This column is dedicated to the memory of John R. O’Brien, Esq., who recently passed due to medical complications associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). John was a source of joy and inspiration for those fortunate to have known him. Twenty years ago, John hesitantly agreed to contribute to my column on MS with two requirements: one, if the column would be valuable to those affected by MS and two, he would remain anonymous. When speaking with his dedicated wife, Sally, it became very apparent that any discussion of John’s life would be diminished if it was defined by the disease because he was committed to turning his “DISABILITY INTO AN ABILITY!”
With the help of his loving wife, family, friends, and devices such as an electric scooter and adaptive car, John not only lived but thrived! He was a skilled lawyer, a respected member of the Bar, and an active member of the community. John served on the executive committee of the Lackawanna Bar Association. In addition, the Lackawanna Pro Bono honored him recently. He also taught business law and healthcare law and coached Prep’s mock trial team.
John shared his thoughts with me about the challenges of redefining life… from Golf Club Champion to living with a physically disabling disease. Anyone who knew him would agree that he succeeded in doing so through his keen intellect and sharp wit and humor…his heart and brain overcompensated for his body! In addition to reading books in Latin and Greek, he had his crossword puzzles published in The New York Times and Los Angeles Times. In September 2023, John conducted an interview with presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin before a full house at the Scranton Cultural Center. Ms. Goodwin later reported that John was the most knowledgeable, effective and enjoyable interviewer she’s encountered.
John’s absence will be deeply felt and his legacy will continue to shape our community for years to come!
Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic disease. While it may lay dormant and stable for a period of time, living a healthy lifestyle will make a positive contribution toward how you and your family live with Multiple Sclerosis. Studies show that a life of family, love, and support are essential to maintain a positive attitude with a chronic illness. This combined with a healthy diet and proper exercise can contribute greatly toward taking control and living a relatively normal life with MS.
As I have mentioned in many other columns, studies show that people with good attitudes and great faith live longer than others. This is especially helpful when living with chronic disease like Multiple Sclerosis. The Cleveland Clinic offers some suggestions how to maintain a positive attitude:
Many sources, including the Cleveland Clinic suggest that exercise, when performed properly, can have a positive impact on Multiple Sclerosis symptoms both physically and psychologically. However, because you have a chronic illness, you should consult with you family physician and physical therapist before beginning an exercise program. They will advise you on the proper type and amount of exercise.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
This column is dedicated to the memory of John R. O’Brien, Esq., who recently passed due to medical complications associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). John was a source of joy and inspiration for those fortunate to have known him. Twenty years ago, John hesitantly agreed to contribute to my column on MS with two requirements: one, if the column would be valuable to those affected by MS and two, he would remain anonymous. When speaking with his dedicated wife, Sally, it became very apparent that any discussion of John’s life would be diminished if it was defined by the disease because he was committed to turning his “DISABILITY INTO AN ABILITY!”
With the help of his loving wife, family, friends, and devices such as an electric scooter and adaptive car, John not only lived but thrived! He was a skilled lawyer, a respected member of the Bar, and an active member of the community. John served on the executive committee of the Lackawanna Bar Association and was recently honored by the Lackawanna Pro Bono. He also taught business law and healthcare law and coached Prep’s mock trial team.
John shared his thoughts with me about the challenges of redefining life… from Golf Club Champion to living with a physically disabling disease. Anyone who knew him would agree that he succeeded in doing so through his keen intellect and sharp wit and humor…his heart and brain overcompensated for his body! In addition to reading books in Latin and Greek, he had his crossword puzzles published in The New York Times and Los Angeles Times. In September 2023, John conducted an interview with presidential historian Doris Kearns Goodwin before a full house at the Scranton Cultural Center. Ms. Goodwin later reported that John was the most knowledgeable, effective and enjoyable interviewer she’s encountered.
John’s absence will be deeply felt and his legacy will continue to shape our community for years to come!
According to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, Multiple Sclerosis affects approximately 400,000 people in the United States. Multiple Sclerosis is second only to trauma as the most common cause of neurological disability for those in early to middle adulthood. MS is almost three times as common in women. Multiple Sclerosis is very uncommon before adolescence or after 50. However, the risk increases from teen years to age 50.
