I am sure that many of you feel as I do…it is hard to believe that I am living in the year 2025! Moreover, I hope you share my sentiments that each year, despite the trials and challenges of each month, week, day, and minute, is a gift, not to be taken for granted and 2025 is no different. And that is why we resolve at this time each year to make a concerted effort to improve ourselves; mentally, physically and spiritually, so that we may live a longer and healthier life, to spend more time with the friends and family we love.
Not surprisingly, getting physically fit and losing weight are the top resolutions to begin each New Year, even 2025. According to the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, 10 million Americans choose to join one of the 45,000 health clubs and hope to get fit and healthy for life. Unfortunately, if starting an exercise program is the hard part, than sticking to it is the hardest part.
Once the initial excitement and enthusiasm wears off after the 2025 new year, so does the discipline and determination necessary to overcome the many distractions in our lives to make exercise a priority for life. Diane Klein, PhD polled long-term exercisers (those exercising at least 3 times per week for more than 13 years) what motivated them to “stick with the program.” The answers are in order of importance. Please note that “appearance” was NOT at the top of the list.
Source: WebMD, Mayo Clinic
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

The number one New Year’s Resolution in the United States is to lose weight. A close second is to gain control over one’s life. One of the best ways to lose weight is thought diet and exercise. It can also be a very effective method to begin taking control of one’s life. This is especially true for those suffering from stress, anxiety and depression. This year make your New Year’s Resolution to “Get a Runner’s High on Life!”
Specifically, aerobic exercise (exercise that increases your heart rate for 30 minutes or more) such as walking, biking, running, swimming, hiking, elliptical & stepper machines to name a few, is the secret to “runner’s high.” This exercise euphoria is not limited to runners alone, but all who engage in aerobic exercise are more likely to experience high energy, positive attitude, and mental wellness – not to mention burn calories.
Physical activity, specifically aerobic exercise, while well known for its importance to one’s physical well-being has also been scientifically proven valuable for preventing and easing stress, anxiety and depression. Studies have found improvement in mental health for groups that engaged in aerobic running, jogging or walking programs, 30-45 minutes 3-5 days per week for 10-12 weeks when compared to a control group and a group in counseling.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.comPaul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

