Ice baths have become a new trend or fad in health and fitness, especially among elite athletes and some celebrities. In fact, it is impossible to scroll through social media without encountering someone “taking the frigid plunge!” However, it is far from a new treatment modality. The Ancient Greeks employed cold-water immersion for fever, pain relief, relaxation and socialization. In fact, Hippocrates documented the use of cold for medicinal purposes for its analgesic benefits.
Ice baths, a type of cryotherapy, is also referred to as cold water immersion (CWI) or cold-water therapy, involves immersing your body in ice water for approximately 5-15 minutes from the neck down at a temperature of 50-59 degrees. The ice baths are commonly used for pain, delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and inflammation and mood elevation.
In theory, the cold water lowers the temperature of your skin and body by vasoconstriction (narrow) of the blood vessels. When you get out of the cold water the vasodilatation (widen) of the blood vessels immediately brings fresh oxygen and nutrient-rich blood back to the tissues to warm the body and in the process, reduce pain, inflammation and promote healing.
Ice baths are not without risk and not everyone reacts the same way to ice immersion. It is recommended that one engages in ice exposure gradually, for short periods and in a controlled setting like a home shower. Furthermore, one must be mindful of age, general health, time of exposure, and water temperature. Remember, body temperature is 98.6 and water temperature of 65-70 degrees will feel very cold so 50-59 degrees can create problems such as:
If you have the following health conditions, ice baths may not be the best therapeutic modality for you. Before you consider trying an ice bath, consult with your physician to avoid potentially serious problems:
What the Science Says –
While some studies have shown that subjects report less muscle soreness following CWI when compared to rest, most studies suggest that the reported effects are placebo. Also, reports of improved circulation, reduced inflammation and improved recovery or performance has not been scientifically validated. In view of this, it is recommended that those considering the use of CWI for pain and inflammation management, reduced muscle soreness, and mood elevation, should consult their physician to determine if the potential risks are worth the purported benefits.
SOURCES: nih; health.com; health.clevelandclinic.org; prevention.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

It is two weeks away from the 28th Steamtown Marathon. After training all spring and summer for the first seven Steamtown Marathons, not a Columbus Day Weekend goes by without my thoughts of this great event.
I would like to introduce this topic with some marathon history. In 490 B.C. Athens was under attack by the Persians and was outnumbered more than two to one. The Athenians fought bravely and defeated the enemy in the town of Marathon. The victory kept the intruders 26 miles away from Athens. To keep the anxious citizens of Athens calm, leaders immediately ordered a foot soldier, Phedippides, to run to the capital city to share the news. Phedippides ran, in full armor, for 26 miles from Marathon to Athens, delivered the message and died immediately. Now, people do the same thing of their own free will!
Each year at this time, dozens of runners preparing for the Steamtown Marathon come to my office with severe shin pain known as shin splints. Unfortunately, in many of these athletes, this problem can lead to a much more severe and advanced problem with shin splints called a stress fracture.
A stress fracture is fatigue damage to bone with partial or complete disruption of the cortex of the bone from repetitive loading. While standard x-rays may not reveal the problem, a bone scan, and MRI will. It usually occurs in the long bones of the leg, mostly the tibia but also the femur (thigh) and foot. Occasionally, it occurs in the arm.
10-21% of all competitive athletes are at risk for stress fractures. Track, cross country and military recruits are at greatest risk. Females are twice as likely as males to have a stress fracture. Other athletes at risk are: sprinters, soccer and basketball players, jumpers, ballet dancers are at risk in the leg and foot. Gymnasts are also vulnerable in the spine while rowers, baseball pitchers, golfers and tennis players can experience the fracture with much less frequency in the ribs & arm.
The problem is much more prevalent in weight bearing repetitive, loading sports in which leanness is emphasized (ballet, cheerleading) or provides an advantage (distance running, gymnastics).
Stress fractures usually begin with a manageable, poorly localized pain with or immediately after activity such as a shin splint. Over time, pain becomes more localized and tender during activity and then progresses to pain with daily activity and at rest.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

Read Health & Fitness Forum Next Monday/Sunday: Preparing Your First Aid Kit For the Steamtown Marathon
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Happy Labor Day! There is little doubt that the workplace has been redefined since the pandemic as many employees continue to work from home. Sitting for many hours at a workstation that may not be optimal has also changed the way we define workplace health and safety. It may be more important than ever to pay close attention to designing an ergonomic workstation, changing position, and stretching regularly to prevent injury.