Multiple sclerosis is considered to be an autoimmune disease. The immune system of the body does not work properly when it fails to attack and protect the body against substances foreign to the body such as bacteria. Instead, the system allows the body to attack normal tissues and create diseases such as MS, rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
In MS, the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system. Each nerve has an outer covering of a fatty material (myelin) for insulation to improve the transmission and conductivity of impulses or messages to and from the brain. The damage to the myelin of the nervous system interrupts the ability of messages to travel to and from the brain, through the spinal cord and to other areas of the body such as the muscles in the arms and legs. Due to this “short circuiting” the brain becomes unable to send or receive messages. In multiple sclerosis, scar tissue or plaques (sclerosis) replaces the fatty myelin in “multiple” areas. This is also called demyelination.
The symptoms associated with MS vary greatly from person to person. The amount, frequency and speed of the demyelination process vary greatly and are directly related to the loss of strength and function in daily activities. Some people are independent and ambulatory with mild and infrequent episodes of weakness and disability and live a relatively normal life. Others suffer from frequent and aggressive episodes that significantly weaken and disable. Some common symptoms in the early stages include: muscle weakness, loss of coordination, blurred vision, pain in the eyes, double vision. Some common symptoms as the disease progresses are: muscle stiffness with muscle spasms, pain, difficulty controlling urination, difficulty thinking clearly.
The diagnosis of MS can be very difficulty in the early stages because the symptoms are often vague and temporary. Also, MS symptoms are very similar to other neurological problems. A neurologist will run several tests to rule out other possible problems. However, an MRI showing demyelination of the nerves is a primary confirmation.
Treatment for MS depends upon many factors and requires consultation with your physician. Some medications can control the frequency and severity of MS symptoms such as pain, weakness, and spasticity. Also, some drugs can slow the progression of certain types of MS. Additional treatments for MS include: diet, exercise, physical therapy, support groups, and counseling for the MS patient and their family. Part II of Multiple Sclerosis will discuss these options in further detail next week.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy - NEXT WEEK: PART II OF II - MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
A myth is a traditional story, idea, or belief, especially one concerning early history of a people or explaining a natural or social phenomenon. It is a widely held but false belief or idea. In medicine, health myths are also widely held beliefs about health issues such as medicines, herbs, treatments, cures, antidotes, etc. which are partially or totally false and unsubstantiated in the scientific literature. This is a partial list of the most common health myths:
SOURCES: WebMd; National Institutes of Health, Mayo Clinic

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article does not intend as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
PEOPLE OFTEN ASK ME, “IS THERE SUCH A THING AS AN EXERCISE RUT?”. THEY WANT TO KNOW WHY THEY DO NOT SEEM TO BE IMPROVING WITH THEIR EXERCISE PROGRAM. They exercise 3-4 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes and they feel frustrated and STUCK in a rut.
The purpose of this column is to offer suggestions to improve or get more out of a “stale” exercise program. Last week’s column offered tips to improve a stale cardiovascular and strength program. We will discuss flexibility and functional training tips, including the components necessary for a healthy mind, body and spirit connection.
Flexibility training involves the careful stretching of the muscles, tendons and joints to improve range of motion in order to safely perform daily activities and sports without injuring or tearing soft tissues. It is probably the most neglected part of the fitness program. However, while the amount of inherent flexibility varies for each person, a minimal range is necessary as it relates to daily activities and sports. For example, as you age it is important to have enough flexibility in your back, hips and knees to wash your feet, put shoes and socks on. After a warm –up activity, perform flexibility exercises slowly and gently. There are two types of flexibility exercises; dynamic and static. Perform dynamic stretching with movement such as pushing the ankle up and down like a gas pedal. Complete passive stretching using an outside force, such as a towel to pull the ankle up to stretch the calf. Dynamic should be performed before an activity (before running or playing tennis) and static performed after the activity is over in order to increase range of motion for future activities.