According to American Association of Retired Persons (AARP), those 50 years old and older are seniors! By this definition, as hard as it is to admit, I am well into senior status and as one, I offer holiday health tips for seniors.
Overindulgence during the holidays causes many seniors to make New Year's resolutions related to diet and exercise. But, this year, I propose that seniors incorporate healthy habits during the holiday season, and you may find that your resolutions are not as hard to keep.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Happy Holidays! Despite political divisions and war in the Middle East and Ukraine, it is at this time of year that we celebrate life with great hope and faith. People of many faiths take time to reflect, respect, and resolve. Christians celebrate Christmas, the miraculous birth of Christ, the Son of God, and the Messiah. Jews celebrate Chanukah, the miraculous festival of lights, when one night’s oil provided enough light and safety for 8 nights. Both major faiths promote healthy lifestyles for the mind, body and spirit. These faiths are grounded in hope, faith, love and peace. It is no surprise that studies repeatedly demonstrate that faithful and spiritual people live longer and healthier lives! At this turbulent time in the world, it is important to note that people of all faiths benefited equally!
I purport, that to be truly healthy, one must have faith because complete health is multidimensional. Socrates preached this message to his students thousands of years before Christ. One must have a healthy mind, which requires intellectual stimulation with attainable goals related to education and intellect. One must have a healthy body by eating well, engaging in physical activity and having attainable goals related to his/her body. Likewise, one must have a healthy spirit with faith, hope, prayer and meditation, comrades and counsel, and set attainable spiritual goals.
How being religious or spiritual has been shown to benefit your mind, body and spirit…
1. Healthy Blood Pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) can lead to heart disease and stroke, which are the leading causes of death in the United States, according to the Centers of Disease Control (CDC). It affects 1 in every 3 adults and only half of these people have their blood pressure under control. Well, religion and spiritually may help …
The health benefits of religion or spirituality are well documented. One study conducted at Duke University Medical Center on 4,000 subjects, older adults who described themselves as religiously active were 40% less likely to have high blood pressure when compared to those less active. Moreover, they were surprised to find that those who described themselves as spiritual rather than religious also were less likely to develop high blood pressure.
2. Greater Sense of Satisfaction: Research also indicates that religious people are more satisfied with their lives than those without faith. A sociology study determined that high satisfaction among church goers may be due to the strong social bonds that are developed within a religious congregation. Regular church attendees see the same people weekly and often more often, when participating in rewarding and gratifying church-related volunteer work.
3. Greater Tolerance for Adversity: In an impressive study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers interviewed 345 late-stage cancer patients to assess their spirituality as it related to their illness. 88% stated that they were religious as it related to their coping mechanisms. It was determined that those using religion for coping demonstrated a 7.4% rate of resuscitation as compared to 1.8% for those not using religion as a coping mechanism.
4. Stronger Immune System: According to a Duke University study of 1,718 older adult participants, those described as “highly spiritual” were 50% less likely to have high levels of anti-inflammatory proteins that weaken the immune system and have been linked to some cancers, viral infections and autoimmune diseases. The outcome was similar for those who attend religious services at least once a week.
5. Greater Longevity Those who attend religious services more than once per week are found to live and additional 7 years when compared to those who never attend services. Again, researchers feel that the social benefits of a belonging to a strong religious community may be a large part of the associated longevity. Additionally, the lifestyle of religious people is often healthier: members of these communities rarely engage in risky and unhealthy behaviors such as smoking, excessive drinking, indiscriminate sex, etc
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Holiday shopping is stressful for your body, causing backache, as well as your wallet. Even the “online shopper” is at risk when you consider the hours sitting with poor posture on your electronic device. But I do believe that “in person” shopping is worse for backache… driving from store to store, getting in and out of the car while bundled in a sweater and winter coat can add stress to your spine. Often, the expert shopper carries package after package from the store to the car, repeatedly. Six, eight, or ten hours later, the shopper arrives home exhausted with the backache slowly increasing, only to realize that 15 or 20 packages must be carried from the car into the house. This dilemma is compounded by the fact that the rain turned to sleet, and the sleet to snow. You are slipping and sliding all the way from the car to the house while carrying multiple packages of various sizes and shapes, fighting through the already developing backache. The shopping bags get wet and tear, forcing you to tilt your body as you carry the packages. Of course, no one is home to help you unload the car and you make the trip several times alone. You get into the house exhausted and crash onto the couch because your backache is too much to do anymore at this point. You fall asleep slouched and slumped in an overstuffed pillow chair. Hours later you wake up with a stiff neck and lower back pain. You wonder what happened to your neck and back.
Plan Ahead: It is very stressful on your spirit, wallet and back to do all of your shopping in the three weeks available after Thanksgiving. Even though we dislike “rushing” past Thanksgiving to the next holiday, try to begin holiday shopping in before
Use the Internet: Supporting local businesses is important. However, Internet shopping can save you lots of wear and tear. Sometimes, you can even get a gift wrapped.
Gift Certificates: While gift certificates may be impersonal, they are easy, convenient and can also be purchased over the internet.
Perform Stretching Exercises: Stretch intermittently throughout the shopping day…try the three exercises below, gently, slowly, hold 3 seconds and relax, repeat 5 times.
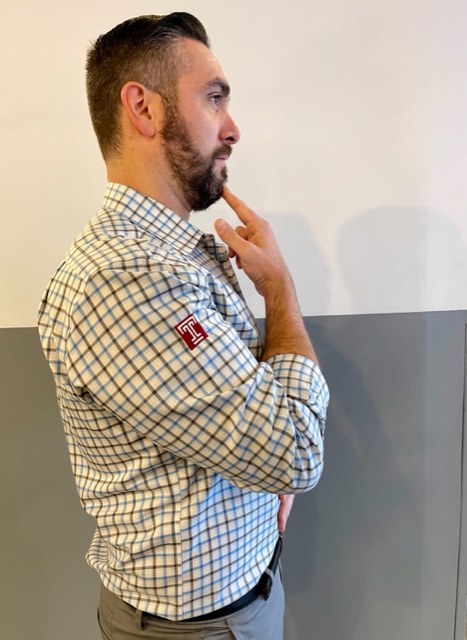
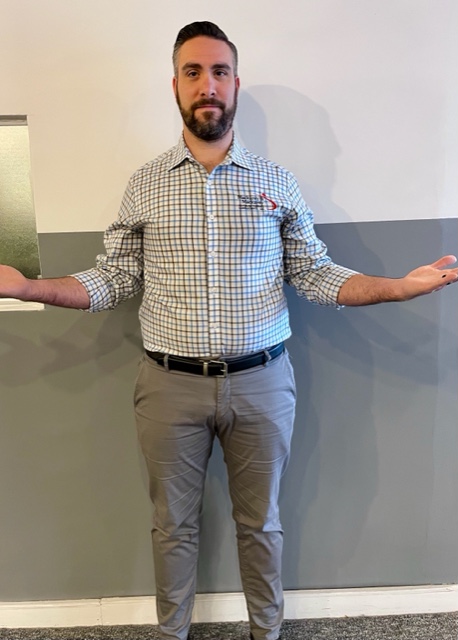



