type, running shoes, running style and mechanics. While not dangerous, again, it is important to respect the stress placed on the body and allow adequate healing…LISTEN TO YOUR BODY!
Creatine kinase is an enzyme found in the brain, skeletal muscles and heart. It is found in elevated levels in the presence of cellular damage to these tissues, for example, following a heart attack. Similarly, significantly elevated creatine kinase levels are found in the blood of runners up to 4 days post marathon, demonstrating extensive tissue damage at the cellular level. It is important to note, that these enzyme markers are present, even if a runner does not experience muscle soreness. So, adequate rest for healing and recovery is required, regardless of soreness.
It is not a coincidence that the runners are more likely to contract colds and flu after intensive training or running 26.2 miles. The immune system is severely compromised after a marathon and without adequate recovery; a runner can become ill and ultimately lose more training time or will underperform.
FALSE: As stated above, enzyme levels that indicate cellular damage to the tissues are present in the post-marathon runner, even in those without significant pain.
FALSE: In addition to rest, drink, drink, drink - 24 ounces of water for every 2 pounds you lose after the marathon. This is based on pre and post exercise weight. You just burned 2,600 calories so avoid diet soft drinks. You need the glucose (sugar) boost. Also, don’t drink alcohol and use minimal amounts of caffeine (the equivalent of 1-2 cups of coffee). First, drink plenty of water and sports drinks (Gatorade) to prevent a diuretic like caffeine from messing up your fluid balance.
FALSE: Studies clearly show that the VO2 Max, (the best measurement of a runner’s endurance and fitness), is unchanged after one week of inactivity. And, after two weeks, the loss is less than 6% and can be regained quickly. Moreover, it is important to remember, without adequate rest and recovery, performance is comprised, not by the loss of VO2 Max, but by muscle-skeletal tissue damage, which renders the leg muscles of the runner weaker. Remember Meb Keflezighi!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

It is one week away from the 27th Steamtown Marathon. This column is dedicated to all the runners preparing for the big day. One small piece of advice; start slowly, avoid the first mile adrenaline sprint downhill, and enjoy the journey! Remember, only one Olympic marathon winner (Juan Zabala, Argentina, 1932) was in the lead at the 5 mile mark. Lesson: The last miles matter more than the first!
Today, I hope to address some common questions for the novice marathon runner or for those coming from other locations to run in the race. What should you pack? How should I dress? What supplies will I need?
Elite runners are so experienced that they know exactly what to pack in preparation for the big marathon day. However, those, running in marathon for the first or second time usually have lots of questions. First, what you need and what you can bring will depend on your support team. If you are running alone and will not have family or friends meeting you along the way, then you are limited to a fanny pack and a few supplies. If you have a support team, then they can carry a bag with supplies, meet you along the course and you can have a sense of security.
Remember; do not do anything different on race day. Try out special clothing, water with supplements and snacks on a practice run. Also, experiment with your best pre-race meal. You will be getting up at 5-6:00am to catch the bus from Scranton to Forest City. You may want to pack breakfast to eat in the high school gym such as; bagel, peanut butter, jelly, banana and coffee or Gatorade. Moving your bowels before the race is a must.
Dress: Columbus Day Weekend in NEPA could bring 30 to 40 degree temperatures when you catch the bus in Scranton and at the 8:00 am race starting time in Forest City.
Clothing:
Accessories:
If you don’t mind the little pack on your butt, a fanny pack can be valuable. In it, you will want supplies such as: small bandages, small roll of medical tape, ibuprofen, antacid tablets, small tube of lubricant, favorite running snack, and extra shoe laces. One might also consider packing a little money, credit card, ID, emergency contact numbers and medical insurance cards. A cell phone is optional.
your supply bag. In the bag, you might consider all of the above fanny pack items and: A change of clothes such as: extra running shoes, socks, shorts, shirt, water proof wind breaker, according to the weather, especially if rain is predicted. Towels, ace bandages, gauze pads and wrap, antibiotic cream, mole skin, sunscreen, petroleum jelly, safety pins, extra water and favorite sport drink, favorite sport snacks, extra ibuprofen, antacid, anti diarrhea medicine, chemical ice pack, mobile phone, money, credit cards, ID, medical insurance cards.
For those with allergic reactions, remember to pack: epinephrine, antihistamine, and other important medications.
Map and directions to the bus or starting line, course map, race number, and get your timing chip.
Enjoy! Enjoy! Smell the roses, take in the fall foliage and chat with a fellow racer. Savor the moment enjoy the day…you are doing something very special!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Like many of you, I have always enjoyed the outdoors...walking, running, biking, hiking etc. However, recently, I have been more concerned about being safe, (getting older and more cautious, distracted drivers) when doing these activities on the side of the road.
Almost 15 percent of all motor vehicle injuries to people happened to those not in cars but while walking, running or hiking, so one needs to be safe. In fact, over 4,000 walkers or runners were fatally hit by a motor vehicle according to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). These statistics continue to increase as the number of distractions to drivers increases (phone calls, texts, etc). Consequently, walkers, runners and cyclists must be more aware than ever to prevent injury from motor vehicles and stay safe.
Source: http://www.runnersworld.com
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