Since 1894 Labor Day has been designated as the national holiday that pays tribute to the contributions and achievements of American workers. Research supports the notion that healthier employees are happier and more productive. When employers encourage healthy behavior and safety at work, they benefit in many ways.
For example, in addition to improving job satisfaction and productivity, healthy employees save money by using less sick time, worker’s compensation benefits and health benefits. For example, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, approximately 75 percent of employers” health care costs are related to chronic medical problems such as obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Deconditioned, overweight employees are more likely to suffer from these preventable conditions and are at greater risk for injury. Employers, please consider using this holiday as an opportunity to start a health promotion program at your workplace…have a health fair, offer healthy snacks, encourage walking, smoking cessation, exercising at lunch, and offer fitness club stipends.
Lower back pain, one of the costliest illnesses to employers, is one example of a problem which can be prevented with a good health and safety program. It is widely accepted in the medical community that the best treatment for lower back pain (LBP) is prevention. Keeping fit, (flexible and strong), practicing good posture, and using proper body mechanics are essential in the prevention of LBP. At our clinic, significant time and effort is spent emphasizing the importance of these concepts to our patients, employees, and the businesses we work with through industrial medicine programs. A comprehensive approach can produce significant reductions in LBP injuries through an onsite safety program which promotes education, wellness, body mechanics, lifting techniques, postural and stretching exercises and ergonomics.
As little as 10 extra pounds puts great stress on your lower back. It also makes it more difficult to maintain good posture. Eat well, exercise regularly and don’t smoke. Smokers have a much higher incidence of LBP and failure from lower back surgery.
Good posture is critical for a healthy back. When sitting, standing or walking maintain a slight arch in your lower back, keep shoulders back, and head over your shoulders. In sitting, use a towel roll or small pillow in the small of the back. Also, consider sitting on a physio ball, which promotes proper posture for part of the day.
Perform postural exercises throughout the day. Most of the day we sit, stand, and reaching forward and bend our spine. These exercises are designed to stretch your back in the opposite direction of flexion. Please perform slowly, hold for 3-5 seconds and repeat 6 times each 6 times per day.
Chin Tuck: Tuck your chin back to bring your head over shoulders.
Shoulder Blade Pinch: Pinch your shoulder blades together.
Standing Extension: While standing, put your hands behind back and extend lower back 10-20 degrees.
Good Body Mechanics and ergonomics are also important in the prevention of LBP. When lifting, think twice. Think about the weight, shape and size of the object. Think about where the object is going and the surface resistance of the floor. Does it require two people to lift? Can I safely lift that high or bend that low?
When bending to lift an object think about safety:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
What medical problems do a carpenter, typist, truck driver, jackhammer operator, violinist, pianist and court stenographer have in common? Carpal tunnel syndrome! Over the past 10-15 years, carpal tunnel syndrome has moved to the forefront in medicine and has become water cooler conversation. So, what is carpal tunnel syndrome and how is it treated?
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve disorder caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist. The median nerve is one of three main nerves that provide sensation to the hand. This nerve specifically supplies sensation to the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger. In CTS, compression on the median nerve occurs as it travels through a narrow passage in the wrist called the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is formed by eight bones in the wrist (the floor of the tunnel) and the transverse carpal ligament, a strong ligament traveling across the roof of the tunnel. Within the tunnel there are nine tendons, which are a bit smaller than a pencil. These tendons share this space with the median nerve. In the case where there is swelling on the structures in the carpal tunnel, a person can experience pins and needles, numbness, and aching in the hand.
To be properly diagnosed, a physician will discuss your symptoms and medical history and examine strength and sensation. A nerve conduction study, electromyography (EMG), and x-ray may be ordered to provide information regarding sensation in the median nerve distribution and confirm compression at the carpal tunnel.
Treatment focuses on the causes. Therefore, treatment suggestions may include activity modification and postural changes during activities. Other suggestions may include frequent rest periods, elevation, and exercises or stretching. Wrist splints are effective in relieving compression at the carpal tunnel and are typically recommended for night wear. Appropriate fit of the splint is vital. Occupational and physical therapists or certified hand therapists can check the fit of prefabricated splints or can fabricate a custom splint. The above-mentioned treatments all focus on decreasing inflammation and compression on the median nerve.
Your physician may order pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medication. A cortisone injection into the carpal tunnel may also be recommended to assist with decreasing inflammation near the carpal tunnel.