Model: Paul Mackarey, PT, DPT, Clinic Director, Mackarey PT
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

While I normally do not address the topic of shoveling snow until January, considering recent weather events, I thought it might be valuable to present it sooner. Much has been written about the dangers of snow shoveling for your heart. However, while not fatal, low back pain is the most common injury sustained while shoveling snow. Heart attacks are also more common following wet and heavy snow.
Snow shoveling can place excessive stress on the structures of the spine. When overloaded and overstressed, these structures fail to support the spine properly. The lower back is at great risk of injury when bending forward, twisting, lifting a load, and lifting a load with a long lever. When all these factors are combined simultaneously, as in snow shoveling, the lower back is destined to fail. Low back pain from muscle strain or a herniated disc is very common following excessive snow shoveling.
Sources: The Colorado Comprehensive Spine Institute; American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

The “first Thanksgiving” was in 1621 between the Pilgrims of Plymouth Colony and the Wampanoag tribe in present day Massachusetts to celebrate the harvest and other blessings of the previous year. In 1789, President George Washington, at the request of Congress, proclaimed Thursday, November 26, as a day of national thanksgiving. In 1863, Abraham Lincoln proclaimed the national holiday of Thanksgiving to be the last Thursday of November.
Americans and Canadians continue to celebrate this holiday as a time for family and friends to gather, feast, and reflect upon their many blessings. Like most, I am very grateful for the simple things; family, good friends, food, shelter, and health. It turns out that being grateful is, not only reflective and cleansing; it is also good for your health!
Grateful people are more likely to behave in a prosocial manner, even when it is not reciprocated. A study by the University of Kentucky found those ranking higher on gratitude scales were less likely to retaliate against others, even when others were less kind. Emmons and McCullough conducted one of the most detailed studies on thankfulness. They monitored the happiness of a group of people after they performed the following exercise:
There are many things in our lives, both large and small, that we might be grateful about. Think back over the past week and write down on the lines below up to five things in your life that you are grateful or thankful for.” The study showed that people who are encouraged to think of things they’re grateful for are approximately 10% happier than those who are not.
Amy Morin, psychotherapist, mental health trainer and bestselling author offers this advice: “Developing an “attitude of gratitude” is one of the simplest ways to improve your satisfaction with life. We all have the ability and opportunity to cultivate gratitude. Simply take a few moments to focus on all that you have, rather than complain about all the things you think you deserve.” So…be grateful and have a happy Thanksgiving!
Source: NIH, Forbes, Amy Morin “13 Things Mentally Strong People Don’t Do.”
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
November is National Hospice Month! During this time, we celebrate the tireless work of the hospice professionals who assist patients and their families during the weeks and months that they journey with a serious or terminal illness.
However, in addition to the service of providing pain and symptom management, assisting with personal care, providing volunteer, counseling and social work services, there may be many other services that your local hospice program may be able to offer to patients, families and caregivers alike.
Please keep in mind that each hospice agency provides unique services to the community. Before you decide, it is important to reach out and ask which agency offers services that best meet your needs.
Some community support programs that are offered by hospice agencies that are routinely available include:
Bereavement Support ---Dealing with the death of a loved one can be a difficult and often lonely endeavor. All hospice agencies offer bereavement services to families of patients that have died. In addition, many hospices offer community support programming to help those who have suffered a loss. Some support programs are in groups, but often individualized help is available. Most times the bereavement services for the community are without charge.
Pet Bereavement Support---The death of a pet can often be quite traumatizing, especially when the pet has been a long-standing member of the family. Hospice agencies are offering bereavement counseling for those who suffered the loss of a pet. Call and reach out if you have suffered a loss and require support.
Dementia Support Groups--- Nancy Reagan always referred to the diagnosis of President Reagan as the ‘long goodbye’. Dealing with a loved one suffering with dementia is difficult---but you do not have to deal with this alone. Many hospices have dementia support groups that educate, support and guide.
Supporting Children through a Loss---Often it is difficult for children to understand or process the death of a parent, sibling, and grandparent or loved one. There are specialized programs for children to understand and live with the loss----developing a new normal. These programs are usually done in a series of 5 sessions so that proper education and guidance can be accomplished.
Community Education Series--- Not only are your local hospices taking the lead to advance end of life care, but many are helping to educate the professional and lay community alike. Ask about monthly seminars, educational programs and other topics of interest to you and your family/co-workers.
