According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), 11.3% of the population in the United States or almost 37.3 million adults and children has diabetes. Unfortunately, the number keeps rising and one-third of these people are not aware that they have the disease. It will be the purpose of this column to raise the level of consciousness through education and offer recommendations for lowering blood sugar levels naturally.
Perhaps no goal is more important to a person with diabetes than maintaining a healthy blood sugar level. When managed over time, healthy blood sugar levels can slow the onset of complications associated with the disease. According to the ADA, pre-diabetes, or impaired glucose tolerance, occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal (110 to 125mg/dl) but below type 2 diabetes levels (126mg/dl). 54 million Americans have pre-diabetes in addition to the 20.8 million with diabetes.
While medications are effective in maintaining blood sugar levels, for those who are borderline, there are effective ways to lower your blood sugar naturally. Your physician will determine which treatment is most appropriate for your problem. Also, maintaining your ideal body weight is always important.
SOURCES: The American Diabetes Association (ADA), CDC, NIH, and Lifescript
Visit your doctor reguLlarly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
November is National Diabetes Awareness Month. This column will present information regarding type 1 and type 2 diabetes and the diagnosis and symptoms of the disease. Next week, Part II will present the role of exercise in the management of the disease.
What is it?
Diabetes is a disease where the hormone insulin is not adequately produced or used by the body. Insulin is needed for cells to take up glucose after it is broken down from sugars, starches and other food that we eat. When working properly, this provides the fuel necessary for activities of daily living. While the exact cause is not completely understood, genetics is known to play a big role. However, environmental factors such as obesity and inactivity have also been found to play a large role.
According to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), 11.3% of the population in the United States or almost 37.3 million adults and children has diabetes. Unfortunately, the number keeps rising and one-third of these people are not aware that they have the disease.
A Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG) or an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) can be used to screen a person for diabetes or pre-diabetes. Due to the fact that it is easier, quicker and cheaper, the FPG is the recommended test by the ADA. A FPG test results between 110 and 125 mg/dl indicates pre-diabetes. A FPG of 126 mg/dl or higher indicates diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the islet cells of the pancreas are destroyed and unable to produce insulin. Without insulin, the cells of the body are unable to allow glucose (sugar) to enter the cells of the body and fuel them. Without the hormone insulin, the body is unable to convert glucose into energy needed for activities of daily living. According to the ADA, 5-10% of Americans diagnosed with diabetes has type 1. It is usually diagnosed in children and young adults.
While type 1 diabetes is serious, each year more and more people are living long, healthy and happy lives. Some conditions associated with type 1 diabetes are: hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis and celiac disease. Some things you will have to know: information about different types of insulin, different types of blood glucose meters, different types of diagnostic tests, managing your blood glucose, regular eye examinations, and tests to monitor your kidney function, regular vascular and foot exams.
While symptoms may vary for each patient, people with type 1diabetes often have increased thirst and urination, constant hunger, weight loss and extreme tiredness.
Type 1 diabetes increases your risk for other serious problems. Some examples are: heart disease, blindness, nerve damage, amputations and kidney damage. The best way to minimize your risk of complications from type 1diabetes is to take good care of your body. Get regular checkups from your eye doctor for early vision problems, dentist, for early dental problems, podiatrist to prevent foot wounds and ulcers. Exercise regularly, keep your weight down. Do not smoke or drink excessively.
Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes as most Americans are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. It occurs when the body fails to use insulin properly and eventually it fails to produce an adequate amount of insulin. When sugar, the primary source of energy in the body, is not able to be broken down and transported in the cells for energy, it builds up in the blood. There it can immediately starve cells of energy and cause weakness.
Also, over time it can damage eyes, kidneys, nerves or heart from abnormalities in cholesterol, blood pressure and an increase in clotting of blood vessels. Like type 1, even though the problems with type 2 are scary, most people with type 2 diabetes live long, healthy, and happy lives. While people of all ages and races can get diabetes, some groups are at higher risk for type 2. For example, African Americans, Latinos, Native Americans and Asian Americans/Pacific Islanders and the aged are at greater risk. Conditions and complications are the same as those for type 1 diabetes.
People with type 2 diabetes experience symptoms that are more vague and gradual in onset than with type 1 diabetes. Type 2 symptoms include feeling tired or ill, increased thirst and urination, weight loss, poor vision, frequent infections and slow wound healing.