A referral to an occupational or physical therapist or certified hand therapist may be made. A therapist can provide information regarding the diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and symptom reduction. They can make recommendations to introduce into daily activities to allow appropriate positioning of the upper extremities. A therapist will also instruct individuals on helpful stretching exercises or fabricate a wrist splint. Other treatments include ultrasound, iontophoresis, and massage. The focus of therapy is to introduce changes and interventions that reduce inflammation at the carpal tunnel to assist with symptom relief.
Surgery, referred to as a carpal tunnel release, may be indicated if symptoms are significant and impair functional activity performance.
To reduce your chances of getting CTS:
Guest Contributor: Nancy Naughton, OTD, CHT, is a Doctor of Occupational Therapy and certified hand therapist, specializing in the rehabilitation of the hand and upper extremity at Hand Surgery Associates, Olyphant, PA.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

While I fully expect to be at the “butt end” of many comments for this column, I feel compelled to address this topic at the request of several patients. It seems that many geriatric physical therapists commonly encounter patients that suffer from constipation which limits their participation in rehabilitation. Ironically, research demonstrates that exercise and activity actually help relieve constipation.
The National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NDDIC) reports that 3.1 million people in the United States suffer from constipation. The NDDIC further reports that this problem leads to almost 400,000 hospitalizations, 1.4 million visits to emergency rooms, 1 million prescriptions and 121 deaths each year. Constipation is defined by the Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine as three or less bowel movements per week. It is also estimated that more than 27 percent of the elderly are affected.
Severe constipation can result in immediate medical attention in some cases due to intestinal obstruction. In addition to infrequent bowel movements, some symptoms include: feeling poorly, weight loss, loss of appetite, abdominal distention and/or pain, and vomiting.
Healthy people must continue to keep active. Get into good exercise habits at a young age and continue through life. Maintaining a consistent schedule of eating and exercise is also helpful. Some simple suggestions for beginning an exercise program for prevention of constipation in the healthy population are:
Depending on your general health and ambulatory status, these endurance exercises may be appropriate for you. Therefore, consider one or two of the following as a good starting point:
IN CONCLUSION: KEEP MOVING YOUR BODY AND YOU WILL KEEP MOVING YOUR BOWELS!
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

PIAA fall sport teams will begin their official practices a soon – including double sessions for high school football. While a warm August may be a wonderful time of year to swim and kayak, it may not offer the best temperature and humidity for athletes playing football, soccer and other sports. One common problem these athletes suffer from is severe muscle cramping. Every year multiple players limp off the practice field in pain and many concerned players, parents and grandparents repeatedly ask me about the problem. What exactly is a muscle cramp? Why does it happen? How can it be prevented?
A muscle cramp is defined as an involuntary contraction or spasm of a muscle that will not relax. The tight muscle spasm is painful and debilitating. It can involve all or part of the muscle and groups of muscles. The most common muscles affected by muscle cramps are gastrocnemius (back of lower leg/calf), hamstring (back of thigh), and quadriceps (front of thigh). Cramps can also occur in the abdomen, rib cage, feet, hands, and arms. They can last a few seconds or 15+ minutes. They can occur once or multiple times. It can cause very tight spasms or small little twitches.
Although the exact cause may be unknown at this time, there are several theories why muscle cramps occur. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, when a muscle is flexible and conditioned, the muscle fibers are capable of changing length rapidly and repeatedly without stress on the tissue. Also, overall poor conditioning or overexertion of a specific muscle leads to poor oxygen/carbon dioxide exchange and build up of lactic acid and cause a muscle spasm. Also, this process can alter muscle spindle reflex activity and stimulate the spinal cord to send a message to the muscle to contract. If uncontrolled this leads to cramps and spasm.
Muscle cramps are more common in hot weather due to loss of body fluids, salts, minerals, potassium, magnesium and calcium. This leads to an electrolyte imbalance which can cause a muscle to spasm.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Despite recent challenges for air travel due to increased volume, severe weather and a nationwide shortage of air traffic controllers, Americans report high levels of enthusiasm for air travel this summer, including travel abroad.
Confession; I recently was on a long trip that required sitting on an airplane for more than six hours…and I wore compression stockings … guess I’m getting older (and wiser)!
Have you noticed that being in a car or on an airplane for more than three hours leads to neck and back pain? Soreness, stiffness and swelling in your legs? With a little planning, preventing or limiting these problems on long trips is possible. Also, as people age and/or develop other health problems, they are more vulnerable to developing a more serious problem associated with long trips; deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or blood clots. But problems with long-distance travel can be avoided. The following tips, based on research and personal experience, can prevent neck, back and leg pain and stiffness and DVT.