Memorial Services--- Hospice agencies routinely celebrate the lives of those patients who have died within the last 6 months or a year. Surrounding yourself with others who have suffered a loss can often be healing and certainly supportive. Call and ask your local hospice about planned memorial services that honor lives well lived through prayer and testimonials.
Volunteer opportunities---There can be no better way to give back to your community than through volunteering opportunities. Hospice offers a wide array of ways to volunteer ranging from direct patient contact to more administrative tasks. Whatever the job, the act of volunteering is what makes hospice care so special.
Mentoring Programs--- As hospice programs are traditionally interdisciplinary in approach; students working with hospice programs are provided an optimal environment to learn not only hospice care, but also the ever-important concept of team. Many hospice agencies work with students regularly from nursing schools, universities and our local medical college.
Transitions Program--- Often patients are referred for hospice services, but do not meet eligibility requirements for this level of care. However, many hospice agencies offer a transitions program, which is a volunteer supported program to monitor the frail elderly in the community and reporting changes back to the physician for advice and guidance. These programs are free of charge, volunteer supported and a valuable asset for the independent senior who may need that extra set of eyes and ears of a skilled volunteer.
So, in honor of National Hospice Month, we say, thank you to all the hospice professionals, volunteers and families who work so diligently to care for those in our community with a serious or terminal illness. But remember too, that your local hospice agency can be a wonderful resource for education, mentoring, dementia support and grief counseling. Ask questions, attend a seminar, inquire about memorial services or look for support when caring for a loved one with dementia. Help, support, guidance and education are available----just make the call to your local hospice agency.
To find out which hospices serve your community, call NHPCO’s HelpLine at 1-800-658-8898 or visit www.caringinfo.org/findahospice.
Medical Contributor: Ralph DeMario, MD, Former CMO, Hospice of the Sacred Heart

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

November is National Hospice Month! Each November, the community of hospice and palliative care professionals celebrates National Hospice Month. Although, at first glance, spotlighting the concept of death and dying may seem a bit gloomy. It’s actually the concept of quality of life and the focus on living that is truly being celebrated.
It is true that hospice serves those patients and their families who are on the journey of a serious or terminal illness. But as any hospice professional from the nurse to the social worker to the volunteer to the pastoral counselor will attest------our focus is ALWAYS on the value of life being maintained and the quality of living for each and every one of our patients.
Placing the focal point of hospice care on living, instead of dying, enables the patient and family to focus on:
Remember that your hospice team will make suggestions to improve your pain and symptoms, all with the ultimate goal of allowing you to live your life as fully and functionally as possible. Pain alleviation will allow for improved activities, help with personal care will conserve energy for visiting with family and friends, and allowing a volunteer into your home will give caregivers much needed time for rest and relaxation.
There are a number of myths surrounding hospice care----and this is good a time as ever to help dispel them…
Myth #1--- Hospice is for patients in the last days of their lives.
Actually, hospice care was designed to care for patients and their families for the last 6 months of their lives----the longer patients are under the care of hospice professionals, the better their symptoms are controlled and the better their quality of living.
Myth #2--- Pain medications are given in large doses to sedate the patient and hasten death…..
Pain medications are used in small of doses as required to control pain, and to maintain patients’ alertness, always focusing on living life to the fullest. Medications are never given to hasten death, only to control pain and maintain quality of life.
Myth #3--- Once patients start hospice services, death will come soon….
The statistics on this issue are interesting. In a major study, patients who received hospice care for congestive heart failure actually lived 29 days longer!!! Also, on average 15% of patients are actually discharged from hospice services because of significant improvement in symptoms.
Myth #4--- Patients receiving hospice services cannot leave the home or travel….
The truth is that patients receiving hospice care can drive, travel as able, go to bingo/hairdresser/casino----actually come and go as they are able. So the goal is to improve symptoms so that patients can enjoy their lives as fully as possible while on the journey of a serious illness.
Although the topic of death and dying has been rather taboo in the US, hospice professionals celebrate the living potential that their patients still have. The focus is on quality of relationships, maintaining a functional lifestyle and living the life they were meant to live. Hospice professionals also celebrate the many lives they have improved, all the lives they have touched and the fact that they were chosen to dedicate their professional lives to helping others live more fully……
To find out which hospices serve your community, call NHPCO’s HelpLine at 1-800-658-8898 or visit www.caringinfo.org/findahospice
Medical Contributor: Ralph DeMario, MD, Former CMO, Hospice of the Sacred Heart