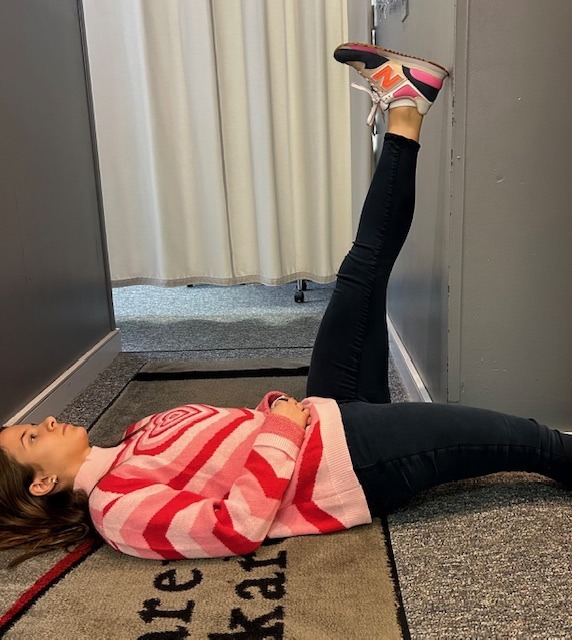

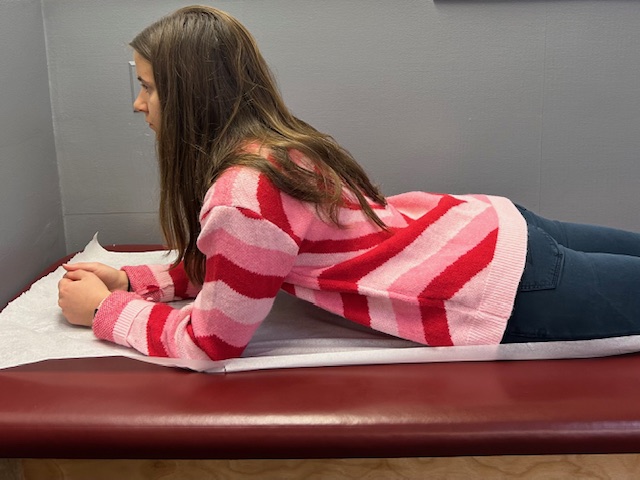
In order to prevent an exercise program from getting stale, one must incorporate all aspects of wellness…a healthy mind, body and spirit!
It is easy for fitness enthusiasts to get so focused on maintaining a routine that they allow their program to become stale and ineffective. It is essential to reassess and update your program to prevent stagnation.
Make sure the routine has all three fundamental components of a well-balanced exercise program; cardiovascular, strength and flexibility training. Moreover, to be truly healthy, one must work toward a “Healthy Mind, Body, and Spirit. Therefore, in addition to traditional exercise one must incorporate the following: nutrition; meditation, relaxation techniques, yoga, core fitness; functional/sports specific training; leisure sports and activities
In order to prevent an exercise program from getting stale, one must incorporate all aspects of wellness…a healthy mind, body and spirit!
While each component offers its own specific benefit, the combination of all three cooperatively provides unique value. Too often, fitness enthusiasts concentrate on the exercises they LIKE or are good at more than the ones they NEED.
Sources: National Institutes of Health; American Council on Exercise
Model: Lily Smith, Physical Therapy Student, University of Scranton, PT aide, Mackarey Physical Therapy

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
PEOPLE WILL OFTEN ASK ME, “IS THERE SUCH A THING AS AN EXERCISE RUT?” THEY WANT TO KNOW WHY THEY DO NOT SEEM TO BE IMPROVING WITH THEIR EXERCISE PROGRAM…they exercise 3-4 times a week for 30 to 45 minutes and they feel frustrated and STUCK in a rut. While initially responding favorably to exercise, after 6 -9 months or more, they do not notice progress in weight loss, strength, tone, endurance or daily function.
The purpose of this column will be to offer suggestions on how to improve or get more out of a “stale” exercise program or an exercise rut. Step one is to build an exercise program that is grounded in the basics. Next step two, which begins after the basics have been mastered, includes the components necessary for a healthy mind, body and spirit connection and translates into functional activities of daily living including work and leisure sports.
