Memorial Day is the unofficial kickoff to summer…outdoor furniture is out, the grill is fired up and the pool is open! This summer try to think of your pleasure puddle in different light…a health spa! It may very well be the exercise of choice for many people. Many have discovered the benefits of moving their limbs in the warm water of a home pool following knee or shoulder surgery. Also, long distance runners who often look for cross training methods without joint compression and arthritis sufferers who are often limited in exercise choices by joint pain from compressive forces when bearing weight, can enjoy the buoyancy effects of water. These are good examples of the benefits or water exercise…aerobic and resistive exercise without joint compression.
Most doctors recommend some form of exercise with arthritis. Pain and fatigue are the most limiting factors for the person with arthritis. Pool exercise may be the answer. With proper technique, adequate rest periods, appropriate resistance and repetitions, water exercise can be very effective.
The following are some of the benefits of water exercise:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our Health and Exercise Forum!
Since 1949 May has been designated as National Mental Health Month for the purpose of eliminating the stigma associated with mental illness by raising awareness. One of the most common mental health conditions is depression. New research from Boston University School of Public Health has found that depression has been increasing in the United States and life with COVID for more than two years has accelerated it rapidly. In 2021 the number of people suffering from depression increased more than 32 percent, affecting 1 in every 3 American adults. However, research also has good news to offer: one of the most understated benefits of exercise is mental health! Specifically, aerobic exercise (exercise that increases your heart rate for 30 minutes or more) such as walking, biking, running, swimming, hiking, elliptical & stepper machines to name a few, is the secret to “runner’s high.” This exercise euphoria is not limited to runners alone, but all who engage in aerobic exercise are more likely to experience high energy, positive attitude, and mental wellness.
Physical activity, specifically aerobic exercise, is a scientifically proven useful tool for preventing and easing depression symptoms. Studies in the British Journal of Medicine and the Journal of Exercise and Sports Science found that depression scores were significantly reduced in groups that engaged in aerobic running, jogging or walking programs, 30-45 minutes 3-5 days per week for 10-12 weeks when compared to a control group and a psychotherapy counseling group.
Depression is the most common mental disorder and is twice as common among women as in men. Symptoms include: fatigue, sleeplessness, decreased appetite, decreased sexual interest, weight change, and constipation. Many of these symptoms are likely to bring an individual to their family physician.
According to research, exercise reduces depression in two ways, psychologically (mentally) and physiological (physically).
Psychological or Mental Benefits of Exercise on Depression:
Physiological or Physical Benefits of Exercise on Depression:

NEXT MONDAY - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey’s "Health & Exercise Forum"!
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's Articles, check out our Health and Exercise Forum!
Summer (and Memorial Day, the kickoff of the gardening season) will be here soon and gardeners in northeast PA are anxious work in their gardens and enjoy the fruits of their labor. Last week, Health & Exercise Forum presented tips for gardeners for preventing hand and arm injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome. This week’s column is dedicated to prevention of lower back and lower body injuries when working in the yard and for gardeners with disabilities.
A relaxing and enjoyable activity for many, gardening can turn dangerous without proper precaution as repetitive stress injuries, back pain, muscle pulls, can stem from raking, weeding, digging and pruning, can turn into serious problems if not treated appropriately. Since prevention is the best approach, the US Dept of Agriculture promotes warm-up exercises and injury prevention tips to help all levels of gardeners avoid serious and long-term injuries while enjoying this popular outdoor activity.
People with various disabilities enjoy gardening at different levels. For example, those suffering from neurological diseases with muscle weakness, paralysis and poor balance as well as those with musculoskeletal problems such as neck and LBP or hip and knee arthritis can safely enjoy gardening at some level. This outdoor labor of love is very therapeutic.
Warm up and stretching is important. Don’t garden first thing in the morning before you have a chance to warm up. Get up, go for a short walk, have breakfast and maybe warm up with a hot shower before working in the garden. Some stretches include:
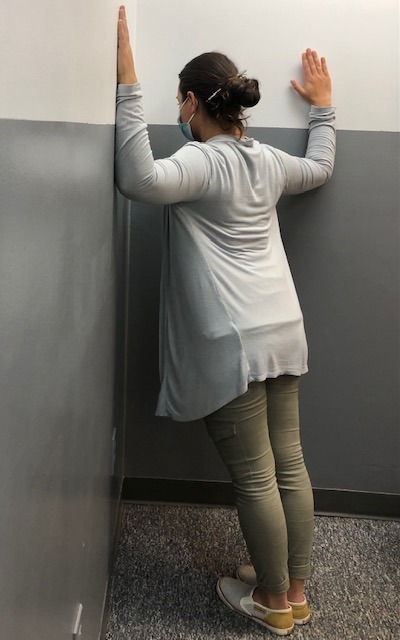