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.comPaul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!

Recently, two patients asked me when I thought it would be safe for them to return to their exercise programs after abdominal surgery. She stated that she was not sure how to properly and safely implement or return to her program.
This column will attempt to ensure a safe return to activity and exercise following general surgery such as gall bladder, appendix, hernia, etc. The post-operative patient has many questions: When is it safe to begin an exercise program? How do I begin? What is the best exercise? Which exercises are best? How do I know if the activity is too intense or not intense enough? Are there safe guidelines?
Before you begin, discuss your intention to exercise with your surgeon and primary care physician. Get medical clearance to make sure you can exercise safely. With the exception of short daily walks, don’t be disappointed if your surgeon requires you to wait at least until your 6 week post-op check-up to begin exercise.
While a 60 minute workout would be the long term goal, begin slowly at 15-20-30 minutes and add a few minutes each week. Make time to warm up and cool down.
Warm-up 5-10 minutes
Strength Training 10-15-20 minutes
Aerobic 10-15-20 minutes
Cool down 5-10 minutes
How to Monitor Your Exercise Program:
First, determine your resting heart rate by taking your HR (pulse) using your index finger on the thumb side of your wrist for 30 seconds and multiply it by two. 80 beats per minute is considered a normal HR but it varies. This is a good baseline to use as a goal to return to upon completion of your workout. For example, your HR may increase to 150 during exercise, but you want to return to your pre exercise HR (80) within 3-5 minutes after you complete the workout.
For those who are healthy, calculating your target heart rate (HR) is an easy and useful tool to monitor exercise intensity.
220 – Your Age = Maximum Heart Rate
EXAMPLE for a 45 year old: 220 – 45 = 175 beats per minute should not be exceeded during exercise.
For those concerned about calories expended during exercise.
NOTE: Keep the level at a light/moderate level for the first four to six weeks and advance to the moderate/heavy at week six. The Very Heavy Level may not be appropriate for 12 weeks post op is for those who have a reasonable fitness level and exercise 4-5 days per week.
Example of Data Found on Fitness Equipment
Remember, this is only accurate if you program your correct height, weight and age.
Level kCal/min MET
Light 2 - 4.9 1.6 – 3.9
Moderate 5 - 7.4 4 – 5.9
Heavy 7.5 - 9.9 6 - 7.9
Very Heavy 10 - 12.4 8 – 9.9
Always secure physician approval before engaging in an exercise program.
If the patient is on beta blockers (Atenolol, Bisoprolol, etc), it is important to use the Borg Rating of Perceived Exertion Scale (RPE) scale to determine safe exercise stress since exercise will not increase HR as expected:
0 - Nothing at all
1 - Very light
2 - Light
3 - Moderate
4 - Somewhat intense
5 - Intense (heavy)
6
7 - Very intense
8
9 - Very, very intense
10 - Maximum Intensity
NOTE: Keep the RPE at 2-3 the first 6 weeks post op and advance to level 3-4 at 8-12 weeks post op. Levels 5-6-7 are for those with a reasonable fitness level and exercise 4-5 days per week. The advanced levels should not be attained until 2-3 months of exercise and 3-4 months post op.
MEDICAL CONTRIBUTOR: Timothy Farrell, MD, is a general surgeon at GCMC.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