Sources: NIH; American Diabetes Association; Harvard Health Publications
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Preventing a fall can not only save your independence but also your life! Preventing injuries from falls reduces the need for nursing home placement. Injuries from falls are the seventh leading cause of death in people over the age of sixty-five.
The following suggestions will assist you in minimizing your risk of a fall:
Following these helpful hints will keep you safe by preventing a loss of balance and a potential fall!
Contributor: Janet M. Caputo, PT, DPT, OCS
Medical Reviewer: Mark Frattali, MD, ENT: Otolaryngology /Head Neck Surgery at Lehigh Valley Health Network

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Last week we discussed the causes of balance loss. Today, we will discuss treatment for this problem. Two primary treatments are medication and vestibular rehabilitation.
Medication for dizziness and loss of balance requires a visit to your family doctor. In a more involved case, your family physician may refer you to a specialist such as an ear, nose and throat physician or neurologist. There are many medications available for loss of balance. While this can be complicated, the specialist will determine the most appropriate one for your balance disorder.
Vestibular rehabilitation for dizziness and loss of balance is a great adjunct to medication to manage your balance disorder. It is a comprehensive program that addresses a wide range of problems that may cause imbalance such as: addressing the inability to tolerate motion, visual changes, providing balance rehabilitation, instruction in repositioning techniques for BPPV (benign paroxysmal positional vertigo), correcting postural dysfunctions, muscle weakness, joint stiffness, offering education for prevention, maintenance and self care after discharge. Through experience and motion, vestibular rehabilitation allows: formation of internal models (one learns what to expect from ones actions), learning of limits (learning what is safe and what is not) and sensory weighting (one sense, either vision, vestibular or somatosensory is selected in favor of another in maintaining balance).
In some minor cases, vestibular rehabilitation may be performed at home. However, more serious cases may require an evaluation by a physician specializing in the dizzy patient such as an ear, nose and throat physician or neurologist. These specialists will determine the nature of your problem and may enroll you in a more structured program under the direction of a physical therapist. Vestibular rehabilitation addresses not only vertigo (i.e. dizziness) but also balance problems.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) and vestibular hypofunction (e.g. unilateral and bilateral vestibular loss) are two causes of vertigo that can be addressed by a vestibular rehabilitation. Your physical therapist will tailor a program designed to address your specific vestibular disorder (i.e. BPPV or hypofunction).
If you have been diagnosed with BPPV, your therapist may take you through an Epley maneuver. In BPPV, particles in the inner ear become displaced and get lodged in an area that produces vertigo. Vertigo is experienced with tilting head, looking up/down and rolling over in bed. The causes include: infection, head trauma and degeneration. During the Epley maneuver the patient is guided through positional changes which clear these particles from the symptomatic part of the ear.
If you have been diagnosed with either unilateral or bilateral vestibular hypofunction, your therapist will most likely design a program to “retrain” your vestibular system with special exercises, including:
If you have a vestibular problem that primarily manifests as loss of balance, exercises to stimulate your balance responses, strengthen your legs, and enhance your joint position sense may be helpful. These exercises encourage reliance on vestibular and/or visual input. The exercises are performed on unstable surfaces (i.e. tilt boards, balance beams, and foam) and include a variety of tasks from simple standing to more complex arm and leg movements requiring coordination.
In addition to the above mentioned treatments, Posturography and Virtual Reality Training are computerized programs that may be used by your therapist to address your vestibular and/or balance problem. Also, Recreational Activities that involve using your eyes while head and body is in motion (i.e. dancing, golfing, tennis, walking while looking from side to side) are shown to be helpful in stimulating balance and vestibular responses. Furthermore, you may consider Alternative Balance Activities (i.e. Yoga, Tai Chi, Pilates) which incorporate slow gentle movements to improve strength, balance and posture as well as relaxation techniques for the anxiety that accompanies dizziness/off-balance.
Whatever you do, just DO NOT give into your dizziness. People that just “give up” become sedentary. A sedentary lifestyle further denies your body the necessary stimuli to challenge your vestibular system and make it stronger. Eventually, these people end up in a vicious cycle because the more they sit the dizzier and more off balance they get which only makes them sit more!
Remember, one fall increases your risk of another fall. It is imperative to determine what caused your fall and take action! Ask your physician or physical therapist to assess your fall risk.
Contributor: Janet M. Caputo, PT, DPT, OCS
Medical Reviewer: Mark Frattali, MD, ENT: Otolaryngology /Head Neck Surgery at Lehigh Valley Health Network

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog: Next Monday Part III on Balance Disorders and Falls Prevention
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate clinical professor of medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, check out our exercise forum!