A DVT is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein. The deep veins pass through the muscles and cannot be seen like the veins just under your skin. While it may occur in your arms, it is much more common in the legs, especially the calf muscle when traveling. When a blood clot forms in a leg vein it usually sticks to the vein wall. Often, pain and swelling lead you to the doctor and treatment is rendered before serious complications develop. However, there are two possible complications. One, a pulmonary embolus, occurs when a part of the clot logged in your deep vein of the calf breaks off and gets lodged in the lung. This is a very serious problem that can be fatal. Two, post-thrombotic syndrome, occurs when you have pain and swelling in your calf after a DVT.
The following risk factors for DVT significantly increase the potential for problems when traveling on long trips by air, more than 5 hours. Trains, cars and buses also create a risk, but air travel creates a greater risk for the following reasons: reduced cabin pressure, reduced cabin oxygen levels, dehydration and alcoholic drinks, which may increase dehydration and immobility.
Airplane seats are “C” shaped and force you to round your neck and back forwards. These exercises are designed to stretch and extend your back in the opposite direction. Please perform slowly, hold for 3-5 seconds and repeat 10 times each hour.
Sitting:
When sitting in an airplane seat, take the neck pillow in the overhead compartment and place it in the small of your lower back. While sitting or standing up, perform postural exercises every 30-45 minutes.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

I wish I could tell you that after turning 50, there are health issues associated with age I plan to be mindful of and address proactively. Unfortunately, that ship has sailed for me well more than a decade ago. So, I share this medical information, not only as a health professional but also as an experienced senior.
Entering the fifth decade is not all dome and gloom. Often, this decade is associated with an established family, gratifying career, good health and acquired self-confidence…realizing that life does not have to be perfect to be wonderful!
However, research tells us that as the body ages, even small changes at the cellular level can be manifested into big changes and problems over time. Nine of ten older adults have some type of chronic disease and eight of ten have more than one. But the good news is that, with a modicum of effort, most of these illnesses can be controlled or prevented, including regular doctor visits, health screening and testing, and lifestyle changes.
While it is normal to experience some weight gain is expected with age. However, uncontrolled, the average person will gain 1-2 pounds per year, leading to 11 pounds per decade, according to the National Institutes of Health. Consequently, almost 45% of Americans between 40 to 60 are obese. Obesity is associated with at least 20 chronic illnesses such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and arthritis.
SCREEN: Body Mass Index (BMI)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications, Surgery
With age, the flexibility of blood vessels loses elasticity and, unchecked, two out of three adults over 60 have high blood pressure. While genetics is a factor, there are a few things that you can control such as diet (salt, calories), exercise, weight, stress, and smoking.
SCREEN: Blood Pressure Test, Lab Tests, Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications
Plaque buildup in the arteries of the heart begins in childhood and advances rapidly with age. 6-7 percent of US adults between the ages of 40 and 60. 20% of men and almost 10% of women between the ages of 60 and 80 have heart disease.
SCREEN: Blood Pressure, Cholesterol testing, Blood Sugar Testing, Imaging (ECG/MRI)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications, Surgery
10 % of Americans have diabetes and the percent only increases with age. Diabetes is associated with many serious chronic illnesses such as heart disease, blindness, kidney disease and others.
SCREEN: Blood Test for blood sugar levels such as A1C, fasting plasma glucose test and random plasma glucose test
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Medications
In many cases osteoarthritis (wear and tear of joints) is often associated with age. However, lifestyle, joint injuries, inactivity, obesity and diabetes play a significant role.
SCREEN: Physical Exam, Functional Scores, Xrays, MRI, CT, US
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, Medications (NSAID’s, Steroids, Viscosupplementation), Bracing, Surgery
Loss of bone density and strength is associated with age and certain metabolic conditions such as early menopause, thyroid disease, prolonged use of blood thinners and steroids. However, a diet rich in vitamin D, regular weight bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, dancing etc can go a long way.
SCREEN: Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, Medications (Oral and Injection)
Losing balance with age is a common problem due to changes in the vestibular system (balance system in the brain), loss of muscle strength and joint flexibility, and compromised vision and hearing. This can often lead to falls, head injuries and fractures.