Make sure your routine has all three fundamental components of a well-balanced exercise program; cardiovascular, strength and flexibility training. While each component offers its own specific benefit, the combination of all three cooperatively provides unique value. Too often, fitness enthusiasts concentrate on the exercises they LIKE or are good at more than the ones they NEED. A well-balanced program includes what you like and need! In fact, recent studies show that those performing all three components surpassed those performing one or any combination of two of the training types when tested for efficient oxygen uptake (VO2 Max), production of HDL (good cholesterol), lower body fat percentage, and lower blood glucose levels.
Cardiovascular exercise is any activity that raises your heart rate and respiratory rate. This type of exercise strengthens the heart muscle and the muscles that assist in breathing. When these muscles are stronger, they in turn work more efficiently to deliver oxygen to your muscles and other parts of the body. Ultimately, these oxygenated muscles can work harder and longer to burn fat during exercise and at rest.
Examples of Cardiovascular Exercises: Running, Brisk Walking, Swimming, Biking, Rowing, Elliptical Training and Stepper Training. Most experts recommend at least 30 minutes of sustained cardio, 3-4 days per week. However, recent studies support the notion of performing 10-15 minutes, twice daily, 4 days per week. For those “stuck” in a fitness or exercise rut, to advance your program, cardio should be performed 5-6 days per week for 45-60 minutes.
Strength training is an activity that provides any type of resistance to muscle contraction to build strength in the muscle. The resistance can be without movement against an immovable object such as pushing against a wall (isometric) or with movement such as lifting up or lowering a weight down against gravity (isotonic/dynamic). There are two types of isotonic muscle contraction; concentric, which involves raising the weight against gravity as the muscle shortens and eccentric which involves lowering a weight against gravity as the muscle lengthens. A standing biceps curl is an example that incorporates both concentric and eccentric contractions. A progressive strength training program includes all three types of muscle contraction. By using the classic bicep muscle curl these photos will demonstrate all three types of muscle contraction:
-Isometric Bicep Muscle Curl – pull up on door knob without allowing any movement of the arm.
-Concentric Bicep Muscle Curl – raise a dumbbell up against gravity as the muscle shortens.
-Eccentric Bicep Muscle Curl – lower a dumbbell slowly (4-6 seconds) against gravity as the muscle lengthens.
Sources: National Institutes of Health; American Council on Exercise

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
NEXT WEEK! Read Stuck in an Exercise Rut…Part II of II:
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
February is National Cancer Prevention Month and March is Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month. Unfortunately, according to a study conducted by Northeast Regional Cancer Institute (NRCI), our area has a higher rate of cancer compared to the rest of the United States. Residents of NEPA must be vigilant! While there is no fool-proof method for cancer prevention, scientific research does support the fact that healthy lifestyle choices are essential.
Source: American Cancer Society

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
I enjoy the privilege of working with people recovering from a wide variety of medical conditions. Many of these conditions can directly affect activities of daily living, particularly, the ability to drive safely: orthopedic and sports injuries, fractures, sprains and strains, joint replacements, hip fractures, shoulder and elbow surgeries and spinal fusions. Despite the many different types of problems, there is one question that is invariably asked, “When can I return to driving?” Unfortunately, the answer is not as simple as the question because it depends on many factors. Furthermore, the implications, such as a serious accident causing further damage to the injury or surgical site or harm to someone else, are significant and possibly critical. So, the next time you ask your physician this question, please follow instructions and be patient…remember, it could be your child or grandchild running into traffic to chase a ball and you would want the driver to be at optimal function to apply the brakes!
In our culture, the inability to drive has a significant impact on lifestyle and livelihood. A study published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, found that 74% of those unable to drive due to injury or surgery are dependent on family and most of the remainder depend on friends. 4% of those unable to drive have no help at all and more than 25% suffer major financial hardship.
The report also found that family physicians, orthopedic surgeons, podiatrists, and physical therapists are keenly aware of this dilemma but often fail to communicate effectively to patients about driving. Most medical professionals express serious concerns about liability regarding return to driving following an injury or surgery. They feel that there is a lack of data to support decisions and inadequate communication among each other. They agree that they must do a better job communicating with patients and their families so they can better prepare for a period of time during their recovery in which they cannot drive.