Northeastern Pennsylvania is home to a large elderly population and many of the medical problems we expect to see are age related. Dedicated medical practitioners are in constant search for new knowledge and information to prevent or delay many age-related problems. One of the most devastating problems associated with aging is the risk of falling and falling.
Loss of balance causes falls. Falls are a leading cause of injury and death. Thirty percent of women and thirteen percent of men over the age of sixty-five will fall. Twenty to thirty percent of these individuals suffer moderate to severe injuries. Preventing falls is not an easy task. A good understanding of the causes of loss of balance and knowledge of a few fall prevention suggestions can enhance your balance and reduce your risk of a fall.
The Falls Risk Self-Assessment below allows and individual to determine their risk of falling to take the appropriate steps for prevention and treatment. The next three weeks will be dedicated to this topic to educate and inform readers and their families to make good decisions.
The Falls Risk Assessment is from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC).
1. YES (2) NO (0)
2. YES (2) NO (0)
3. YES (1) NO (0)
4. YES (1) NO (0)
5. YES (1) NO (0)
6. YES (1) NO (0)
7. YES (1) NO (0)
8. YES (1) NO (0)
9. YES (1) NO (0)
10. YES (1) NO (0)
11. YES (1) NO (0)
12. YES (1) NO (0)
Add up the number of points for each YES answer. If you have scored 4 or more points you may be at risk for falling.
Accordingly, 0-1 = Low Risk; 1-2 = Moderate Risk; 3-4 = At Risk; 4-5 = High Risk; 5-6 = Urgent; > 6 = Severe
Low Moderate At Risk High Risk Urgent Severe
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Listen to your body and talk to your doctor.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
Next Monday Part II of III on Balance Disorders and Falls Prevention
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate clinical professor of medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Paul's articles, check out our exercise forum!
Runners will attempt to conquer 26.2 miles from Forest City to downtown Scranton in the 26th Annual Steamtown Marathon this Sunday. Participants may want to consider new research that suggests the use of compression socks may prevent post race blood clots.
Completing the long and arduous 26.2 mile journey is not an easy task. In fact, the mechanical and physiological toll on your body is tremendous; from painful joints, muscles, tendons, to black and blue toes. Not so obvious, however, is the damage to your deep veins and tissues of the circulatory system. New research indicates that strenuous endurance exercise, such as marathon running, stimulates the clotting mechanisms in your body in response to the multiple micro traumas sustained over 2 or more hours. While most healthy athletes will naturally heal from post exercise clot formation, others may be at risk…those traveling more than 1 hour (by car, bus, train or plane). The risk increases substantially for those with a longer period of travel/sitting post-race, history of previous trauma, blood clots or have the genetic predisposition for clot formation.
Compression socks are familiar to most people as the tight knee-high support stockings worn after a surgical procedure such as a knee or hip replacement to prevent blood clots. They are made with a special fabric and weave design to provide graduated compression (stronger compression at foot and ankle and less at the top of the sock) to promote better circulation and movement of fluids from the foot, ankle and calf back to the upper leg and ultimately the heart. Compression socks work similarly in runners. As the stagnant fluid with lactic acid and other byproducts of exercise is removed from the space, fresh blood, nutrients and oxygen is replaced to foster healing of micro damage to tissue and promote more efficient use of the muscles.
The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research published a study that found wearing compression socks improved running performance. However, similar studies have failed to support this claim. One finding that has been repeatedly supported in the literature, including The British Journal of Sports Medicine, found that compression socks worn in soccer players and runners improved the rate and magnitude of recovery. Moreover, recent studies, including a study with the Boston Marathon, have demonstrated the reduction in clotting mechanisms in those wearing compression socks AFTER the marathon, as compared with those wearing “sham” socks. Benefits seem to be less obvious for short duration activities or when running 10km or less.
In conclusion, only time will tell if compression socks will improve performance in runners will or be merely a fad based on placebo or true fact supported by scientific research. Based on current wisdom, these socks may offer value and benefit AFTER activities of long duration (more than 1 hour) or long distance running (more than 10km) to expedite the recovery from exercise-induced blood clot formation, muscle soreness from the accumulation of lactic acid and other muscle damage byproducts.