SCREEN: Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test, Morse Fall Scale
TREATMENT: Physical Therapy – Falls Prevention Program/Balance Training , Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Environmental Modification, Vision/Hearing Testing
Almost 10% of adults between the ages of 55 and 65 have some form of vision and/or hearing loss. This can lead to many problems such as balance and falls as well as isolation and depression.
SCREEN: Regular Hearing Tests/Vision Testing
TREATMENT: Corrective Devices
Both men and women suffer from bladder problems with age... especially frequency and control. It can impact lifestyles in many ways. Often adults fail to hydrate properly, especially when traveling, to control urgency. This can lead to other health problems.
SCREEN: Urine Analysis, PSA, Imaging, CT Urogram, Urine Cystoscopy, Ultrasound,
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Lifestyle, Avoid Caffeine and heavy lifting, Medications, Surgery
As the body ages, so too do the cells that make it up. Often these cells change into cancer different parts of the body. Skin, colon, breast, prostate, lung, throat, etc. Today, however, much progress has been made for early detection and treatment.
SCREEN: Physical Exam (Skin Exams), Lab Tests (blood work, PSA), Imaging (CT, Mammography, MRI), Genetic Testing, Pap Smears, HPV Tests, Colonoscopies/Stool Tests, Multi-Cancer Early Detection (MCED)
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, Medications, Chemotherapy, Radiation, Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy Surgery specific to the cancer type.
Age related mental health issues are vastly unreported and diagnosed. Medical problems can contribute to mental health such as high blood sugar levels and some infections. Overall, lifestyle, environmental factors and family structure and support are particularly important.
SCREEN: No Single Test – Combination of Tools including - Neurological and Cognitive Tests, Brain Scans (CT/MRI), Blood tests, Genetic Testing
TREATMENT: Diet, Exercise, Physical Therapy, Lifestyle, (avoid excessive toxins like alcohol and nicotine), Medications, Environmental Modifications.
SOURCES: WebMD, NIH, Mayo Clinic, Alzheimer’s Association, American Cancer Society, American Heart Association, American Diabetes Association

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Happy Father’s Day! It is my hope that this information will be helpful to all the fathers who enjoy working in the yard! It is not too late to buy dad a new cart or kneeling pads for the yard. Last week, Health & Fitness Forum presented tips for gardeners for preventing hand and arm injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome. This week’s column is dedicated to prevention of lower back and lower body injuries when working in the yard and for gardeners with disabilities.
A relaxing and enjoyable activity for many, gardening can turn dangerous without proper precaution as repetitive stress injuries, back pain, muscle pulls, can stem from raking, weeding, digging and pruning, can turn into serious problems if not treated appropriately. Since prevention is the best approach, the US Dept of Agriculture promotes warm-up exercises and injury prevention tips to help all levels of gardeners avoid serious and long-term injuries while enjoying this popular outdoor activity.
People with various disabilities enjoy gardening at different levels. For example, those suffering from neurological diseases with muscle weakness, paralysis and poor balance as well as those with musculoskeletal problems such as neck and LBP or hip and knee arthritis can safely enjoy gardening at some level. This outdoor labor of love is very therapeutic.
Warm up and stretching is important. Don’t garden first thing in the morning before you have a chance to warm up. Get up, go for a short walk, have breakfast and maybe warm up with a hot shower before working in the garden. Some stretches include;
Note: These exercises should never be painful when completing them. You should only feel a gentle stretch. Hold the stretch10 seconds and repeat 5 times before you garden and every 2-3 hours while working. Should you experience pain, please consult your family physician or physical therapist.