Recent studies published in the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS) and the Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery (JFAS),determined that there are two significant components in the decision of safely returning to driving after an injury or surgery; the time required for healing and the time required for a return of function. Additionally, it was found that those wearing a surgical shoe or walking boot demonstrated a significantly slower braking response time even in healthy/non-injured individuals wearing the shoe/boot.
During the time required for healing, in addition to the fear of an additional trauma from a motor vehicle accident to the healing body part, there is a general concern about the potential damage that may come from over using the body part to drive before it is adequately healed. For example, a healing fracture in the right lower leg might be compromised or delayed if one must suddenly and forcefully apply the brakes. Also, during this time, it is not unusual for post-injury or post-surgery patients to use pain medications, including narcotics. This will also compromise judgment and reaction time while driving.
Most orthopedic conditions heal in 6 to 8 weeks. However, as many of you may fully know, once a cast or splint is removed, you are not ready to run or jump. Depending on the severity of the injury, it may take many weeks of aggressive physical therapy to regain strength, range-of-motion, agility and dexterity to function at a safe level for a full return to daily activities, including driving.
The current research reinforces the fact that driving safely requires good function of the entire body. For example, just because you broke your shoulder bone but did not fracture your right leg does not mean that you are able to drive safely. Wearing a sling after arm surgery also compromises driving. First, you need a stabilized and healed injury prior to driving. Then, you must work in rehab to make modifications to return to safe driving. Apply the same scenario to injuries or surgery to the spine (neck and lower back).
*Based on research using driving simulators
7 TIPS TO KNOW WHEN YOU ARE READY TO DRIVE:
Remember, every case is unique and there is no substitute for communication with your orthopedic surgeon, podiatrist, family physician and physical therapist.
Visit your doctor regularly and listen to your body.
Keep moving, eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and live long and well!

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
American Heart Month is not just for lovers. Long after the Valentine’s roses wilt, our hearts will require special attention for a long healthy life. It is the goal of The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute to motivate Americans to adopt healthy lifestyles to prevent heart disease.
A recent study by the Center for Disease Control (CDC) found that while many Americans believe that they are “young at heart”, it turns out that many have hearts older than their actual age. For example, the study found that the average American male heart is eight years older and the average American female heart is five years older than their chronological age.
The CDC’s findings may offer some explanation for the fact that many Americans die from heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure when compared to other people around the globe. Furthermore, while more Americans use heart medications more than other people in the world, heart attack and stroke continue to be the leading cause of death in the US, killing more than 80,000 each year.
The CDC has developed a new test to determine “Heart Age,” which has been found to be a much more reliable indicator of a person’s risk for heart disease. The heart age test will determine if your heart is older, younger or average for your age, which can be much more important for longevity than chronological age.
The CDC is encouraging people to take matters into their own hands …be proactive. In addition to calculating your Body Mass Index ((BMI), the CDC is asking people to use an online calculator to determine their heart age. The calculator will give a person a more accurate percentage of risk for heart attack or stroke. Based on the outcome, one must see their family physician or cardiologist to discuss the results and implement a plan.
Heart Age is very easy to use: You just need to enter your age, sex, blood pressure, whether you are treated for high blood pressure, whether you smoke or have diabetes, and your body mass index (BMI), with a handy calculator if you don’t know it. The tool gives you your risk for heart disease in the next ten years, compared with normal.
Visit: www.framinghamheartstudy.org or www.heartfoundation.org
Enter: sex, blood pressure, (list if controlled), diabetes (list if controlled), smoking history, and body mass index (BMI), a simple height/weight calculation found on-line at www.bmicalculator.cc
Example: A 53 year old women with an acceptable BMI, may actually find that she is at great risk for suffering a heart attack or stroke because she smokes cigarettes and has uncontrolled high blood pressure. The calculator includes all the significant factors proven by science to affect a person’s risk of heart attack or stroke. These include: blood pressure, weight, BMI, blood sugar, cholesterol, age, sex and smoking history.
Example: 50 year old male smoker has uncontrolled high blood pressure of 140/96, no history of diabetes, and a BMI of 30 has a predicted heart age of 72 years. A female with a similar profile would have a heart age of 74 years.