It is this author’s opinion that this product is worth a try. However, whenever you try something new for your sport, trials should occur during practice and if successful used during competition. Consider trying a lower compression to begin (the socks come in different degrees of compression). Even if one is hesitant to use the product while running, it appears the greatest value of the sock is after a prolonged training session or competition to reduce exercise-induced muscle soreness and prevent blood clots, especially in athletes at risk for clotting and those traveling for an hour or more after the race. Additionally, in view of the fact that some studies which showed only minimal to moderate improvement in well-trained athletes, it may be that those in greater need, such as deconditioned individuals attempting to begin a fitness program and novice weekend athletes, may benefit more from compression socks than elite athletes.
TAKE HOME: Runners, cyclists, triathletes, soccer players and others participating in endurance sports should consider compression socks, if not during the activity, certainly following the activity for 24 to 48 hours…especially those at risk for blood clots and those traveling for more than one hour after the race.
Sunday consider trying compression socks and see if they work for you during and more importantly, after your long training runs.
Where to find compression socks:
2XU Compression Racing Sock – www.2XU.com
Scranton Running Company – Olive Street - Scranton
Visit your family doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Studies have shown a recent escalation of joint replacements in a much younger and more active group than previously noted…the baby boomer! While the end result is mostly physical, the cause is often psychological. We all know the personality type: type A, hyperactive, goal-oriented, driven, possessed and highly organized – almost at all costs! Many of you have seen fitness enthusiasts running through the streets at 5:30 AM for 5-10-15 miles each day. Moreover, many of these runners have more activities planned later in the day: golf, tennis, ski, swim, play sports with their kids. Well, after 20 years of this behavior, many of these enthusiasts are now suffering the effects of long term multiple micro traumas. They are suffering from what orthopedic surgeons at the University of Pennsylvania call “Boomeritis! Boomeritis is inflammation of the baby boomer from overuse. Lower back pain, hip, groin, and knee pain is almost a daily event.
As baby boomers continue to enjoy sports with the same vigor and intensity as when they were younger, they are finding that their older bodies just can’t keep up. While these individuals often succeed in finding the balance of fitness and craziness, they have had times when they took it too far. Furthermore, nearly all compulsive exercisers suffer from over training syndrome. When take too far compulsive behavior is rationalized by insisting that if they didn’t work to extreme then their performance would suffer.
*Each sign is worth 1 point:
If you have two or more of the warning sings, consult your family physician to rule out potentially serious problems.
Avoid weight bearing exercises two days in a row. Run one day, walk, swim or bike the next.
Use the elliptical instead of the treadmill.
Avoid squatting…deep squatting is bad for your hips and knees. Even when gardening, use a kneeling pad instead of bending down and squatting.
Visit your family doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at GCSOM.
For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Fall is here, cross-country running season has begun and the 26th Steamtown Marathon is only a few weeks away! With that in mind, running injuries, some very specific to women, are on the increase…
While driving to or from work have you noticed more local running enthusiasts in the past few years? Moreover, have your noticed that most of the runners are women? Scranton Running Company has contributed to NEPA’s participation in a national trend; more women are engaged in running than men! Female runners account for 9.7 million runners (57%) while 7 million males run on a national level.
With this surge, the female runner has been subjected to a host of related injuries, including shin splints, which often lead to stress fractures. New research has found that stress fractures may be related to the loss of weight and body mass associated with the sport.
A recent study from Ohio State University found that female runners with a Body Mass Index (BMI) below 19 may have a higher risk of developing stress fractures than women with a BMI of 19 or above. Furthermore, the study also found that these women took longer to recover from these injuries.
According to Timothy Miller, MD, “When body mass index is very low and muscle mass is depleted, there is nowhere for the shock of running to be absorbed other than directly into the bones. Until some muscle mass is developed and BMI is optimized, runners remain at increased risk of developing a stress fracture,”
The study also found that female runners with a BMI of 19 or higher with severe stress fractures required 13 weeks to recover from their injuries and return to running. Runners with a BMI lower than 19, however, took more than 17 weeks to recover.
They concluded that women should know their BMI and consult with a medical professional to maintain a healthy number. Additionally, women should cross-train and include resistance training to improve the strength and muscle mass of the lower extremities to prevent injury.
The current BMI wisdom, according to the National Institutes of Health, is 19.8 for men and 24 for women, however, strong and competitive women tend to have a BMI of 26. A BMI of 18 is considered malnourished.
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight of adult men and women over 20 years of age, according to the National Institutes of Health.