Corner Stretch: Stand facing a corner wall with arms and shoulders at 90 degrees. Lean into corner and stretch shoulders and back. (PHOTO 1)
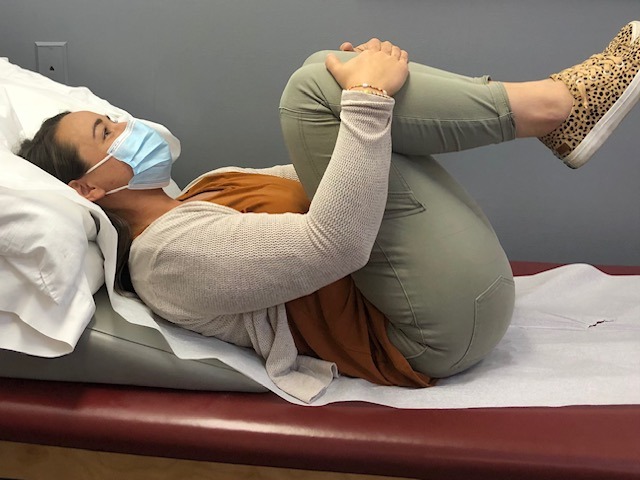
Knees to Chest Back Stretch: While lying on your back, bring both knees up towards your chest. (PHOTO 2)
Note: These exercises should never be painful when completing them. You should only feel a gentle stretch. Hold the stretch10 seconds and repeat 5 times before you garden and every 2-3 hours while working. Should you experience pain, please consult your family physician or physical therapist.
Source: Karen Funkenbusch, MA; Willard Downs, PhD.: U. S. Department of Agriculture - Agricultural Engineering Extension
Model: Ashley Ottaviani, PTA

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. Access all of Dr. Mackarey's articles at our Health and Exercise Forum!
Farmers and gardeners in NEPA always say that Memorial Day, the “kick off” day for planting without the fear of frost, however, it is not too early to start to prepare…not only the beds but your body! While gardeners are anxious to work in their gardens and enjoy the fruits of their labor, a relaxing and enjoyable activity can turn dangerous quickly. Precautions are necessary as repetitive stress injuries such as shoulder and elbow tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome can stem from raking, weeding, digging and pruning. Additionally, simple scrapes, blisters, and bites can turn into serious problems if not treated appropriately. Since prevention is the best approach, the American Society of Hand Therapists (ASHT) promotes warm-up exercises and injury prevention tips to help all levels of gardeners avoid serious and long-term injuries while enjoying this popular outdoor activity.
ASHT recommends following these upper extremity warm-up exercises prior to gardening:
Note: These exercises should never be painful when completing them. You should only feel a gentle stretch. Hold 10 seconds and repeat 5 times. Should you experience pain, please consult a physician or hand therapist.


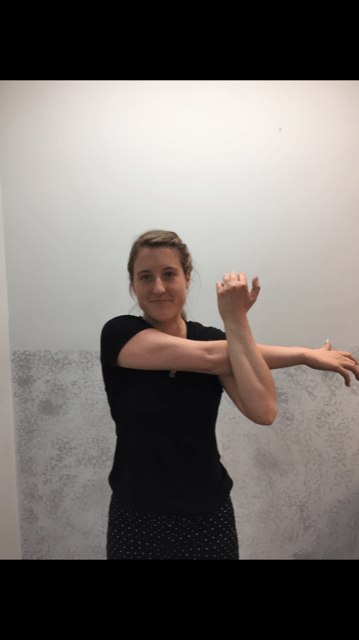
1. Forward Arm Stretch: Fold your hands together and turn your palms away from your body as you extend your arms forward. You should feel a stretch all the way from your shoulders to your fingers. (PHOTO 1)
2. Overhead Arm Stretch: Fold your hands together and turn your palms away from your body, but this time extend your arms overhead. You should feel the stretch in your upper torso and shoulders to hand. (PHOTO 2)
3. Crossover Arm Stretch: Place your hand just above the back of the elbow and gently push your elbow across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. This stretch for the upper back and shoulder and should be performed on both sides. (PHOTO 3)
Professional Contributor: Nancy Naughton, OTD, CHT, is an occupational therapist and certified hand therapist practicing in NEPA. Model: Heather Holzman