To some, the solution may be obvious and for others it may be impossible. In the previous example of the 50 year old smoker, if he quit smoking for one year, he would halve reduced his heart age by 14 years (15 years for a woman). If he would reduce his blood pressure to 120, he would reduce his heart age by 6 years (10 years for a woman). And, if both risk factors were removed, he would reduce his heart age by 19 years (23 for a woman).
In the above examples, the 53 year old man does not have to take his 72 year old heart age as a death sentence.
BY THE WAY…I took the test:
Male: 65
Systolic Blood Pressure: 110
No high blood pressure or diabetes; non smoker
BMI: 22.5
HEART AGE: 62
SOURCES: WWW.CDC.GOV

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria no longer respond to the drugs designed to kill them. For more than a decade, the Centers for Disease Control along with other national and international agencies has supported an initiative called “Antibiotic Stewardship” the hallmark of which is the judicious, appropriate use of antimicrobials.
It’s told in some sobering statistics from the CDC, World Health Organization, and Food and Drug Administration:
Patients and providers must take equal responsibility. When we get sick, we often feel we need an antibiotic right away. In fact, we often demand one. A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018 found that to achieve a patient satisfaction rating in the 90th percentile physicians needed to prescribe antibiotics 75% of the time. Is this the correct approach to therapy? Are we using antibiotics too readily? What are the consequences of profuse antibiotic use?
In which of the following situations are antibiotics warranted?
A. Cold symptoms (runny nose, sore throat, headache) with a fever of 101F for 2 days
B. Cold symptoms lasting 12 days with persistent stuffiness and headache
C. Cold symptoms for 3 days with yellow-green mucous discharge
D. all of the above
The correct answer is B. Let’s discuss the reasons. Symptoms experienced as part of the common cold can include green/yellow sputum, cough, runny nose, stuffiness, sore throat, headache, fever, and mild muscle aches. This illness is caused by a virus, most likely a rhinovirus. Currently, 160 identified strains of rhinovirus are know.
Antibiotics work to destroy bacteria, not viruses since they have no activity against viruses. Antibiotics target specific bacterial structures or functions. Common bacterial targets for antibiotics include the cell wall (amoxicillin), ribosome activity (azithromycin), and bacterial DNA (levofloxacin). All of those are lacking in the very primitive structure of a virus. So, you could sit in a bathtub full of penicillin and not cure your cold with an antibiotic because there is simply nothing for the antibiotic to destroy in the viral structure.
Why are antibiotics appropriate after 10 days with cold symptoms? The typical common cold lasts between five and ten days with symptoms peaking around three or four days and waning at day six. If symptoms are consistent or regress and then become worse it is likely a sign of bacterial superinfections (super = on top of).
Usually, we carry certain bacteria with us as part of our “normal flora”. The mouth, nasal passages, large intestines, and skin host the most bacteria in the body. These bacteria work with our body and provide various “services” including protection against other more dangerous bacteria, digestion of food, and production of vitamins. A viral infection disturbs the normal balance of bacteria, allowing for proliferation and subsequent bacterial infection.
Why should we be careful about antibiotic use?
Antibiotics are not innocuous substances. They have significant side effect profiles. Adverse drug reactions associated with antibiotics can be less severe and consist of mild rash or nausea. More serious reactions include heart arrhythmias, tendon rupture, Stevens Johnson Syndrome (severe skin rash resembling thermal burns), and liver and kidney damage. Remember – every drug – not only antibiotics – has the potential to cause unpredictable adverse reactions
The most compelling reason to be careful about antibiotic use is resistance. Each time bacteria are exposed to an antibiotic, some are destroyed but others adapt to resist the antibiotic and live to see another day (remember Darwin’s Survival of the Fittest?). Antibiotics are unique in that the more they are used, the less effective they become. When antibiotics are used inappropriately – not taking them on schedule, for the right duration, taking them for a viral illness – bacteria have a chance to adapt to overcome the antibiotic activity. The resistant bacteria may go on to set up a resistant infection in you or that bacteria may be transmitted to others.
There are several ways we can combat this problem according to the Joint Commission on Healthcare Accreditation 2020 Standards. It is important to identify the causative agent if possible.