BMI = (weight in pounds / height in inches squared) X 703)
Example 1: a person who weighs150 pounds and is 68 inches (5 feet 8 inches) tall has a BMI of 22.8
Example 2: a person who weighs 110 pounds and is 66 inches (5 feet 5 inches) tall has a BMI of 17.7
Underweight < 18.5%
Normal weight 18.5 to 24.9%
Overweight 25 to 29.9%
Obesity 30 and over
A stress fracture is fatigue damage to bone with partial or complete disruption of the cortex of the bone from repetitive loading. While standard x-rays may not reveal the problem, a bone scan, and MRI will. It usually occurs in the long bones of the leg, mostly the tibia (shin bone) but also the femur (thigh) and foot. Occasionally, it occurs in the arm.
FEMALE RUNNERS WITH BMI LOWER THAN 19 – is a primary risk factor.
10-21% of all competitive athletes are at risk for stress fractures. Track, cross country and military recruits are at greatest risk. Females are twice as likely as males to have a stress fracture. Other athletes at risk are: sprinters, soccer and basketball players, jumpers, ballet dancers are at risk in the leg and foot. Gymnasts are also vulnerable in the spine while rowers, baseball pitchers, golfers and tennis players can experience the fracture with much less frequency in the ribs & arm.
The problem is much more prevalent in weight bearing repetitive, loading sports in which leanness is emphasized (ballet, cheerleading) or provides an advantage (distance running, gymnastics).
Stress fractures usually begin with a manageable, poorly localized pain with or immediately after activity such as a shin splint. Over time, pain becomes more localized and tender during activity and then progresses to pain with daily activity and at rest.
Source: Ohio State University, Science Daily
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy!
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Paul's Articles, visit our exercise forum!
Ankle swelling is a common symptom that occurs when your body retains fluid in the lower legs, ankles and feet. Most people have experienced it at some point in their lives and it often resolves on its own with elevation and muscle movement. While it is usually benign and occurs on both sides of the body, in some instances immediate medical attention is required. The most common causes of ankle swelling are:
Prolonged Positions – you have probably noticed swelling in your ankles and feet after a long trip by plane or car. Some may also experience symptoms after a long day at work sitting or standing in one position for an extended period of time. It may be the most common cause of lower leg swelling and easiest to resolve.
Diet- excessive salt in your diet is associated with swelling in the lower legs, especially when associated with other risk factors for swelling such as organ function or obesity.
Varicose Veins – when the valves in the blood vessels which carry blood from the legs back to the heart are damaged, blood and fluid can collect in the lower legs. Prolonged standing or sitting without intermittent movement with worsen the condition.
Pregnancy – during pregnancy, the body retains more fluids than usual and most women experience some form of swelling in the lower legs, ankles and feet.
Medications – certain drugs can cause fluid retention in the lower legs such as: anti-inflammatory medications, steroids, diabetes medications, antidepressants and cardiac medications.
Blood Clots – blockages in the blood vessels of the lower leg can limit the movement of fluid from the legs back to the heart. It is often present in only one leg and associated with warmth, pain, and cramping. It is a serious condition and requires immediate medical attention.
Trauma/Infection – after a trauma or injury such as an ankle sprain, bruise or fracture, the damaged tissue leaks fluid surrounding the affected area. Also, when specific area of the lower leg can becomes infected, as in the case of a cut or splinter in the ankle or foot that has not healed properly, swelling occurs in the surrounding tissues. These situations are often associated with warmth, pain and limited to the side of the injury. Treatment to injured tissues and the infection is required.
Lymphedema – swelling in the lower leg can occur when there is a blockage in the lymphatic system is blocked or when lymph nodes are removed in surgery for cancer. Medications, massage, compression garments, and elevation, can address the symptoms.
Obesity – due to the excessive weight placed on the tissues of the legs, ankle and feet and adipose tissue in the abdomen compressing blood vessels, obesity is one of the most common causes of lower leg swelling. It also complicates all of the above conditions associated with swelling in the legs.
Diseases – such as those of the kidney, heart, and liver are associated with swelling in the lower legs.
Change Positions – on a long plane ride or sitting all day at school or work – get up and walk around every 30-45 minutes. Set a timer on your phone to remind you.
Exercise – regular exercises keeps the muscles and blood vessels in you lower extremities healthier. Also, intermittent movement of the leg muscles throughout the day, even when sitting, serve to prevent swelling. Try ankle pumps and toe curls.
Elevation – when sitting or lying down, try elevating your ankles and feet on a pillow to allow gravity to assist fluid movement in your legs.