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” Next Week: “Prevention of Gardening Injuries” Part II of II.
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. Access of all of Dr. Mackarey's articles at our Health and Exercise Forum.
After a long winter, spring is finally in the air as indicated by the warm (summer-like) temperatures last week. While your mind may be ready to play golf (and other outdoor activities), however, it is important to remember that without proper warmup and preparation, the risk of injury can increase substantially. PGA professionals benefit tremendously from sport science, physical therapy and fitness programs on tour year round. Amateur golfers in northern climates require diligence and planning to prepare for the game after 4-6 months off to avoid injury.
Muscle strains, ligament sprains, neck and LBP is prevalent in the early season for golfers, especially for the amateur. The reasons are many: general deconditioning after winter inactivity, poor golf swing mechanics, excessive practice, inadequate warm-up and poor flexibility and conditioning. The very nature of the golf swing can create great stress on the body, especially after time off.



NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM
Access all of Dr. Mackarey's articles at our Health and Exercise Forum
After a long winter, spring is finally in the air as indicated by the warm (summer-like) temperatures last week. While your mind may be ready to play golf (and other outdoor activities), however, it is important to remember that without proper warmup and preparation, the risk of injury can increase substantially. PGA professionals benefit tremendously from sport science, physical therapy and fitness programs on tour year round. Amateurs in northern climates require diligence and planning to prepare for the game after 4-6 months off to avoid injury.
Muscle strains, ligament sprains, neck and LBP is prevalent in the early season for golfers, especially for the amateur. The reasons are many: general deconditioning after winter inactivity, poor golf swing mechanics, excessive practice, inadequate warm-up and poor flexibility and conditioning. The very nature of the golf swing can create great stress on the body, especially after time off.
Get to the course early enough to make time to stretch before you play and hit a few balls at the range. Always start with low irons and work up to driver. Take a hot shower before an early morning round and use compression shorts and shirts on cool days. Do Not Bounce or Overstretch! Stretch slowly, holding for 10-20 seconds:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” Next Week: Part II - Preseason Golf Tips.

This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician.
For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles visit our Health and Exercise Forum
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), 32.2 million adults and children, 10.5% of the population in the United States, have diabetes. Unfortunately, one-third of these people are not aware that they have the disease. It will be the purpose of this column to raise the level of consciousness through education and offer recommendations for lowering blood sugar levels naturally.
Perhaps no goal is more important to a person with diabetes than maintaining a healthy blood sugar level. When managed over time, healthy blood sugar levels can slow the onset of complications associated with the disease. According to the ADA, pre-diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance, occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal (110 to 125mg/dl) but below type 2 diabetes levels (126mg/dl). 54 million Americans have pre-diabetes in addition to the 20.8 million with diabetes.
While medications are effective in maintaining blood sugar levels, for those who are borderline, there are effective ways to lower your blood sugar naturally. Your physician will determine which treatment is most appropriate for your problem. Also, maintaining your ideal body weight is always important.
**This column is based on information from local physicians Kenneth Rudolph, MD, Gregory Borowski, MD, the American Diabetes Association L (ADA), and Lifescript