For example, a sore throat should not be treated with antibiotics until a throat culture or rapid strep test is obtained and a bacterial cause is identified. According to the Infectious Disease Society of America, 90 percent of adult sore throats have a viral cause, not bacterial. Avoid unneeded clinic or urgent care visits and utilize OTC and non-drug measures to manage non-bacterial infection symptoms.
Mislabeled allergy status leads to more expensive, less optimal antibiotic choices, more complex administration, increased resistance rates, and more treatment failures. The most common listed drug allergy in the US is Penicillin. According to the CDC, 10% percent of patients reports an allergy, however, < 1% of patients have a true allergy precluding penicillin or penicillin-like agents (the biggest class of antibiotic agents).
Vaccines may prevent bacterial infections or prevent viral infections which will avert a bacterial superinfection. Here are two examples of where vaccines can lower antibiotic use. The pneumococcal “pneumonia” vaccine protects against the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. Following the current guidelines for vaccination during childhood and adulthood decreases pneumococcal infections. According to the CDC, this vaccine has reduced pneumococcal infections by more than 90% in children. In addition, antibiotic-resistant pneumococcal infections have decreased in the United States since the pneumococcal vaccine was introduced.
The shingles vaccine also minimizes antibiotic use. The shingles vaccine “Shingrix”, is currently approved for individuals 50 years old (and older) as a two-dose series. Not only does it effectively prevent the occurrence of shingles, a painful, debilitating re-emergence of the chickenpox virus, but also reduces the risk of a potential secondary bacterial skin superinfection. Vaccine prevention of viral illness may subsequently eliminate antibiotic use.
Educating patients and prescribers will lead to the proper use of antibiotics to curb antibiotic resistance.
Guest Author: Dr. Gretchen Welby, PharmD, MHA
Dr. Welby received degrees from Keystone College and Philadelphia College of Pharmacy and Science. She received a Master of Health Administration Degree from the University of Scranton and a Doctor of Pharmacy degree from Temple University. She is currently the Academic Director of the Physician Assistant Program at Marywood University where she teaches Anatomy, Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Pharmacology.

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!
Ice baths have become a new trend or fad in health and fitness, especially among elite athletes and some celebrities. However, it is far from a new treatment modality. In fact, the Ancient Greeks employed cold-water immersion for fever, pain relief, relaxation and socialization. In addition, Hippocrates documented the use of cold for medicinal purposes for its analgesic benefits.
Ice baths, a type of cryotherapy, is also referred to as cold water immersion (CWI) or cold water therapy. This involves immersing your body in ice water for approximately 5-15 minutes from the neck down at 50-59 degrees. The ice baths are commonly used for pain, delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS), and inflammation and mood elevation.
In theory, the cold water lowers the temperature of your skin and body by vasoconstriction (narrow) of the blood vessels. When you get out of the cold, water the vasodilatation (widen) of the blood vessels. Immediately, this brings fresh oxygen and nutrient-rich blood back to the tissues to warm the body and in the process, reduce pain, inflammation and promote healing.
If you have the following health conditions, ice baths may not be the best therapeutic modality for you. Before you consider trying an ice bath, consult with your physician to avoid potentially serious problems:
While some studies have shown that subjects report less muscle soreness following CWI when compared to rest, most studies suggest that the reported effects are placebo. Also, reports of improved circulation, reduced inflammation and improved recovery or performance has not been scientifically validated. In view of this, it is recommended that those considering the use of CWI for pain and inflammation management, reduced muscle soreness, and mood elevation, should consult their physician to determine if the potential risks are worth the purported benefits.
SOURCES: nih; health.com; health.clevelandclinic.org; prevention.com

EVERY MONDAY – Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” via Blog
EVERY SUNDAY in "The Sunday Times" - Read Dr. Paul J. Mackarey “Health & Exercise Forum!” in hard copy
This article is not intended as a substitute for medical treatment. If you have questions related to your medical condition, please contact your family physician. For further inquires related to this topic email: drpmackarey@msn.com
Paul J. Mackarey PT, DHSc, OCS is a Doctor in Health Sciences specializing in orthopaedic and sports physical therapy in Scranton and Clarks Summit. Dr. Mackarey is in private practice and is an associate professor of clinical medicine at Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine. For all of Dr. Mackarey's articles, visit our exercise forum!