Low-Sodium Diet – read the labels on your food and you will be shocked by how much sodium is in most foods, especially canned soups and vegetables. But, there are low-sodium options and don’t add more salt to your food.
Weight Loss – maintaining a healthy BMI is the single best thing you can do, not only for lower leg swelling, but for your overall health and wellness.
Compression Socks – for most people, over-the-counter compression socks will adequately prevent fluid retention in the lower legs. For comfort, begin with the lightest compression possible. 12-15 or 15-20 mm of mercury is a good start and put them on as soon as you get up in the morning, before swelling begins.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in ”The Sunday Times - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Paul's articles, check out our exercise forum!
Fall in NEPA is one of my favorite times of year. For outdoor enthusiasts, there is nothing more refreshing than activities in the bright sunshine and crisp, clean air. The hot humid summer weather can be a deterrent to outdoor activities and this time of year provides an opportunity to get fit by beginning a walking program. For many who have not maintained an active lifestyle or have health issues, it is challenging to know where to begin. Moreover, beginning without a good plan can lead to injury and leave you discouraged. For example, those overweight and de-conditioned should not start a walking program too aggressively. Walking at a fast pace and long distance without gradually weaning into it will most likely lead to problems.
There is probably nothing more natural to human beings than walking. Ever since Australopithecus, an early hominin (human ancestor) who evolved in Southern and Eastern Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, that our ancestors took their first steps as committed bipeds. With free hands, humans advanced in hunting, gathering, making tools etc. while modern man uses walking as, not only a form of locomotion, but also as a form of exercise and fitness. It is natural, easy and free...no equipment or fitness club membership required!
“There’s no question that increasing exercise, even moderately, reduces the risks of many diseases, including coronary heart disease, breast and colon cancer, and Type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Jennifer Joyce, MD, professor of family medicine at GCSOM. “Research has even shown that you could gain two hours of life for each hour that you exercise regularly.” According to the American Heart Association, walking as little as 30 minutes a day can provide the following benefits:
Anything is better than nothing! However, for most healthy adults, the Department of Health and Human Services recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous aerobic activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous aerobic activity. The guidelines suggest that you spread out this exercise during the course of a week. Also aim to do strength training exercises of all major muscle groups at least two times a week.
As a general goal, aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity a day. If you can't set aside that much time, try several short sessions of activity throughout the day (3 ten or 2 fifteen minute sessions). Even small amounts of physical activity are helpful, and accumulated activity throughout the day adds up to provide health benefit.
Remember it's OK to start slowly — especially if you haven't been exercising regularly. You might start with five minutes a day the first week, and then increase your time by five minutes each week until you reach at least 30 minutes.
For even more health benefits, aim for at least 60 minutes of physical activity most days of the week. Once you are ready for a challenge, add hills, increase speed and distance.
Keeping a record of how many steps you take, the distance you walk and how long it takes can help you see where you started from and serve as a source of inspiration. Record these numbers in a walking journal or log them in a spreadsheet or a physical activity app. Another option is to use an electronic device such as a smart watch, pedometer or fitness tracker to calculate steps and distance.
Make walking part of your daily routine. Pick a time that works best for you. Some prefer early morning, others lunchtime or after work. Enter it in your smart phone with a reminder and get to it!
Studies show that compliance with an exercise program is significantly improved when an exercise buddy is part of the equation. It is hard to let someone down or break plans when you commit to someone. Keep in mind that your exercise buddy can also include your dog!
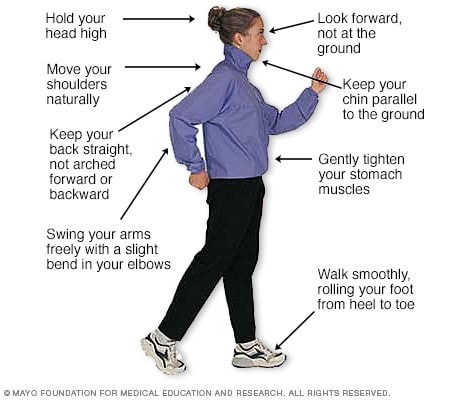
Like everything, there is a right way of doing something, even walking. For efficiency and safety, walking with proper stride is important. A fitness stride requires good posture and purposeful movements. Ideally, here's how you'll look when you're walking:
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Sources : Sapiens.org; WebMD; Mayo Clinic

NEXT MONDAY BLOG and in print in THE SUNDAY TIMES TRIBUNE – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!”
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Paul Mackarey's articles, check out our exercise forum!