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our Health and Exercise Forum
Diabetes is a disease in which the hormone insulin is not adequately produced or used by the body. Insulin is needed for cells to take up glucose after it is broken down from sugars, starches and other food that we eat. When working properly, this provides the fuel necessary for activities of daily living. While the exact cause is not completely understood, genetics is known to play a big role. However, environmental factors such as obesity and inactivity have also been found to play a large role.
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA), 10.5% of the population in the United States or almost 34.2 million adults and children has diabetes. Unfortunately, one-third of these people are not aware that they have the disease.
A Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG) or an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) can be used to screen a person for diabetes or pre-diabetes. Due to the fact that it is easier, quicker and cheaper, the FPG is the recommended test by the ADA. A FPG test results between 110 and 125 mg/dl indicates pre-diabetes. A FPG of 126 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
Type 1diabetes occurs when the islet cells of the pancreas are destroyed and unable to produce insulin. Without insulin the cells of the body are unable to allow glucose (sugar) to enter the cells of the body and fuel them. Without the hormone insulin, the body is unable to convert glucose into energy needed for activities of daily living. According to the ADA, 5-10% of Americans diagnosed with diabetes has type 1. It is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
While type 1 diabetes is serious, each year more and more people are living long, healthy and happy lives. Some conditions that may be associated with type 1 diabetes are: hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis and celiac disease. Some things you will have to know: information about different types of insulin, different types of blood glucose meters, different types of diagnostic tests, managing your blood glucose, regular eye examinations, and tests to monitor your kidney function, regular vascular and foot exams.
While symptoms may vary for each patient, people with type 1diabetes often have increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss and extreme tiredness.
Type 1 diabetes increases your risk for other serious problems. Some examples are: heart disease, blindness, nerve damage, amputations and kidney damage. The best way to minimize your risk of complications from type 1diabetes is to take good care of your body. Get regular checkups from your eye doctor for early vision problems, dentist, for early dental problems, podiatrist to prevent foot wounds and ulcers. Exercise regularly, keep your weight down. Do not smoke or drink excessively.
Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes as most Americans are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. It occurs when the body fails to use insulin properly and eventually it fails to produce an adequate amount of insulin. When sugar, the primary source of energy in the body is not able to be broken down and transported in the cells for energy, it builds up in the blood. There it can immediately starve cells of energy and cause weakness. Also, over time it can damage eyes, kidneys, nerves or heart from abnormalities in cholesterol, blood pressure and an increase in clotting of blood vessels.
Like type 1, even though the problems with type 2 are scary, most people with type 2 diabetes live long, healthy, and happy lives. While people of all ages and races can get diabetes, some groups are at higher risk for type 2. For example, African Americans, Latinos, Native Americans and Asian Americans/Pacific Islanders and the aged are at greater risk. Conditions and complications are the same as those for type 1 diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes experience symptoms that are more vague and gradual in onset than with type 1 diabetes. Type 2 symptoms include feeling tired or ill, increased thirst and urination, weight loss, poor vision, frequent infections and slow wound healing.
**This column is based on information from local physicians Kenneth Rudolph, MD, Gregory Borowski, MD and the American Diabetes Association and Harvard Health Publications