The following guidelines to prevent injury and foster healthy gardening for those with and without disability:
Source: Karen Funkenbusch, MA; Willard Downs, PhD.: U. S. Department of Agriculture - Agricultural Engineering Extension

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
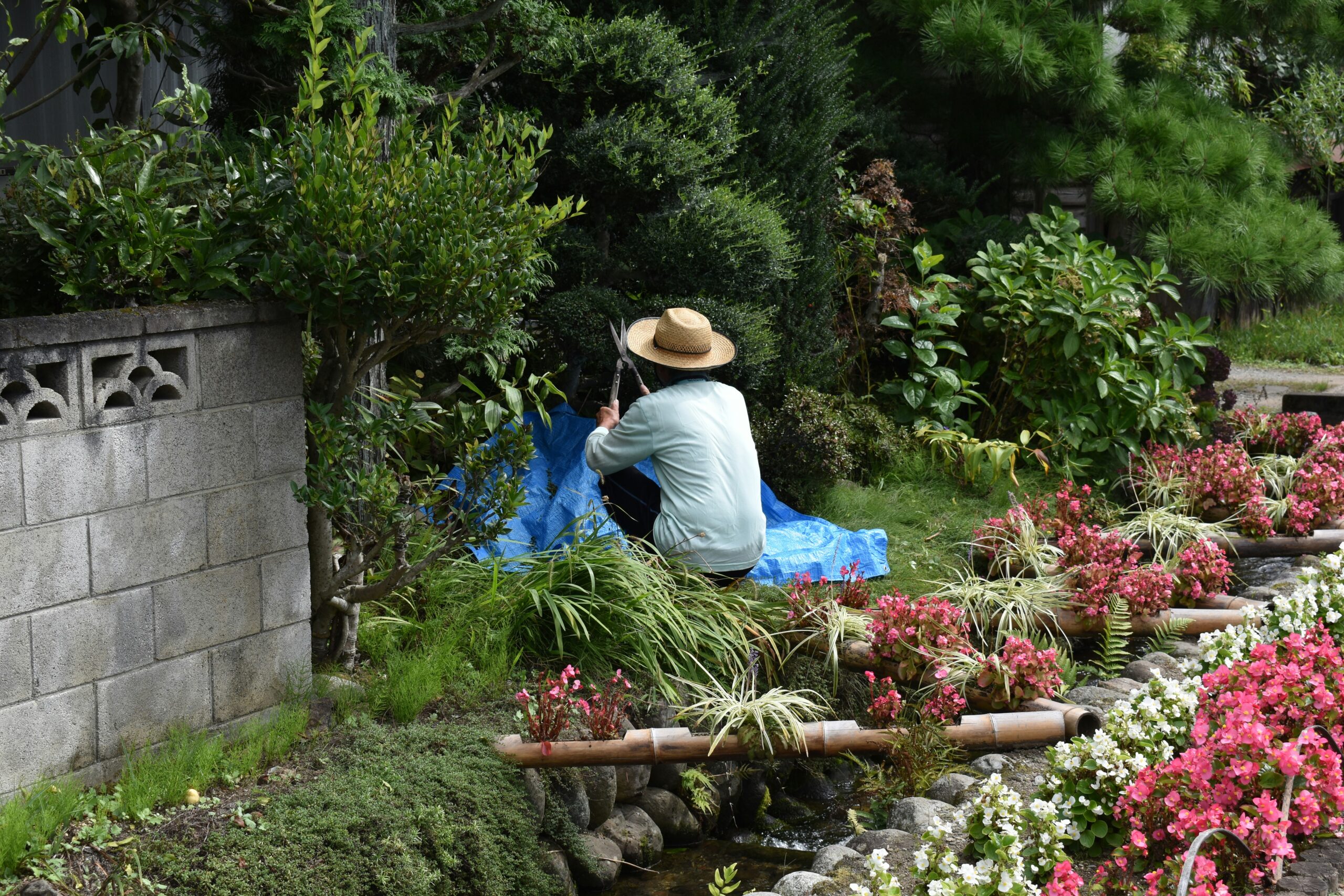

Farmers and gardeners in NEPA always say that Memorial Day, the “kick off” day for planting without the fear of frost, however, this year we have had an unusually cold and wet spring… but it is not too late to start…not only for the beds but your body! While gardeners are anxious to work in their gardens and enjoy the fruits of their labor, a relaxing and enjoyable activity can turn dangerous quickly. Precautions are necessary as repetitive stress injuries such as shoulder and elbow tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome can stem from raking, weeding, digging and pruning. Additionally, simple scrapes, blisters, and bites can turn into serious problems if not treated appropriately. Since prevention is the best approach, the American Society of Hand Therapists (ASHT) promotes warm-up exercises and injury prevention tips to help all levels of gardeners avoid serious and long-term injuries while enjoying this popular outdoor activity.
ASHT recommends following these upper extremity warm-up exercises prior to gardening:
Note: These exercises should never be painful when completing them. You should only feel a gentle stretch. Hold 10 seconds and repeat 5 times. Should you experience pain, please consult a physician or hand therapist.
ASHT recommends the following guidelines to prevent injury and foster healthy gardening practices:
Professional Contributor: Nancy Naughton, OTD, CHT, is an occupational therapist and certified hand therapist practicing in NEPA.

Next Week: “Prevention of Gardening Injuries” Part II of II.
EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