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
One of the most common questions I receive from patients is related to the management and care of their cast or splint. Given the fact that one may have to live with a cast or splint for four to six weeks (sometimes less, sometimes more), many people have concerns about hygiene, swelling, pain and function while wearing a cast…
Casts or splints are used to support and protect bones and soft tissues after injury or surgery. A broken bone or severe ankle sprains are two good examples. Consequently, the immobilization provided by a cast or splint protects the injury, allows healing with proper alignment, and reduces pain, swelling and muscle spasm.
Casts, half- casts or splints are made of plaster or fiberglass. A doctor or assistant individually makes them for each person and injury. In addition, custom-made splints are often made by occupational therapists for the hand or physical therapists and certified prosthetists for other body parts such as the trunk or limps. Fiberglass splints are made with Velcro straps and are removable, which could be used for the wrist for carpal tunnel or the foot for ankle sprains.
Both plaster and fiberglass come in rolls, while fiberglass comes in different colors, which are dipped in water and wrapped around the injured part. It is often necessary to apply the cast to the joint above and below the injury. Then, the material will dry and harden in minutes. The cast must fit the shape of the injured part snuggly, but comfortably. If a cast is applied to a new injury or immediately after surgery, the cast will be too big once the swelling subsides. At this point, a new cast is applied. Padding is used under the cast to protect the skin. Sometimes special padding can be used under fiberglass to allow the cast to get wet in the shower or pool.
Most fractures or severe sprains require 4-6 weeks of casting, sometimes less, sometimes more. Often, once the cast is removed, a removable half-cast or splint is applied. This allows the injured part to be washed and exercised several times a day without the splint and then reapplied.
The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons offers the following recommendations for cast care and warning signs of cast problems:
Warning signs: if the above recommendations fail to provide a reduction in swelling or pain or if you have the following warning signs, contact you doctor:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body. Keep moving, eat healthy foods, and exercise regularly.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
Access all of Dr. Mackarey's articles in our Health Care Forum!
Pain is different than discomfort! Muscle soreness and “feeling the burn” can occur during a normal healthy exercise routine. However, you should never experience a sharp, deep, intense, or lingering pain during or after exercise. In fact, if the soreness lasts more than 24-48 hours, than you did more damage than benefit to your muscles and other tissues and it is time to scale back and take time off. If necessary, use RICE (rest, ice compression and elevation). It is important to get in tune with your body and learn the difference between muscle strain and fatigue discomfort and pain from soft tissue damage from overuse and overload. Find the proper amount of weight and repetitions and gradually increase over time.
There is no solid evidence that stretching alone before a sport or activity prevents injury. In fact, over stretching may be counterproductive before a sport as it may weaken the muscle. The current wisdom on the matter is; never stretch a cold muscle. Instead, warm up for 5-10 minutes by actively moving the extremities and light jogging or biking and THEN lightly stretch the arms, legs, back etc. More vigorous stretching should be performed to improve the flexibility of tight muscles (ie calf and hamstring muscles) and best done after your workout but not before a sporting activity (tennis, basketball, etc.).
It depends on your body type and hormones! It is very unlikely that women and prepubescent males will bulk up from lifting weights…especially light weights (blame or thank hormones). It will, however, increase metabolism and fat burning efficiency which can lead to weight loss and good muscle tone. Stick with low resistance and high repetitions for best results.
It is not possible to target an area of the body to burn more fat! It is very common for women to ask for a specific exercise to reduce the fat in their buttocks, thighs, and abdomen. Regretfully, it is not possible to target weight loss in these areas or other body parts. In fact, when you lose weight through diet and exercise, the caloric expenditure will be evenly distributed throughout the body. However, once the adipose tissue in a specific part of the body such as the abdomen is reduced from general weight loss, targeting the area with exercises specific to that muscle group will improve the tone and definition for a leaner look in that region.
Sure, it would be great to dedicate 60 minutes 5 -6 days a week for exercise. But for most of us who work and raise a family it is not practical. The good news is that the research supports 30 minutes of exercise 3-5 days a week. Moreover, evidence shows that 10 minutes, three times a day, 5 days per week will help you attain the 150 minutes a week supported in most exercise studies.
Most people with the most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, feel better when they are moving. That is not to say that they don’t have increased symptoms when they OVERDO it. An exercise program specifically designed for a person’s problem and limitations will improve their symptoms and function. For example, if an individual has arthritis in their knees, they should use an exercise bike (partial weight bearing) or swim (buoyancy effect of water) instead of walk or run (full weight bearing) for aerobic exercise.
Furthermore, they would do far better with light cuff weights in a sitting or lying position to strengthen their legs than performing squats or lunges. It is important to remember, the weight gain and joint weakness and stiffness associated with a sedentary lifestyle will do more harm to an arthritic joint than a proper exercise program.
Not unless you are planning a killer workout! The number one reason most of us exercise is to lose or control body weight. High calorie sports drinks are counterproductive and unnecessary. If you do not plan on exercising for more than 60 minutes, good old fashion H2O is more than adequate. However, if you plan to do a “killer” workout for more than 60 minutes and may incorporate a high intensity interval training (HIIT) program, than a sports drink with electrolytes and other nutrients, may be of value.
For most of us, effective resistance training is not about the equipment. It is safe to say, caveman was pretty fit and strong despite the fact that he never went to a gym and lifted weights. He did however, lift, push, pull, and carry heavy stones, timber, and animals for day-to-day survival. So too, it is for modern man, the body does not distinguish between the resistance provided by a elastic band, dumbbell, or cable with pulleys and weight stacks. As long as the basic principles of strength training are applied, (isolating a muscle or muscle group, loading the muscle with enough force to bring it to fatigue without causing tissue damage, and allowing for adequate rest and recover) than the muscle will gain strength regardless of the type of resistance.
First, let me confess that I love to run and up until recently, ran almost daily. However, now that I am over 60, I had to find new forms of aerobic exercise which would be kinder and gentler to my joints. So, I mix it up between biking (indoors and outdoors, recumbent and upright), brisk walking or hiking, elliptical and stepper and swimming laps. Again, like the caveman weightlifting example, the body (heart and lungs) does not know what is causing an increase in heart rate for 30, 45 or 60 minutes, it only knows that it must respond to allow the body to function under this stress. And, in the process it becomes conditioned to the point that it will work much more efficiently when not under stress with a lower heart and respiratory rate and blood pressure at rest.
Those over 50 would be well-advised to engage in low-impact aerobics on a regular basis. For example, if you want to run two to three days per week, do not run two days in a row and consider performing low impact exercise in between. Some examples of low impact aerobics are walking, treadmill walking, swimming, elliptical trainer, and an exercise or road bike.
Change is necessary with age! For many years, I have repeatedly preached about the value of engaging in an active lifestyle throughout life. It is especially important to be active as one gets older to maintain mobility and independence. However, many take this advice to an extreme and refuse to accept the inevitable changes that occur in the body with age. They run, jump, lift and throw like a teenager and often fail to modify their activity or exercise regimen appropriately for their age. Consequently, they suffer from multiple injuries, including muscle tears, tendonitis, bursitis, impingement, and advanced osteoarthritis.
Keep in mind, everyone ages differently. One person at 60 years of age may be the equivalent of another at 50. However, change with age is inevitable, so be kind to your body…it’s the only one you have! It is always prudent to consult your physician and physical therapist for a program designed specifically for your needs.

NEXT MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
Access all of Dr. Mackarey's articles in our Health Care Forum!